What Is Retrieval Augmented Generation and How It Works
So, what exactly is Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)? It sounds a bit technical, but the idea is actually super simple. Think of it as giving your favorite AI a library card and a super-fast research assistant. Before it answers your question, it can look up real-time, external information. This one simple step makes the AI's answers dramatically more accurate, current, and trustworthy. It's a real game-changer.
Why Your AI Sometimes Gets Things Wrong
Ever asked an AI chatbot about a recent event and gotten an answer that feels like a time capsule from a year ago? That’s not a glitch. It's a core limitation of how standard Large Language Models (LLMs) are built.
Picture a brilliant historian who has memorized every book published up to 2022. They can speak with incredible depth about anything before that date. But ask about this morning’s news, and they’ll draw a complete blank. Standard LLMs are just like that historian—their knowledge is frozen in time, ending when their training data was collected. This creates a "knowledge cutoff."
This core limitation causes two major headaches for us users:
- Outdated Information: The model simply can't tell you about new product releases, breaking news, or internal company updates that occurred after its training. Ask it who won last night's game, and it will have no clue.
- AI Hallucinations: When an LLM doesn't know the answer, it sometimes tries to fill in the blanks by guessing based on patterns it learned during training. This can result in answers that sound confident but are completely made up—a phenomenon known as "hallucination." It's a bit like a student bluffing their way through an exam.
Expert Opinion: "The primary purpose of RAG is to improve the contextual accuracy and relevance of AI-generated content," an AI architect might tell you. "By incorporating real-time external data, RAG ensures that the responses generated by LLMs are not only accurate but also up-to-date and contextually appropriate."
The RAG Solution: A Live Fact-Checker for Your AI
If a standard LLM is a historian with a dusty, static library, RAG gives that historian a live internet connection and a team of research assistants. Before generating a single word, a RAG system first performs a quick search on a specific, up-to-date knowledge base. This could be anything from your company's private documents and the latest news articles to a technical product manual.
First laid out in a foundational 2020 paper, this approach was a breakthrough. It fused powerful search (retrieval) with the creative power of generative AI, effectively grounding the model’s answers in verifiable facts. This directly combats hallucinations by forcing the AI to build its response from real data, not just its pre-existing, static knowledge.
In short, RAG turns an LLM from a closed-book exam-taker into an open-book research expert. It finds the relevant facts first, then uses its incredible language skills to weave that information into a perfect, coherent answer. This elegant process solves the core knowledge problem and makes AI a much more reliable tool for just about any real-world task. Addressing these kinds of problems is a major focus in the field, and you can see how new memory architectures are also helping to overcome AI limitations.
How a RAG System Actually Works Step-by-Step
To really get what Retrieval-Augmented Generation is all about, let’s pull back the curtain and see what’s happening under the hood. The best way to think about it is with a simple analogy: imagine a brilliant but slightly forgetful professor who needs to write a paper on a fast-moving topic. To help out, she hires an incredibly fast research assistant.
Their process for writing the paper is a perfect mirror of how a RAG system works. It’s not one single action but a smooth, multi-step workflow designed to find and deliver the best possible information.
This process directly solves the core problem with standard LLMs: their knowledge is frozen in time. When you ask them about something new, they often come up short, as you can see below.
