What Is Natural Language Processing Explained Simply
Ever found yourself marveling at how your phone finishes your sentences, or how a voice assistant like Siri or Alexa just gets what you’re asking? That’s not magic—it’s Natural Language Processing (NLP).
Think of NLP as a specialized field of artificial intelligence focused on one thing: teaching computers to understand, interpret, and even generate human language. It's the essential bridge that finally lets us talk to our devices on our own terms, without needing to learn complicated code. It's built for beginners and anyone curious about the AI popping up everywhere.
What Is Natural Language Processing?
At its core, Natural Language Processing is about making computers work with our messy, nuanced, and often unpredictable language. It’s more than just recognizing words on a screen; it’s about grasping the context, intent, slang, and even the sentiment behind what we say or type.
A computer, by itself, sees "I'm feeling blue" as just a string of characters. It has no idea what that means. But an NLP model can learn from countless examples that, in this context, "blue" is a stand-in for sadness, not the color. This ability to decipher true meaning is the engine behind so many of the smart tools we now take for granted. If you're curious about the bigger picture, you can get a great primer by understanding AI technology and its foundational concepts.
The Ultimate Translator Analogy
Here’s a friendly way to think about it: imagine you have a world-class translator. This person doesn't just swap words from one language to another. They pick up on your tone of voice, your sarcasm, and the subtle cues in your phrasing to figure out what you really mean.
For example, if you say, "Oh, great, another meeting," your translator knows you're probably not thrilled. That's precisely the goal of NLP. It takes our unstructured, often chaotic language and breaks it down into something a machine can analyze and act upon.
The process of turning our words into something a computer can use involves a few key stages. Here’s a simple breakdown of how that works.
How NLP Bridges the Human-Computer Gap
| Stage | What It Does for the Computer | A Human Analogy |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Input & Preprocessing | Cleans up the raw text or speech. This means correcting typos, removing filler words (like "um" or "the"), and standardizing the format. | Listening carefully and mentally filtering out background noise or stutters to focus on the key words someone is saying. |
| 2. Feature Extraction & Modeling | The computer identifies key patterns, relationships, and the underlying structure of the language. It turns words into numerical representations (vectors) it can work with. | Recognizing the grammar, identifying the subject and verb, and connecting the concepts in a sentence to understand its overall meaning. |
