Understanding AI Technology: A Friendly Guide for Beginners
If the term ‘Artificial Intelligence’ feels like a huge, complicated puzzle, you’re in the right place. Let's break it down together into simple ideas that actually make sense. At its most basic, AI is the science of making machines smart—giving them the ability to learn, reason, and solve problems in ways that feel surprisingly human. Think of it less like a sci-fi robot and more like a clever assistant that’s already helping you out every day.
What Is AI and How Does It Actually Work?

Before you picture futuristic robots, it's helpful to know that AI is already woven into your daily life, often working quietly in the background to make things a little bit smoother and smarter.
It’s the magic behind Netflix suggesting a movie you end up loving, or Waze finding a clever shortcut to get you out of a traffic jam. These systems aren't just following a rigid script; they're using data to make intelligent decisions in real-time.
The Core Idea: Learning from Data
At its heart, AI works by finding patterns. It plows through massive amounts of information—far more than any person could ever process—to learn, adapt, and make predictions. This whole process is driven by algorithms, which are really just sets of rules a computer follows to get a job done.
Think about how you’d teach a toddler to recognize a cat. You'd show them pictures, pointing out the key features: pointy ears, whiskers, a long tail. After seeing enough examples, the child starts identifying cats all on their own. AI learns in a very similar way, but its "pictures" are digital data. For example, a spam filter in your email learns what junk mail looks like by analyzing thousands of emails you’ve marked as spam in the past.
This ability to learn from experience is what makes AI so different from simple automation. It’s not just doing what it’s told; it's figuring things out for itself.
From Simple Rules to Smart Decisions
The earliest AI systems were built on strict "if-then" logic. A classic example would be in a chess program: "if a piece is threatened, then move it to a safe square." This works fine for straightforward tasks, but it falls apart when faced with the messy, unpredictable nature of the real world.
Modern AI takes a completely different route. Instead of having every possible scenario programmed into it, it’s trained on vast datasets to build its own understanding. This is what allows an AI system to do some incredible things:
- Recognize Speech: Your voice assistant, whether it's Siri or Alexa, learns to understand different accents and unique phrasing by analyzing thousands of hours of spoken language.
- Identify Objects: A self-driving car’s camera can tell the difference between a person and a streetlamp because it’s been trained on millions of images from the road.
- Personalize Content: Your social media feed curates posts it thinks you'll find interesting based on your past activity—everything you’ve liked, shared, or commented on.
As AI expert Andrew Ng puts it, "AI is the new electricity." He means that just like electricity transformed countless industries a century ago, AI is now poised to do the same, fundamentally changing how we live and work.
Ultimately, getting a handle on AI technology means understanding this fundamental shift from programming to training. We give the AI the data and a goal, and it figures out the best way to achieve it. It’s a dynamic, ever-evolving process that’s becoming more a part of our world every single day.
How AI Learns: The Magic Behind The Machine
So, how does a computer go from a blank slate to making smart decisions? It all comes down to learning, a lot like how we do, but on a mind-boggling scale. This learning process is the engine driving artificial intelligence, and it’s a field of computer science known as Machine Learning (ML).
Let's stick with our toddler analogy. Think about teaching them to recognize a dog. You wouldn't hand them a textbook with rules defining every possible breed. Instead, you just point and say, "dog." After seeing enough pictures—big dogs, small dogs, fluffy dogs, sleek dogs—they start to connect the dots on their own.
AI does something very similar. It chews through massive amounts of data—images, text, numbers, you name it—to find patterns and build its own understanding. This is exactly how your email filters out junk and your favorite streaming service seems to know what you want to watch next.
The Different Ways AI Can Learn
Just like people have different learning styles, AI has a few main ways of taking in information. The two most common methods are kind of like learning with a teacher versus figuring things out for yourself. Grasping these is key to understanding AI technology as a beginner.
-
Supervised Learning (Learning with a Teacher): In this approach, the AI gets a dataset where all the answers are already provided. It’s like giving a student flashcards with a picture on one side and the correct word on the back. For example, an AI might be fed thousands of emails that have been clearly labeled "spam" or "not spam." By studying these examples, it learns the tell-tale signs of junk mail (like weird links or urgent money requests) and can start filtering your inbox on its own.