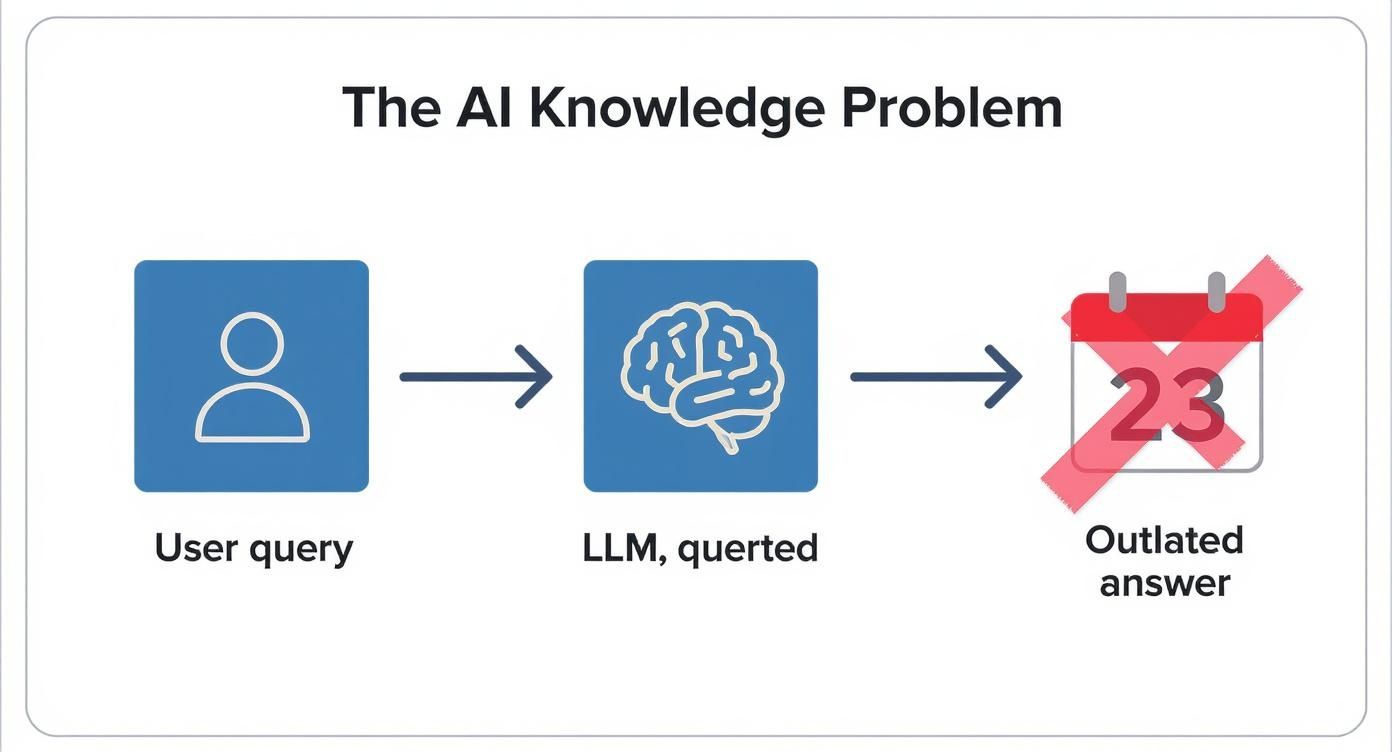
This "knowledge gap" is exactly what RAG was built to fix. It acts as a bridge, connecting the LLM's powerful reasoning abilities to fresh, relevant information.
Phase 1: The Indexing Phase (Building the Library)
Before our professor can even ask a question, the research assistant has to get the library in order. This crucial prep work is the Indexing Phase. The assistant doesn't just pile books onto a shelf; they meticulously go through every document, article, and report you give them—your unique "knowledge base."
For each chunk of information, the assistant creates a compact summary, almost like a detailed index card that captures its core meaning. These "cards" are then organized into a high-tech digital filing system known as a vector database.
But this isn't your grandma's card catalog, organized alphabetically. It's organized by meaning. So, a document about the "employee vacation policy" gets filed right next to one about "paid time off rules," even if the words aren't the same. This semantic layout makes finding relevant context lightning-fast later on.
A Word From Experience: The quality of this indexing phase will make or break your entire RAG system. If you feed it messy, irrelevant data—'garbage in'—you're guaranteed to get useless, frustrating answers—'garbage out.' The foundation of a reliable RAG pipeline is always clean, well-structured data.
Phase 2: The Retrieval Phase (Finding the Right Pages)
Okay, now the real-time action starts. The professor asks her assistant a direct question, something like, "What's our company's policy on remote work for new hires?" This kicks off the Retrieval Phase.
The assistant doesn't just guess. Instead, they take the professor's question, race over to that special vector database, and instantly scan it for the most relevant index cards. They pull out the exact pages from the internal company handbooks that talk about remote work, new employee onboarding, and employment rules. This all happens in milliseconds.
The key here is precision. The assistant doesn't just dump the entire employee handbook on the professor's desk. They retrieve only the specific, highly relevant snippets needed to answer that one question.
Phase 3: The Generation Phase (Writing the Answer)
With a small stack of perfectly relevant documents in hand, we hit the final step: the Generation Phase. The research assistant hands over this curated information to the professor.
Now the professor—our LLM—gets to do what she does best. She takes the fresh, factual information from the documents and synthesizes it with her own massive internal knowledge of language, grammar, and context. She doesn't just copy and paste; she weaves it all together to write a brand new, coherent, and perfectly worded answer.
The final response is grounded in the facts from your documents, making it trustworthy and accurate. It’s the perfect blend of the LLM's incredible language skills and the specific, up-to-date knowledge from your own data.