| 3. Output Generation | Based on its analysis, the model produces a useful response. This could be an answer to a question, a translated sentence, or a sentiment score. | Formulating a thoughtful reply, summarizing what you just heard, or simply nodding to show you understand. |
This three-step process—clean, analyze, respond—is the fundamental workflow that powers almost every NLP application.
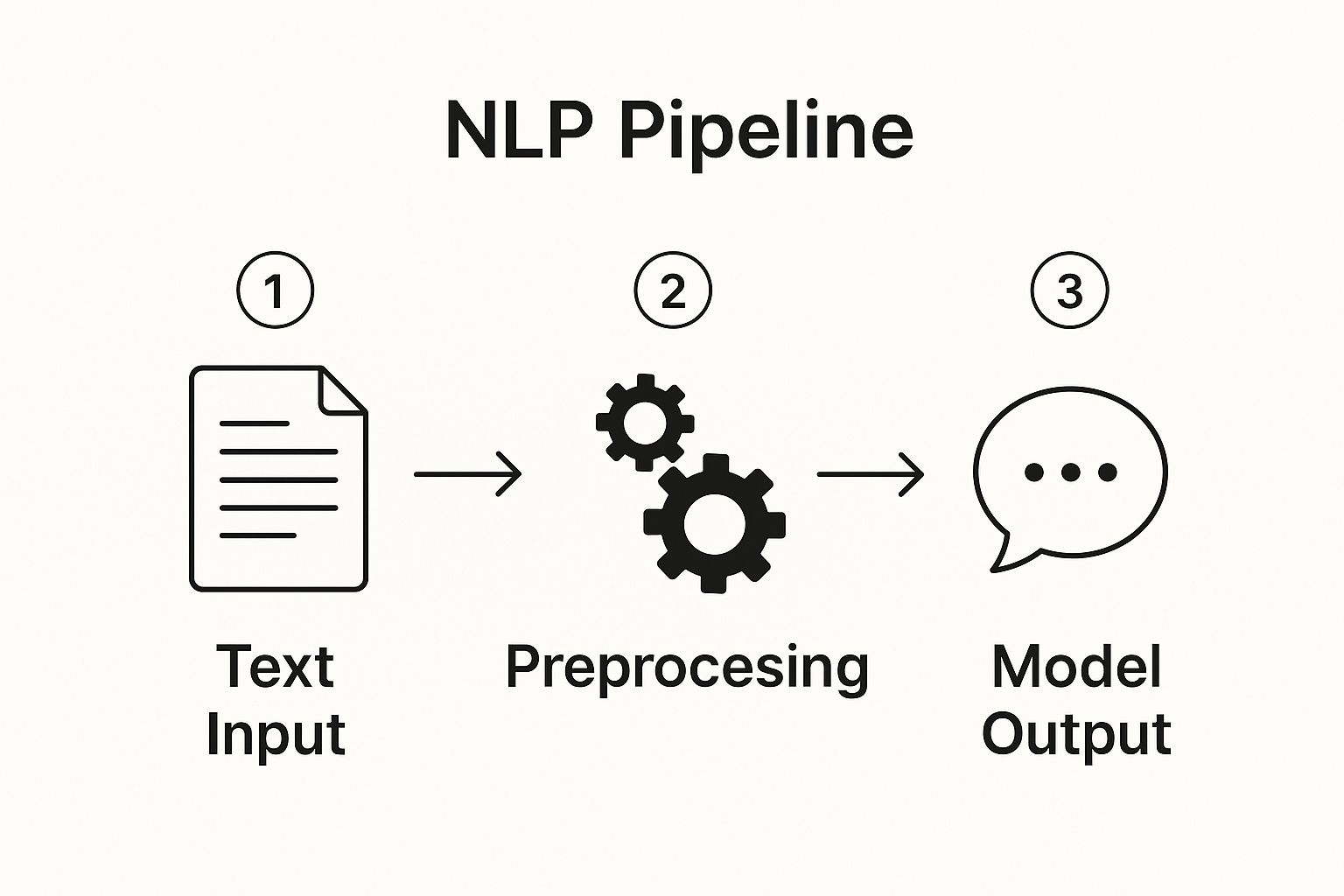
As you can see, it all starts with raw human language, which gets refined and structured before the model can produce a meaningful result.
Why Is NLP So Important Today?
NLP has become absolutely vital because we're swimming in a sea of human language data. Think about it: social media posts, customer reviews, emails, support tickets, voice notes—it's a massive, unstructured treasure trove of information. NLP provides the keys to unlock it.
Here’s why it’s become so indispensable:
- Automating Repetitive Work: Instead of a person manually tagging support tickets, NLP can automatically categorize them by topic (e.g., "Billing Issue," "Technical Problem"), freeing up humans for more complex tasks.
- Analyzing Data on a Massive Scale: A company can use NLP to sift through 10,000 customer reviews in minutes, instantly getting a pulse on public sentiment without needing a single person to read them all.
- Making Technology More Accessible: Features like real-time translation and voice-to-text dictation break down communication barriers, making information and tools available to more people than ever before.
In the end, NLP is the invisible force making our technology feel less like a machine and more like a helpful partner. It’s constantly working behind the scenes to make our interactions smoother, smarter, and far more intuitive.
The Surprising History of Teaching Machines to Talk
To really get a feel for how incredible today's AI conversations are, we need to take a trip back in time. The idea of teaching machines our language isn't some new-age concept; it’s a fascinating journey that started long before anyone had a smartphone in their pocket.
https://www.youtube.com/embed/Uuz8ZTV5vdA
It all began in the 1950s, when computers were enormous, room-sized behemoths. Pioneers like Alan Turing were already asking a simple but profound question: could a machine think? And if it could think, could it talk like a person? This was more than just a tech problem—it was a philosophical puzzle that kicked off an entirely new field.
The formal discipline of Natural Language Processing (NLP) sprouted from these early ideas. In 1950, Alan Turing published his famous paper, "Computing Machinery and Intelligence," which introduced what we now call the Turing Test. It was a simple way to measure a machine's ability to hold a conversation that was indistinguishable from a human's. A few years later, in 1957, Noam Chomsky's work on generative grammar gave researchers a formal way to think about the structure of language, a crucial first step. You can dive deeper into the origins of NLP on Spotintelligence.com.
