What Are AI Agents? A Simple Guide to How They Work
If you've heard the term "AI agent" buzzing around, you're not alone. So, what exactly is it? Think of an AI agent as an autonomous entity that can perceive its environment, make decisions, and take actions to hit a specific goal for you. It's the difference between asking an AI to draft a report and having an AI that drafts, formats, and emails the report on its own.
So What Are AI Agents, Really?
Let’s use an analogy. A standard AI model, like the one powering a chatbot, is like a brilliant but passive research librarian. You ask a question, and it gives you a fantastic, well-sourced answer from its vast library of knowledge. It's amazing for finding information, but it can't step out from behind the reference desk.
An AI agent, on the other hand, is like a dedicated personal assistant you’ve hired. You give it a high-level goal, like "plan my weekend trip to San Diego," and it gets to work.
This ability to take initiative is what sets agents apart. The agent doesn't just hand you a list of flights and hotels. Instead, it can:
- Perceive: It looks at your calendar to see when you're free.
- Decide: It crunches the numbers on flight prices and sifts through hotel reviews to find the best fit for your budget and preferences.
- Act: It goes ahead and books the flight, reserves the hotel room, and even drops the itinerary right into your calendar.
This end-to-end task execution is exactly why many experts see AI agents as the next major leap for artificial intelligence.
The A-Team: AI Agents vs. AI Models vs. Chatbots
To really nail down the differences, let's get specific. A simple chatbot is often just following a pre-written script. A powerful AI model, like a large language model (LLM), is a master of generating human-like text, code, or images. But an AI agent is built for action—it connects the model's reasoning abilities with the power to execute tasks in the real world.
The market is already catching on to this shift in a big way. The AI agents market is expected to rocket from USD 7.84 billion in 2025 to USD 52.62 billion by 2030, fueled by an incredible 46.3% compound annual growth rate. This boom is all about combining the brain of an AI model with the hands of an autonomous system. You can explore the full market analysis on MarketsandMarkets.com for a deeper dive.
To help you quickly tell these terms apart, here's a simple breakdown of what makes each one unique.
AI Agent vs AI Model vs Chatbot At a Glance
| Characteristic | AI Agent | AI Model (e.g., LLM) | Simple Chatbot |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | To act and achieve goals autonomously | To generate content or predict outcomes | To converse based on predefined rules |
| Autonomy Level | High (can make decisions and execute tasks) | None (requires human prompts to act) | Low (follows a script or simple logic) |
| Core Capability | Planning, reasoning, and task execution | Pattern recognition and content creation | Answering specific, programmed queries |
| Interaction | Interacts with digital environments and tools | Responds to inputs within a session | Follows a conversational flow or script |
| Example Use | Booking travel, managing inventory, coding | Writing an article, translating text, summarizing | Answering FAQs, checking order status |
This table shows the clear progression: chatbots converse, models create, and agents do.
Expert Opinion: “The move from passive AI models to active AI agents is like the jump from a search engine to a personal assistant," says Dr. Evelyn Reed, a leading AI researcher. "One finds information for you; the other gets things done for you. This is the evolution that will transform AI from a tool we use into a partner we collaborate with.”
Ultimately, while models and chatbots are incredible tools for communication and creation, AI agents are the ones that actually perform tasks. They are the systems that will soon manage our schedules, optimize complex supply chains, and even help us build and deploy software. Grasping this distinction is key to understanding where this technology is really taking us.
How an AI Agent Thinks and Acts
To really get what makes an AI agent tick, we need to pop the hood. It’s not magic—it's a very logical, step-by-step process that actually mirrors how we make decisions every single day. At its core, an AI agent runs on a simple but powerful cycle.
Think of an agent as having three essential parts:
- Senses (Perception): These are its inputs, the tools it uses to "see" its digital environment. This could be anything from scanning new emails and checking a stock price API to simply getting a new command from you.