This three-step dance—indexing, retrieving, and generating—is the heart of Retrieval-Augmented Generation. It’s an elegant system that turns a general-purpose LLM into a specialized expert, armed with the exact information needed to answer questions with precision.
To make the difference crystal clear, let's look at a side-by-side comparison of how a standard LLM handles a query versus one enhanced with RAG.
Standard LLM vs RAG-Powered LLM
This table breaks down how each system approaches a user's question, from the initial query to the final answer.
| Stage | Standard LLM Process | RAG-Powered LLM Process |
|---|---|---|
| User Query | Receives the user's question directly. | Receives the user's question and sends it to the retriever. |
| Information Sourcing | Relies solely on its internal, pre-trained knowledge base. | First, retrieves relevant information from an external vector database. |
| Context Building | Has no external context; the query is all it has to go on. | Augments the original query with the retrieved context before sending it to the LLM. |
| Answer Generation | Generates an answer based on potentially outdated or generic training data. | Generates a specific, context-aware answer using both its internal knowledge and the fresh, provided information. |
| Result | Answer may be inaccurate, generic, or include "hallucinations" (made-up facts). | Answer is highly relevant, factually grounded in the provided data, and more trustworthy. |
As you can see, the RAG process introduces a crucial fact-checking and context-enriching step that fundamentally changes the quality and reliability of the final output. It's the difference between asking a knowledgeable stranger and consulting a world-class expert who just read your company's latest report.
The Three Essential Components of a RAG System
To really get what Retrieval-Augmented Generation is, you have to meet the key players that make the magic happen. A RAG system isn't just one monolithic AI; it’s more like a small, highly specialized research team. Each member has a critical role, and together, they produce answers that are smart, accurate, and tied to real-world information.
Let's break down this AI dream team. Every RAG system is built on three core components working in perfect sync.
1. The Large Language Model (The Eloquent Communicator)
At the core of the whole operation is the Large Language Model (LLM). This is the "generator" part of RAG—the eloquent communicator. It’s the component most people know, the AI engine responsible for understanding complex language, reasoning, and crafting text that sounds like it came from a human.
You've probably heard of the big ones, like OpenAI's GPT-4 or Google's Gemini. The LLM's primary job isn't to know everything on its own. Its real talent is being an expert at explaining things. It takes the raw facts handed to it by the other components and spins them into a smooth, coherent, and genuinely helpful answer.
2. The Retriever (The Hyper-Efficient Researcher)
Next up is the Retriever. If the LLM is the communicator, think of the Retriever as the team's hyper-efficient researcher. Its one and only job is to take a user's question and instantly dig up the most relevant snippets of information from a massive knowledge base.
How does it pull this off so quickly? The Retriever doesn't painstakingly read every document every time you ask something. Instead, it relies on a clever shortcut using numerical representations called embeddings. Both your query and all the documents in the knowledge base are converted into these embeddings. The Retriever then does a high-speed search to find the document embeddings that are mathematically closest to your query's embedding. This means it finds information based on contextual meaning, not just simple keyword matches.
A Word of Experience: The quality of your Retriever is everything. A brilliant generator can't fix a bad retrieval. If the Retriever pulls up junk or irrelevant information, the final answer will be flawed, no matter how articulate the LLM is.
3. The External Knowledge Base (The Curated Library)
Finally, we have the External Knowledge Base. This is the specialized, private library that the Retriever has access to—the single source of truth for the entire system. This library can be loaded with just about anything you want the AI to be an expert on:
- Internal company documents like HR policies or technical manuals.
- Up-to-the-minute news articles or financial reports.
- A history of customer support tickets and their solutions.
- A full product catalog with real-time inventory levels.
This data isn't just thrown into a folder. It's typically stored in a specialized vector database. These databases are built from the ground up to store and search through those numerical embeddings at incredible speeds. Popular tools for this job include Pinecone, Weaviate, and Milvus. A vector database is like a library organized by concepts and meaning, not just by alphabetical order, allowing the Retriever to find exactly what it needs in a flash.
Giving an AI access to this kind of organized, searchable data is what provides it with a reliable and fast-access memory. It’s a crucial step in building systems that have what many in the field call "long-term memory," a topic we dive into deeper in our article on how new architectures are helping AI have long-term memory. Together, these three components—the communicator, the researcher, and the library—form the powerful trio that makes RAG such a game-changer for AI applications.