The First Attempts at Digital Conversation
One of the most well-known early experiments was a program from the 1960s called ELIZA. Developed at MIT, ELIZA was built to act like a psychotherapist. Its method was surprisingly simple: it mostly just rephrased what you said back to you as a question.
For instance, if you typed, "I'm worried about my job," ELIZA might reply with, "Why are you worried about your job?" It felt surprisingly real, but ELIZA didn't actually understand a single word. It was just an expert at pattern matching, a clever parlor trick that showed everyone just how hard true comprehension would be. These first systems were entirely rule-based.
Expert Opinion: Dr. Emily Carter, a computational linguist, notes, "Early NLP researchers spent countless hours hand-crafting complex grammatical rules. It was like trying to write a complete instruction manual for a language as messy and inconsistent as English—an almost impossible task that revealed the severe limitations of this rigid approach."
This approach meant that for a computer to process a sentence, a programmer had to manually code every single grammatical rule and every possible word combination. There was zero flexibility. If the program saw a word or phrase that wasn't in its rulebook, it would simply crash.
The Problem with Rules and Rigidity
Imagine trying to explain a joke to someone using only a dictionary and a grammar textbook. You could define all the words and diagram the sentence, but the actual humor—the context, the cultural nuance, the timing—would be completely lost. That was the core problem facing early NLP.
These rule-based systems just couldn't handle the beautiful chaos of human language:
- Ambiguity: Take the sentence, "I saw a man on a hill with a telescope." Who has the telescope? You, or the man? We use context to figure this out instantly, but a rule-based system would get stuck.
- Idioms and Slang: Phrases like "break a leg" or "spill the beans" are nonsensical if taken literally. Without a massive, pre-programmed list of every idiom, the system would fail.
- Constant Evolution: Language is alive. New words, phrases, and slang emerge all the time, making it impossible for a hand-coded rulebook to ever stay current.
The sheer difficulty of making these clunky, rule-based systems work made one thing crystal clear. For machines to truly talk, they couldn't just follow a list of commands. They needed to learn. This realization paved the way for a huge shift in thinking that would change the course of AI forever.
From Rules to Learning: The Big Shift in NLP
Early attempts to teach computers our language were, to put it mildly, a bit clumsy. Think of it like trying to teach someone English by just handing them a massive, convoluted grammar textbook and hoping for the best. That was the essence of rule-based NLP. Programmers would spend countless hours writing out explicit instructions for every grammatical structure and linguistic exception they could imagine.
As you can guess, this approach was fragile. The moment a sentence popped up with a bit of new slang or an unexpected structure, the whole system would grind to a halt. It quickly became obvious that the beautiful, messy, and constantly evolving nature of human language just couldn't be captured by a fixed set of rules. Something had to change.

The Dawn of a New Era: Machine Learning
So, what if a computer could learn language more like we do—through sheer exposure and experience? This question sparked a revolution. The 1980s and 90s saw a monumental shift away from those hand-coded rules and toward data-driven, statistical methods.
This new approach completely flipped the script. Instead of telling the computer how to understand language, developers started showing it language in action. By feeding algorithms millions of sentences, articles, and books, these systems began to pick up on patterns all on their own. This leap was made possible by more powerful computers and, of course, the explosion of digital text. You can dig deeper into this crucial period by exploring the history of Natural Language Processing on aveni.ai.
These new models learned that "king" and "queen" are related, not because someone programmed a rule, but because the words consistently appeared in similar contexts across vast datasets. They figured out that "I'm feeling blue" is about sadness, not color, by analyzing how that phrase was used in countless real conversations.
Why This Shift Was So Important
Moving to a learning-based model had a huge impact. It’s what turned NLP from a niche academic field into the powerful, practical technology we see all around us today. This statistical method gave NLP models the ability to finally grapple with the ambiguity and nuance that define human communication.
This change brought some game-changing advantages:
- Adaptability: Machine learning models can be constantly fed new data. When language evolves with new slang or idioms, the models can learn and evolve right along with it. No complete rewrite needed.
- Scalability: Writing rules for every language on Earth is an impossible task. A machine learning model, however, can be trained on text from virtually any language, making the technology far easier to scale globally.