- A Brain (Reasoning): This is the decision-making engine, typically a Large Language Model (LLM). It takes in all that sensory information, weighs it against the ultimate goal, and starts putting together a plan.
- Hands (Action): These are the agent’s tools for getting things done. It could be sending an email, clicking a button on a website, or running a line of code.
These three components work together in a continuous feedback loop, something we often call the Perceive-Think-Act cycle. The agent is constantly sensing its surroundings, thinking about the best next move, and then acting on that decision.
This diagram highlights the fundamental difference between a standard AI model's passive process and an AI agent's active, looping one.
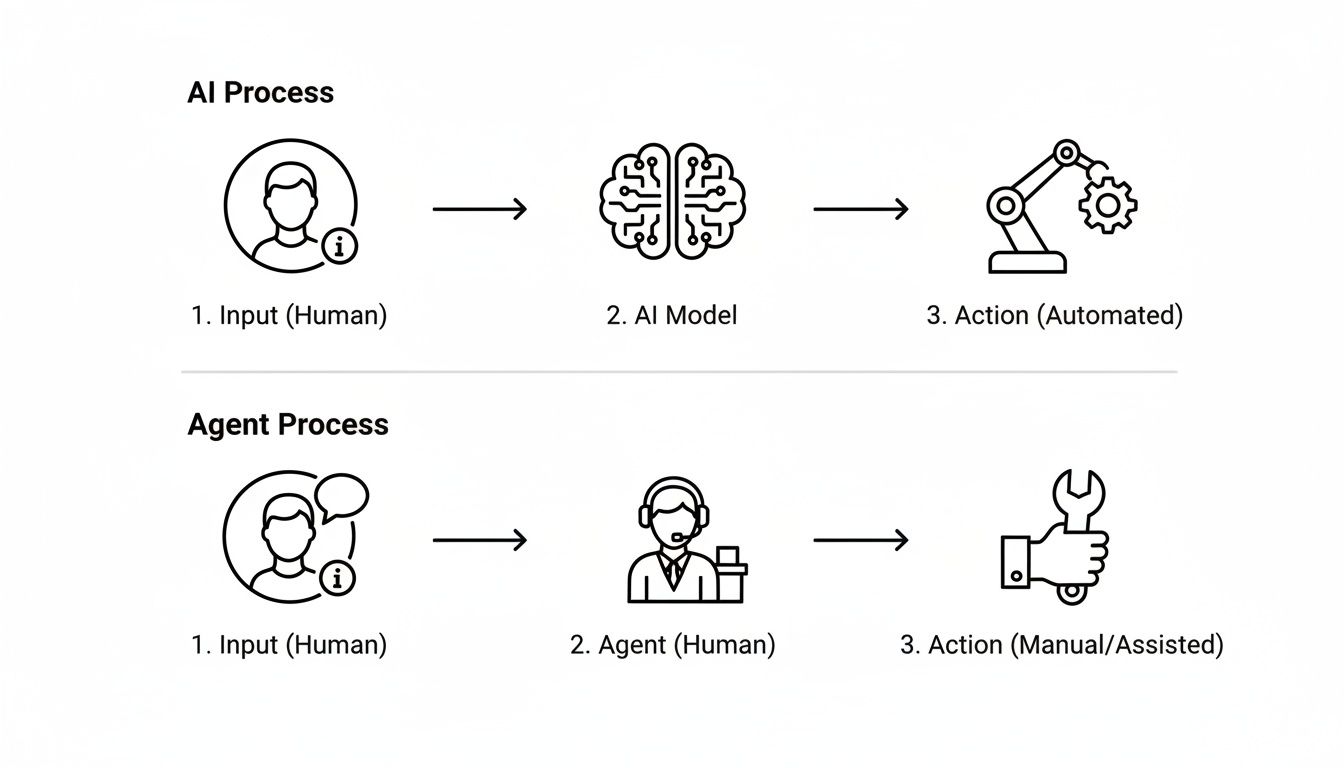
The key takeaway is that "Action" step. It’s what turns the AI from a passive information generator into an active problem-solver.