Practical Use Cases for RAG in the Real World
Theory and technical diagrams are a great start, but the true power of Retrieval-Augmented Generation really clicks when you see it solving actual problems. RAG isn't just an academic concept; it's a practical tool that businesses are using right now to make their AI systems dramatically smarter, more reliable, and genuinely useful.
Let's look at how RAG is being put to work across different industries, turning frustrating digital experiences into seamless solutions.

Next-Generation Customer Support Chatbots
We've all been there: stuck in a loop with a chatbot that can only handle the most basic, pre-scripted questions. Ask about a new product or a specific error, and it hits a wall, forcing you to wait for a human agent. This is where RAG completely changes the game.
Imagine a chatbot for a major electronics company. This bot is plugged into a RAG system connected to a constantly updated knowledge base containing:
- The latest product manuals and technical specs.
- Up-to-the-minute troubleshooting guides.
- A history of resolved customer support tickets.
- Current warranty information and return policies.
When you ask, "My new TX-400 speaker won't connect to Bluetooth after the latest firmware update," the RAG system instantly finds the specific troubleshooting steps for that model and that exact firmware version. The LLM then uses this fresh information to generate a clear, step-by-step guide to get you connected in seconds. No more endless hold music.
Internal Knowledge Management and Employee Onboarding
Big companies have mountains of internal documents—HR policies, project plans, technical guides, and meeting notes—often scattered across different platforms. Finding one specific piece of information can feel like a digital scavenger hunt.
An internal RAG-powered search tool acts as a corporate "super-librarian." A new engineer can ask, "What are the coding best practices for our Python backend services?" and get an answer synthesized directly from the official engineering handbook, recent architectural decision records, and even relevant code repository documentation. This massively speeds up onboarding and boosts productivity by giving every employee instant, accurate answers.
Expert Opinion: The magic here is grounding the AI's response in verifiable company truth. A generic LLM might guess what a good coding practice is, but a RAG system will tell you your company's specific, approved practice and can even cite the internal document it came from. This builds immense trust and reliability.
The adoption of RAG in the enterprise has exploded because it delivers this kind of real-time, contextually relevant information. In fact, companies have seen up to a 30% increase in response accuracy and a 25% improvement in user engagement when using RAG-based systems. Salesforce, for example, integrated RAG into its customer service AI, which led to higher satisfaction by feeding the system fresh, company-specific documents. This approach avoids expensive model retraining and builds trust, as RAG can provide citations for its answers.
Financial Analysis and Market Research
The world of finance moves at the speed of light. An analyst needs information that isn't just accurate but current down to the minute. A standard LLM with a knowledge cutoff from last year is practically useless for making real-time decisions.
A financial firm can deploy a RAG system connected to live data streams, including:
- Real-time stock market data feeds.
- Quarterly earnings reports the moment they're released.
- Breaking news from trusted financial sources.
- Internal market analysis and research papers.
An analyst can simply ask, "Summarize the key takeaways from Acme Corp's latest earnings call and its impact on their main competitors' stock prices this morning." The RAG system retrieves the just-released earnings transcript, pulls the latest market data, and cross-references internal analysis to generate a concise, actionable summary on the spot.
Legal and Compliance Research
Legal professionals spend a huge portion of their time sifting through immense volumes of case law, statutes, and complex legal precedents. A RAG system can make this process incredibly efficient.
A lawyer can connect a RAG system to a massive, private database of legal documents specific to their field. They can then ask complex questions like, "What precedents exist for intellectual property disputes involving AI-generated art in the Ninth Circuit?" The system can instantly pull relevant case summaries and legal arguments, saving hundreds of hours of manual research.
From customer-facing bots to highly specialized professional tools, these examples show that RAG is more than just a technical upgrade; it's a fundamental shift in how we interact with AI. It makes AI a reliable partner that can access and reason over specific, up-to-date information. This same core concept also powers emerging technologies like voice-based retrieval. You can learn more about how Speech-to-Retrieval (S2R) is creating a new approach to voice search in our related article.
A Balanced Look at RAG: The Pros and Cons
Retrieval-Augmented Generation is an incredibly powerful approach, but it's not a silver bullet. Like any tool, you need to know when—and when not—to use it. Getting a clear-eyed view of its strengths and weaknesses is the first step to deciding if it’s the right fit for your project.
Let's dig into the honest pros and cons you'll face in the real world.