- Handling Ambiguity: Statistical models are built for ambiguity. They can calculate the most probable meaning of a word based on its context, effortlessly solving problems that would completely stump a rigid, rule-based system.
Expert Opinion: "The biggest breakthrough wasn't a single algorithm, but a change in philosophy," says AI strategist Ben Riley. "We stopped trying to force language into the rigid box of computer logic and instead started building logic that could adapt to the fluid nature of language."
This fundamental leap from rules to learning is the engine behind the sophisticated language tools we rely on daily. Your spam filter doesn't just have a list of "bad words"; it has learned the statistical fingerprints of what junk mail looks like. And your translation app isn't just a simple dictionary; it understands the contextual patterns that make a sentence sound natural.
How NLP Actually Works Under the Hood
Alright, so we know NLP has moved beyond stiff, rule-based systems. But what’s really going on inside the machine? Let's pop the hood and look at how a computer takes our messy, nuanced language and makes sense of it—without getting buried in technical jargon.

Think of it like cooking a complex dish. You don't just toss everything in a pot. First, you have to chop the vegetables, measure the spices, and get all your ingredients prepped. NLP starts the same way with a process called tokenization.
It's just a simple term for breaking a sentence down into its smallest useful parts, or "tokens." So, a sentence like "This pizza is absolutely delicious!" gets chopped up into individual pieces: ["This", "pizza", "is", "absolutely", "delicious", "!"]. This first step turns a solid block of text into manageable chunks the computer can start to analyze.
The Two Sides of the NLP Coin: Understanding vs. Generating
NLP really boils down to two core capabilities: understanding language and generating it. Think of it as reading comprehension versus writing an essay. A truly smart system needs to do both. One side is called Natural Language Understanding (NLU), which focuses on interpreting what's being said. The other is Natural Language Generation (NLG), which is all about creating a response.
Let's break down how these two sides work together.
Side 1: Natural Language Understanding (NLU) – The Art of Listening
Once the text is broken into tokens, the real work begins. The system has to figure out the meaning and intent behind the words. This is the domain of NLU—it’s all about reading, interpreting, and comprehending.
Several key tasks power NLU:
- Sentiment Analysis: This is the machine's emotional radar. It determines the tone of a piece of text, figuring out that "I loved this movie" is positive while "The service was a disaster" is negative. Companies rely on this to sift through thousands of customer reviews in seconds.
- Named Entity Recognition (NER): Think of NER as a digital highlighter. It scans text to find and categorize key information, like names of people (Elon Musk), organizations (Google), locations (New York City), and dates (October 31st). For example, it can pull "Dr. Smith" and "next Tuesday" from an email to help you schedule a meeting automatically.
- Part-of-Speech Tagging: Remember diagramming sentences in grammar class? This is the automated version. It labels each word as a noun, verb, adjective, and so on. Understanding a word's role is fundamental to grasping the structure and meaning of the entire sentence.
These NLU tasks are what allow a chatbot to understand your question, a spam filter to flag a suspicious email, and a search engine to deliver exactly what you were looking for.
Side 2: Natural Language Generation (NLG) – The Art of Replying
Understanding is only half the battle. To be useful, the system has to respond. This is where Natural Language Generation (NLG) comes in. If NLU is the brain's reading comprehension, NLG is its ability to formulate a clear, coherent reply.
After the NLU components figure out what you want, the NLG system takes that structured data and crafts a human-like response. This might be a simple confirmation like, "Okay, playing your 'Workout' playlist" from your smart speaker, or a detailed, multi-paragraph answer from an AI like ChatGPT. It's the part of the process that assembles words and phrases into grammatically correct sentences that actually sound natural.
To make it clearer, here’s a look at how NLU and NLG compare.
Understanding vs. Generating: The Two Sides of NLP
| Aspect | Natural Language Understanding (NLU) | Natural Language Generation (NLG) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | To read and interpret the meaning of human language. | To create and produce human-like language from data. |
| Core Function | Analysis and comprehension. It deconstructs language into structured information. | Synthesis and creation. It constructs language from structured information. |
| Example Application | A customer service bot analyzing a complaint to identify the core issue and urgency. | A weather app creating the sentence: "Expect light rain starting around 3 PM today." |
This constant dance between understanding and generating is the engine that powers modern NLP. One side listens, and the other side talks.