The Surprise Party Planner in Action
Let's make this real with a familiar scenario. Imagine you give an AI agent a goal: "Plan a surprise birthday party for my friend Alex next month."
Here's how it would tackle this using that Perceive-Think-Act loop:
- Perceive: The agent starts by gathering intel. It might access your contacts for a list of Alex’s friends, scan your calendar for open dates, and even start browsing local venues and bakeries online.
- Think: Now the reasoning kicks in. The LLM brain breaks the big goal into smaller, manageable tasks: find a date everyone can make, book a venue, create an invitation list, order a cake, and send the invites. It starts weighing options, noticing that one venue is cheaper while another has better reviews.
- Act: The agent starts executing. It might begin by emailing a Doodle poll to the guest list to lock down the best date. Based on those responses, it could then interact with a venue's booking website to reserve the space and place an online order for the cake.
And this cycle just keeps repeating. After sending the poll (an Action), the agent will monitor the replies (Perception), analyze the results (Think), and then book the final date (another Action). This iterative process is what lets the agent handle complex, multi-step projects all by itself.
Expert Opinion: "The real breakthrough with agents isn't just that they can 'think' with an LLM, but that they can act, fail, and learn from the outcome," notes AI strategist Ben Carter. "When an agent's attempt to book a flight fails, it doesn't just stop. It perceives the error, thinks about an alternative—like trying a different airline—and then acts again. That's a fundamental shift."
Learning From Experience
This ability to react and adapt is what really sets advanced agents apart. They use specific techniques to get better over time. Every action provides a piece of feedback. If an action leads to a successful outcome (like a confirmed booking), the agent learns that was a good move. If it hits an error, it learns to avoid that path next time.
This trial-and-error learning is a core concept in machine learning. To get a better sense of how machines learn from outcomes, you can learn more about reinforcement learning in our detailed guide. This mechanism is what allows an AI agent to become more effective and efficient as it completes more tasks, moving from a simple instruction-follower to a genuinely capable digital assistant.
Exploring the Different Types of AI Agents

AI agents aren't all cut from the same cloth. Just like a professional team is made up of specialists, AI agents are designed with different levels of complexity and skill. Getting a handle on these types helps clear up what an agent can really do, from simple reflex actions to complex, value-based decisions.
Let's walk through the main categories, starting with the most basic and working our way up to the most sophisticated. I'll use some everyday examples to make these concepts stick.
Simple Reflex Agents
At the bottom of the ladder, we have Simple Reflex Agents. These guys are all about instinct. They operate on a straightforward "if this, then that" basis, reacting to what's happening right now without any memory of the past.
Think of your smart thermostat. Its world is pretty simple: it senses the current room temperature. If the temperature dips below your setting (the condition), it kicks on the heat (the action). It doesn't remember being cold an hour ago or check the weather forecast. It just deals with the here and now. Another great example is an email filter that automatically sends emails with the word "unsubscribe" to your spam folder. Simple, direct, and immediate.
Model-Based Reflex Agents
Take a step up, and you get Model-Based Reflex Agents. These agents are a bit more clever because they maintain an internal "model" of how the world works. This lets them make sense of situations even when they can't see the full picture, using past information to guide their present actions.
A Roomba is a classic example. It doesn't just blindly bump into furniture and turn around. It actually builds a mental map of the room as it goes.
- It remembers: The agent keeps track of where it’s already cleaned and the location of obstacles.
- It infers: Even if its sensors can't see around a corner, its internal map helps it predict what’s there.
This internal model allows the Roomba to clean in a structured, efficient pattern rather than just wandering aimlessly. It’s the difference between just reacting and acting with a real sense of your surroundings.
This kind of advanced capability is driving huge growth. The AI agents market is projected to rocket from USD 5.9 billion in 2024 to USD 105.6 billion by 2034, reflecting a massive 38.5% compound annual growth rate. This boom is fueled by the demand for agents that can navigate complex scenarios, which is exactly what these more advanced types are built for. You can explore the research from Global Market Insights to see the full market breakdown.