The Big Wins: Why RAG Is a Game-Changer
The upsides of using RAG are compelling, which explains why it's quickly become a go-to architecture for building serious AI applications. The primary benefits really boil down to accuracy, trust, and keeping things current without breaking the bank.
-
Dramatically Reduces Hallucinations: First and foremost, RAG keeps your LLM grounded in reality. By forcing the model to build its answer from specific, retrieved documents, you anchor it to a source of truth. This is the single most effective way to combat the dreaded AI "hallucination," where a model just makes things up.
-
Enables Source-Citing and Trust: Because the system knows exactly which documents it used, it can show its work. Providing citations is a massive step forward for building user trust, especially in high-stakes fields like legal tech, medical information, or financial analysis where verifying a source is non-negotiable.
-
More Agile and Cost-Effective to Update: RAG is often far more practical than constantly fine-tuning a massive LLM on new data. Retraining is a slow, expensive, and computationally brutal process. With RAG, keeping your AI’s knowledge fresh is as simple as adding new documents to your vector store. It’s faster, cheaper, and way more manageable.
The Hurdles: What to Watch Out For
While the benefits are clear, building a RAG system isn't just plug-and-play. It introduces new layers of complexity that require real planning to get right. The common stumbling blocks usually pop up around the implementation itself, performance bottlenecks, and the quality of your data.
-
Increased Architectural Complexity: A RAG pipeline has more moving parts than a simple LLM API call. You have to select, set up, and integrate an embedding model, a vector database, and the generator model. Getting them all to play nicely together demands a solid understanding of both information retrieval and AI engineering.
-
Potential for Slower Response Times: The two-step "retrieve-then-generate" process naturally adds a bit of latency. This can make response times slower compared to a direct query to a standard LLM. For real-time chat applications where every millisecond counts, this delay has to be carefully measured and optimized.
-
Heavily Dependent on Data Quality: This is the big one. Your RAG system is only as good as the information you give it. If your knowledge base is a mess—full of outdated, irrelevant, or poorly structured documents—your AI's answers will be a mess, too.
The Golden Rule of RAG: The most important thing to remember is "garbage in, garbage out." The quality of your source documents is the single biggest factor determining your system's success. Clean, well-organized data isn't a "nice-to-have"; it's a prerequisite.
Neglecting data quality will lead directly to unreliable, untrustworthy, and ultimately useless outputs. Acknowledging these potential obstacles from the start helps you build a more resilient and effective system.
Evaluating RAG: A Balanced View
To help you weigh the decision, here’s a quick summary of the primary advantages and potential challenges you'll encounter when implementing a Retrieval-Augmented Generation system.
| Advantages of RAG | Potential Challenges of RAG |
|---|---|
| Grounded in Facts: Provides answers based on verified sources, drastically reducing hallucinations. | Complex Setup: Involves multiple components (retriever, vector store, generator) that need integration. |
| Builds User Trust: Can cite sources, making outputs verifiable and more reliable. | Latency Issues: The two-step process can lead to slower response times compared to a direct LLM call. |
| Cost-Effective Updates: Cheaper and faster to update the knowledge base than to retrain an entire LLM. | Data Quality is Critical: "Garbage in, garbage out" – success depends entirely on a clean, relevant knowledge base. |
| Reduces Knowledge Cutoffs: Easily keeps the model's knowledge current with the latest information. | Requires Expertise: Demands skills in both information retrieval and large language models. |
| Domain-Specific Expertise: Allows you to create expert systems on proprietary or niche data. | Tuning is an Art: Finding the right chunk size, embedding model, and retrieval strategy can take trial and error. |
Ultimately, for most applications that require factual accuracy and up-to-date knowledge, the benefits of RAG far outweigh the implementation hurdles. It represents a practical and powerful way to make LLMs genuinely useful and trustworthy.
The Future of RAG and AI Knowledge
https://www.youtube.com/embed/_R-ff4ZMLC8
Retrieval-Augmented Generation has quickly become a go-to technique in modern AI, but what we see today is really just the starting point. The core idea—marrying a search engine's knack for finding facts with a language model's fluency—is evolving at a breakneck pace. To get a sense of where RAG is headed, it helps to look back at where it came from.
While the "RAG" paper dropped in 2020, the dream of merging information retrieval with natural language processing is anything but new. The concept’s roots stretch all the way back to early question-answering systems in the 1970s and even saw commercial light with services like Ask Jeeves in the 90s.