Why Is This So Hard, Anyway?
The process might sound straightforward, but human language is a minefield of ambiguity. The same word can mean completely different things depending on how it's used.
Just try to make sense of this sentence: "I decided to bank my winnings from the poker table at the new bank on the river bank."
A person instantly understands the three distinct meanings of "bank" (to deposit, a financial institution, the edge of a river) from the surrounding context. For a computer, this is an enormous challenge. This ambiguity is precisely why it has taken decades for NLP to become as effective as it is today. By converting words into numerical representations (known as vectors) that capture contextual relationships, modern systems can finally navigate this complexity with impressive accuracy.
NLP Is Already Part of Your Daily Life
You might think of Natural Language Processing as some far-off, complex technology locked away in a data science lab. But the truth is, you're interacting with it all day, every day. It's the invisible engine running in the background of the apps and devices you probably use without a second thought.
Let's pull back the curtain on a few examples. You’ll quickly realize that NLP isn't some abstract concept—it’s woven directly into your daily routine.
Your Email Inbox Is an NLP Masterclass
Ever wonder how your inbox magically separates important messages from a flood of junk? That's classic NLP at work.
Spam filters are one of its oldest and most powerful applications. They do more than just flag words like "free" or "congratulations." These systems analyze everything—the phrasing, the sender's reputation, the structure of links—to calculate the probability that a message is junk. They’ve been trained on billions of emails, learning the subtle patterns of what spam looks and sounds like.
But it doesn't stop there. Think about features like Gmail’s "Smart Reply." That’s NLP in real-time. It reads an incoming email, understands its core message—is it a question? a simple confirmation?—and then suggests short, fitting responses like "Sounds good!" or "I'll get back to you soon." It's a small touch, but it’s a perfect example of NLP making your life a little easier.
Smart Assistants and Predictive Text
If you've ever asked Siri for directions, told Alexa to set a timer, or used Google Assistant to check a fact, you’ve had a direct conversation with an NLP system.
- Voice Assistants: When you say, "Hey Alexa, what's the weather like in Boston tomorrow?" a whole sequence of NLP tasks kicks off. The device instantly converts your speech to text, figures out your intent (you want a weather forecast), pulls out the key details (Boston, tomorrow), fetches the data, and then crafts a spoken response that sounds completely natural.
- Autocorrect and Predictive Text: Your smartphone’s keyboard is another great example. It’s constantly analyzing what you type to predict the next word you’re likely to use. This isn't just a simple dictionary lookup. It’s a sophisticated model that understands grammar and context, guessing what makes sense based on how millions of people write.
These tools perfectly illustrate the two sides of NLP we've been talking about: first understanding your language (NLU), then generating language in return (NLG).
Expert Opinion: "The best applications of NLP feel invisible," remarks Sarah Jenkins, a UX designer specializing in AI interfaces. "The technology succeeds when it integrates so seamlessly into a task that the user doesn't even notice the complex processing happening in the background. It just feels intuitive."
Beyond Basic Commands
NLP’s reach extends far beyond these simple, everyday tasks. It’s now breaking down language barriers and even helping us create new things.
Ever used Google Translate to make sense of a menu in another country? That’s NLP performing a minor miracle in your pocket. The app doesn't just do a clunky word-for-word swap; it analyzes the full sentence to capture the intended meaning, something that was science fiction just a couple of decades ago. We're also seeing an explosion of powerful AI writing assistants. If you're curious about how this is being used professionally, you can explore the different AI tools for content creation to see how NLG is fundamentally changing work for writers and marketers.
From the way your social media feed groups posts by topic to the chatbot that answers your question on a shopping website, NLP is the quiet force making our technology feel more human. It’s not a futuristic idea anymore—it’s a practical, hardworking part of modern life.
What Comes Next for AI and Language
The race to teach machines our language is moving at an incredible speed. The NLP applications we use today are already impressive, but what's just around the corner is even more mind-bending—along with some serious problems we still need to solve. Right now, the entire conversation is dominated by Large Language Models (LLMs), the engine behind tools like ChatGPT.
These massive models are fed an almost unimaginable amount of text, which allows them to generate writing that feels creative, nuanced, and eerily human. This is a huge leap from just analyzing text or following simple commands. We're now seeing AI engage in complex dialogue, write functional code, and even brainstorm entire campaigns, fundamentally changing how many businesses operate and how to use AI for marketing.