Goal-Based Agents
Next up are Goal-Based Agents. These agents don't just react or follow a map—they actively plan to reach a specific, long-term goal. They think ahead, considering the future consequences of their actions to choose the best path to a desired outcome.
Your GPS navigation app is the perfect example. You give it a clear goal: "Get me to the coffee shop."
The app then gets to work, evaluating different routes and weighing factors like traffic, distance, and road closures. It isn’t just deciding on the next turn; it’s plotting the entire journey from start to finish. If a surprise traffic jam pops up, it can recalibrate on the fly to find a new, better path to that same destination.
Utility-Based Agents
Finally, we arrive at the most sophisticated type: Utility-Based Agents. These agents are designed to make the best choice, not just a good enough one. They do this by calculating the "utility"—or the desirability—of different outcomes, which is crucial when dealing with conflicting goals or when some results are clearly better than others.
Consider an automated stock trading agent. Its objective isn't just to "buy stock." It's operating with a much more nuanced goal: maximize profit while minimizing risk.
An investment agent has to juggle multiple factors: a stock's potential for growth, the risk of it tanking, and how that single trade impacts the entire portfolio. For example, it might choose a slightly less profitable but much safer stock over a high-risk, high-reward option. By assigning a utility score to each option, the agent picks the action with the highest expected value. This leads to far more sophisticated and optimal decisions than a simple goal-based agent could ever make.
This ability to weigh the pros and cons makes utility-based agents incredibly powerful for complex decision-making in finance, logistics, and resource management. They don't just get the job done; they get it done in the most beneficial way possible.
AI Agents You Can Use in Real Life
Now that we’ve covered the theory, let's talk about how these agents are showing up in the real world. This is where the rubber meets the road—seeing how these smart systems are already making a real difference for businesses and individuals alike. From answering customer questions to organizing your hectic schedule, AI agents are officially out of the lab and into our daily lives.
The growth here is pretty incredible. A recent survey found that by 2025, a whopping 79% of companies plan to have AI agents integrated into their operations. Many are already seeing the payoff, with two-thirds reporting a solid boost in productivity. This isn't just a niche trend; it's creating a huge economic wave. Just look at North America, where the US market for AI agents pulled in USD 2.2 billion in 2024 alone. You can discover more insights about these AI agent statistics on Citrusbug.com.
These numbers aren't just hype. They prove that AI agents are practical, valuable tools being put to work right now.
Agents for Customer Service
One of the first places you’ll see AI agents in action is customer support. Companies are setting up sophisticated agents to handle questions, solve common problems, and walk customers through processes, often without a human ever needing to step in.
Picture this: a customer has an issue with their recent order. Instead of sitting on hold, they start a chat with an AI agent. In just a few moments, the agent can:
- Understand the problem: Using natural language processing, it figures out what the customer needs.
- Find the right info: It securely connects to the company's internal systems to pull up the specific order details.
- Get it done: Based on what it finds, it can process a refund, schedule a replacement, or give an accurate shipping update.
This whole thing takes seconds. The customer gets an instant answer, and the human support team is freed up to tackle the more nuanced, high-stakes problems that really need a personal touch.
Agents as Personal Assistants
AI agents are also becoming seriously powerful personal assistants, helping us wrangle the chaos of modern life. They can plug into all your different apps and services to organize your day, knock out administrative chores, and keep you on track.
For instance, you could tell an agent, "Find a 30-minute slot for a meeting with my team next week and book it." The agent gets to work, checking everyone’s calendars, finding a time that works for all, sending the invites, and even booking the virtual meeting room. All from one simple command.