Of course, the big public moment was IBM Watson's victory on Jeopardy! in 2011, which brilliantly showed how powerful a system could be when it pulls from many different sources to nail a complex question. This long journey shows a clear, consistent goal: make machines better at finding and using knowledge. You can get a more detailed look at how RAG has evolved using data with LLMs on infracloud.io.
From Simple Retrieval to Advanced Reasoning
The next wave of RAG is all about making the retrieval part of the equation smarter, more dynamic, and way more analytical. The future isn't just about fetching one perfect document; it's about pulling insights from many sources to build a truly comprehensive answer.
Here are a few of the most interesting developments on the horizon:
-
Multi-Hop Retrieval: Think of this like a detective following a breadcrumb trail. Instead of running one search and calling it a day, the system performs a series of searches. The answer from the first query feeds into the second, allowing the AI to connect the dots on complex questions like, "Who was the CEO of the company that acquired our biggest competitor?"
-
Graph RAG: Rather than sifting through disconnected text documents, this approach taps into knowledge graphs—intricate networks of interconnected data points. This gives the AI a map of how people, places, and events relate to one another, paving the way for much deeper, more insightful answers.
Expert Opinion: This shift toward multi-step reasoning is a huge deal. The RAG systems of tomorrow won't just be fact-checkers. They'll be research assistants that can explore a topic, figure out the important sub-questions on their own, and then synthesize a complete summary without needing a human to guide every step. It’s a massive leap toward more autonomous AI.
The Rise of Agentic RAG
Perhaps the biggest evolution we're seeing is the emergence of Agentic RAG. The simplest way to think about it is giving the RAG system a mind of its own. An AI agent can autonomously decide if it needs to search for new information, what it should look for, and which tool is the right one for the job.
For example, when you ask a question, the agent might first ask itself, "Do I already know enough to answer this well?" If the answer is no, it could decide to query a specific internal database, then check a public news API, and finally stitch all the findings together.
This ability to act autonomously and use different tools will make RAG systems incredibly powerful and flexible. It’s blurring the line between a simple Q&A bot and a proactive, intelligent partner. This, right here, is where practical AI is truly going.
Common Questions About RAG Answered
As you start to wrap your head around Retrieval-Augmented Generation, a few practical questions almost always pop up. Let's tackle some of the most common ones to really solidify your understanding of how this AI technique works in practice.
Is RAG the Same as Fine-Tuning an LLM?
Not at all, and it's a great question! They're two very different paths to the same destination: making an AI more knowledgeable and relevant.
Think of it this way:
- Fine-tuning is like sending a brilliant student to medical school. You're fundamentally retraining the model on a specialized dataset, permanently altering its internal "brain" to make it an expert in a specific domain. It’s a deep, involved, and permanent change.
- RAG, on the other hand, is like giving that same brilliant student an open-book test with a library card. The student's core knowledge hasn't changed, but they can now pull in fresh, external information on the fly to answer any question you throw at them.
These two approaches aren't rivals, either. You can absolutely use them together. Some of the most powerful systems out there use a fine-tuned model as the generator inside a RAG framework, getting the best of both worlds.
Why Is a Vector Database So Important for RAG?
A vector database is the secret sauce—it’s the hyper-efficient library that makes the "retrieval" part of RAG possible. Instead of just searching for keywords like a traditional search engine, it organizes information based on its contextual meaning.
Here’s how it works: all your documents are converted into numerical representations called vectors, which capture the essence of their meaning. When you ask a question, your query also gets turned into a vector. The database then performs a near-instant search to find document vectors that are mathematically closest to your query vector. This "semantic search" is light-years ahead of simple keyword matching and ensures the LLM gets context that’s genuinely relevant.
Expert Opinion: Your choice of a vector database is absolutely critical. It’s the engine of your entire RAG system. A fast, scalable vector database is the difference between an application that feels instant and one that lags, especially when you're sifting through millions of documents.
Can I Build a Simple RAG Application Myself?
Yes, you definitely can! Thanks to some incredible open-source tools, building a basic RAG app has never been more straightforward. It's a fantastic weekend project if you're curious.
Frameworks like LangChain and LlamaIndex offer pre-built components that do most of the heavy lifting for you. With just a bit of code, you can link a pre-trained LLM (from providers like OpenAI or Hugging Face) to your own documents and a simple vector store. While a production-ready, enterprise-grade system is a serious engineering effort, building a small proof-of-concept is a great way to learn for anyone with some programming skills.
At YourAI2Day, we are dedicated to providing the latest news, research, and tools in AI. Stay informed about technologies like RAG and more by exploring our content at https://www.yourai2day.com.