The Next Frontier of Challenges
But this rapid progress has also brought some tough challenges to the surface. As NLP gets woven deeper into our daily lives, researchers are wrestling with some complex, deeply human problems. Nailing these solutions is critical if we want AI that's genuinely helpful and fair for everyone.
Here are a few of the biggest hurdles we face:
- Understanding Nuance and Sarcasm: AI is getting pretty good with literal meaning, but it often stumbles over the subtle layers of human communication. Sarcasm, irony, and dry humor are still major sticking points because their real meaning is often the complete opposite of the words on the page.
- Tackling Algorithmic Bias: NLP models learn from the world's text data, and unfortunately, that data is filled with our own societal biases. If developers aren't extremely careful, these models can easily end up repeating and even amplifying harmful stereotypes about gender, race, and culture.
- Grasping Real-World Context: An AI might process the words in a conversation perfectly, but does it truly understand the situation? For example, asking an AI "Is it cold outside?" requires it to know your current location and the time of year—a kind of common-sense reasoning our current systems are still working hard to develop.
Expert Opinion: "The future of NLP isn't just about building bigger models; it's about building wiser ones," says AI ethicist Dr. David Chen. "The next great leap will be in creating systems that can understand the unspoken context, adapt to cultural norms, and operate with a stronger ethical framework."
Ultimately, the future of NLP is a push toward creating more responsible and context-aware AI. The goal isn't just to build systems that can process words, but ones that understand the human world behind them. This is the key to a future where our interactions with technology feel more natural, equitable, and genuinely intelligent.
Got Questions About NLP? We've Got Answers
Let's tackle some of the most common questions people have when they first start digging into Natural Language Processing. Think of this as a quick-reference guide to clear up any lingering confusion and help you get a solid grasp of the essentials.

Is NLP Just Another Name for AI?
That’s a great question, and the answer is no, but they're definitely family. The simplest way to think about it is that Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the broad field of making machines smart. NLP is a specialized, vital part of that field.
Essentially, NLP is a branch of AI that's laser-focused on one thing: teaching computers to understand and use human language. So, while all NLP is a form of AI, not all AI involves language—some AI focuses on image recognition, self-driving cars, or playing chess.
Why Is Human Language So Hard for Computers to Learn?
Because human language is beautifully, maddeningly complex. We swim in an ocean of ambiguity, sarcasm, slang, and cultural context that we process without even thinking about it. Computers, on the other hand, start from zero.
Take a simple word like "run." It could mean to physically jog, to operate a business, a tear in a stocking, or a series of events. We instantly get the right meaning from the surrounding words, but a machine has to be painstakingly taught how to spot those contextual clues. This inherent messiness is what makes building effective NLP systems such a monumental task.
Expert Insight: "The biggest challenge in NLP isn't just teaching a machine vocabulary; it's teaching it common sense," explains a lead researcher from a top AI lab. "The true goal is to help it understand the unspoken context that shapes nearly every human conversation."
What's the Difference Between NLU and NLG?
Natural Language Understanding (NLU) and Natural Language Generation (NLG) are two sides of the NLP coin. They work in tandem to make human-computer conversations possible.
-
NLU is the listening part. Its job is to deconstruct what a human says or writes to figure out the actual intent. When you ask Alexa for the weather, NLU is the process that deciphers your spoken words into a command it can act on.
-
NLG is the talking part. It takes structured data—like a weather forecast—and turns it into a natural, human-sounding sentence. After NLU understands your request, NLG crafts the response you hear: "The forecast shows a high of 75 degrees with sunny skies."
How Can I Start Learning About NLP?
Getting started is easier than you might think, and you definitely don't need a Ph.D. The best way to begin is by becoming more aware of the NLP you interact with every single day.
Notice how your email client flags spam, how your phone suggests the next word you want to type, or how a chatbot understands your customer service query. From there, plenty of beginner-friendly online tutorials can introduce you to the core ideas. Starting with real-world examples helps build an intuitive foundation before you dive into the deeper technical stuff.
At YourAI2Day, our mission is to make complex AI topics easy to understand. We offer the latest news, detailed guides, and helpful tools to keep you informed. Explore more at our official site: https://www.yourai2day.com.