Expert Opinion: "The beauty of modern AI agents is their accessibility. You don't need to be a developer to benefit," explains tech journalist Maria Chen. "With user-friendly platforms, anyone can create simple agents to automate personal tasks like organizing their messy download folder, summarizing a pile of unread articles, or even monitoring prices for a product they want to buy. It’s about giving everyone their own personal-duty automator."
Agents in Software Development
The software development world is also getting a major shake-up from AI agents. These specialized agents are like tireless coding partners that can write, debug, and even test code.
A developer might hand off a task like, "Build a user login page with a password reset feature." The AI agent can then generate the code, spot potential bugs before they become a problem, and suggest ways to make it more secure and efficient. This dramatically speeds up development, letting engineers focus on creative problem-solving instead of getting bogged down in routine coding. Many of these agents rely on advanced methods to generate accurate code and information; you can learn more about Retrieval-Augmented Generation in our article to see how they pull from vast knowledge bases to get the job done.
Understanding the Risks and How to Use Agents Safely

AI agents are undeniably powerful, but letting any piece of software act on your behalf means you need to be smart about it. Handing over the keys requires a clear-eyed view of what can go wrong. A cautious, thoughtful approach is the best way to tap into their benefits without running into trouble.
This isn’t about fear-mongering; it's just about being prepared. You wouldn't hand a brand-new employee the company credit card and full system access on their first day, right? You should treat AI agents the same way, setting up common-sense guardrails as you integrate them into your workflow.
When you peel it all back, the main challenges really come down to two things: accuracy and security. Let’s dig into what those actually mean in the real world and how you can stay in the driver's seat.
The Challenge of AI Hallucinations
One of the weirdest and most talked-about quirks of modern AI is the "hallucination." This is just a fancy term for when the AI confidently makes something up that sounds completely real but is totally false. It’s one thing when a chatbot does it, but it’s a whole different ballgame when an autonomous agent acts on that bogus information.
Imagine tasking an agent with pulling market data for a big report. If it hallucinates a key statistic and plugs it into a presentation that automatically gets sent to your boss, the fallout could be serious. Because agents are built to do things, a hallucination isn't just a wrong answer—it's a potentially damaging action.
Security and Data Privacy Concerns
The other big one is security. The moment you give an AI agent access to your email, company files, or customer database, you've created a new potential weak spot. Granting sweeping permissions without thinking it through is like leaving the front door of your office wide open overnight.
An agent with full access to your inbox, for example, could accidentally leak sensitive client data if you give it a vague or poorly worded instruction. The trick is to operate with a "least privilege" mindset: give the agent access only to the specific tools and data it absolutely needs to do its job, and nothing more.
Expert Insight: "Think of AI agent permissions like a digital keycard," advises cybersecurity analyst David Lee. "You wouldn't give a single keycard access to every room in a building. Instead, you grant access only to the necessary areas. This same principle of setting clear boundaries is fundamental to using agents securely."
Best Practices for Safe Agent Use
The good news is that you don't need a PhD in computer science to use AI agents safely. It mostly comes down to a bit of foresight and common sense. The broader questions around AI safety are complex, and we cover them in more detail in our guide on whether AI is safe to use.
For now, here are a few simple, practical steps to get started on the right foot:
- Start with Low-Stakes Tasks: Don't ask an agent to rebalance your investment portfolio on its first run. Have it do something simple, like summarizing articles or sorting your downloads folder. This lets you see how it works in a safe, controlled setting.
- Set Clear Boundaries and Permissions: Before you let an agent loose, carefully review and lock down its access. If its job is just to read your calendar to find open slots, make sure it can't also send emails or delete events.
- Keep a Human in the Loop: For anything important, treat the agent as a co-pilot, not the pilot. Let it do the research, draft the email, or outline the plan, but make sure a human gives the final "go" before any critical action is taken.
- Monitor and Review Agent Actions: Every so often, check the agent’s activity log. This is your window into what it's been doing. It helps you catch any weird behavior early and fine-tune your instructions for better, more reliable results.
Getting Started: How to Build Your First AI Agent
Ready to jump in and build your first AI agent? It’s a lot more accessible than you might think, and you definitely don’t need to be a programmer to get started. The trick is to begin with a small, manageable problem you want to solve and then explore the user-friendly tools that have popped up.
Think of it as a simple, step-by-step process. The goal isn't to build a world-changing system on day one, but to get a feel for automation by tackling a small, repetitive task in your own workflow. That's how you build confidence.
Find Your First Automation Project
The best place to start is by noticing the little points of friction in your daily routine. What are the tedious, manual things you find yourself doing over and over?
These are perfect candidates for your first AI agent:
- Information Gathering: Do you spend the first 30 minutes of your day piecing together news from five different websites? An agent can fetch all of it and hand you a single, neat summary.
- Price Tracking: Waiting for that one gadget to finally go on sale? An agent can watch the retail sites for you and ping you the second the price drops.
- File Organization: If your "Downloads" folder is a digital junk drawer, an agent can be set up to automatically sort files into the right folders based on type or name.
"The first step is always the hardest, but with AI agents, it's more about curiosity than complexity," says innovation consultant Anya Sharma. "Just ask yourself, 'What's one boring task I'd love to never do again?' That question is the perfect launchpad."
Explore Beginner-Friendly Tools
Once you have a task in mind, it’s time to find the right tool for the job. A ton of platforms now offer no-code or low-code interfaces, which means you can build agents using simple drag-and-drop actions and plain English prompts.
Look for tools that excel at connecting different apps and services—that’s where agents really start to shine. A great first project could be an agent that scours the web for the best deal on a product or one that compiles your daily news briefings into an email. The whole idea is to get your hands dirty and move from learning to doing as quickly as possible.
Frequently Asked Questions About AI Agents
Even after diving into the details, you might still have a few questions buzzing around. It's a new and fast-moving space, after all. Let's tackle some of the most common questions I hear and clear up any lingering confusion.
Are AI Agents the Same as Robots?
That's a great question, and the answer is no, but they're often connected. Here's a simple way to look at it: the AI agent is the "brain," and the robot is the "body."
An AI agent is pure software. It lives in the digital world, doing things like digging through data, navigating websites, or managing your inbox. A robot, on the other hand, is a physical machine designed to interact with the real world.
Now, an AI agent can absolutely be the brain inside a robot, directing its movements and actions. But the agent itself doesn't need a physical form to exist—it can run entirely on a server or your laptop.
Do I Need to Be a Coder to Use an AI Agent?
Not anymore, and this is what makes the current moment so exciting. While the core technology is built by developers writing complex code, a whole new wave of tools is being designed for the rest of us.
"The rise of no-code and low-code platforms means you can create a powerful AI agent using simple drag-and-drop interfaces and plain English," a recent report from TechForward noted. "If you can write a clear set of instructions for a person, you can build an agent to handle your tasks."
These platforms are intentionally designed to be user-friendly. They're breaking down the technical walls and putting serious automation power into the hands of marketers, founders, and creators, which is why we’re seeing them pop up everywhere.
What Is the Future of AI Agents?
In a word: teamwork. Today, we mostly use a single agent for a single purpose. The next frontier is the widespread use of multi-agent systems, where entire teams of specialized agents collaborate on complex goals.
Think about launching a new product. You could have:
- A "researcher" agent scanning the web for market trends and competitor data.
- A "data analyst" agent crunching those numbers to pull out key insights.
- A "strategist" agent using those insights to draft a marketing plan.
- And a "creative" agent generating a presentation to pitch the whole idea.
These agents will talk to each other, passing tasks back and forth just like a human team. We'll also see them become more seamlessly embedded in the apps we use every day, working behind the scenes to make everything we do a little bit smarter and a lot more efficient.
At YourAI2Day, our mission is to keep you ahead of the curve as AI continues to evolve. We're constantly tracking the latest breakthroughs and what they mean for you. To keep learning, explore the latest in AI on YourAI2Day.com.