-
Unsupervised Learning (Learning on Its Own): This time, the AI is handed a big pile of data with no labels or answers. Its job is to find hidden patterns and group similar things together without any help. Imagine giving a kid a box of mixed-up toys and watching them sort everything into piles of cars, dolls, and blocks. E-commerce sites use this to group customers with similar shopping habits for personalized marketing campaigns. For instance, Amazon might notice a group of people who buy running shoes also tend to buy fitness trackers, and then suggest that product to the next person who buys shoes.
These learning models are the foundation for countless AI tools we use every single day, from simple recommendations to much more complicated tasks.
Going Deeper with Neural Networks
When AI has to tackle really complex problems, like understanding human speech or recognizing a specific face in a crowd, it often uses a more advanced technique called Deep Learning. Its design is actually inspired by the structure of our own brains.
Deep Learning uses what are called artificial neural networks, which are made up of layers of interconnected digital "neurons." Each layer gets good at recognizing one specific feature. When you show a deep learning model a photo of a dog, the first layer might just spot basic shapes. The next might pick out edges and textures, a later one might identify an ear or a tail, and the final layer puts all those clues together to confidently say, "Yep, that’s a dog."
As Yoshua Bengio, one of the pioneers in the field, puts it, the real power of deep learning is its ability to automatically discover complex structures in huge datasets. This is what allows AI to take on tasks once thought to be exclusively human.
This layered approach is what’s behind some of the most impressive AI today, including virtual assistants like Alexa and the complex systems that guide self-driving cars.
AI is More Accessible Than Ever
Not too long ago, building and training these powerful learning models was incredibly expensive and demanded huge amounts of computing power. But things have changed—fast.
The efficiency and affordability of AI have improved at an astonishing pace, tearing down the barriers that once kept it out of reach for most companies and even individuals. Between November 2022 and October 2024, the computational cost to run top-tier AI models dropped by more than a 280-fold. This is thanks to smaller, smarter models and massive hardware improvements. You can read the full research about these AI cost reductions to see just how quickly the field is moving.
This rapid progress means that understanding how AI works is no longer just for data scientists. It's becoming a crucial skill for all of us as these smart systems weave themselves deeper into our work and daily lives, making the magic behind the machine a little less mysterious.
Exploring The Different Kinds of AI
Not all AI is created equal. Think of it like a toolbox—you wouldn't use a hammer to turn a screw. Different AI systems are built for very different jobs, and knowing the difference is the first real step to understanding what AI is all about.
At the highest level, AI splits into two big categories: the highly specialized systems we use every day, and the kind of all-purpose intelligence that, for now, lives mostly in science fiction.
The Specialist: Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI)
Pretty much every AI you interact with today falls under this umbrella. Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI), sometimes called "Weak AI," is designed to do one specific thing incredibly well. It operates within a tightly defined set of rules and can't step outside its designated lane.
It’s the silent partner powering your favorite apps and devices. They are absolute masters of a single trade:
- Siri and Alexa are brilliant at understanding voice commands to set timers or play music, but you can’t ask them to write a marketing plan.
- The facial recognition on your phone unlocks it in a split second, but it has no idea who you are as a person or what your face means.
- Netflix’s recommendation engine is a pro at figuring out what you should watch next, but it can’t diagnose a strange noise your car is making.
These systems are hyper-focused specialists. Their intelligence is a mile deep but only an inch wide. They are incredibly powerful tools, not conscious thinkers.
The All-Rounder: Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
This is the AI you’ve seen in the movies. Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), or "Strong AI," describes a theoretical AI with the flexible, adaptive intelligence of a human being. An AGI could learn, reason, and apply its smarts to solve just about any problem you throw at it, just like a person can.
A true AGI would be a machine that can perform any intellectual task that a human being can. It wouldn't just be good at one thing; it would be capable of understanding and learning across a vast spectrum of disciplines.
As of today, AGI doesn't exist. While advanced models like ChatGPT show astonishing flexibility, they are still fundamentally narrow systems trained on huge, but specific, datasets. Building a genuine AGI is a monumental challenge, raising all sorts of technical and ethical questions that researchers are still just beginning to tackle.
To get a better sense of how these AI systems actually work, from the data they're fed to the hardware that powers them, this diagram breaks it down nicely.
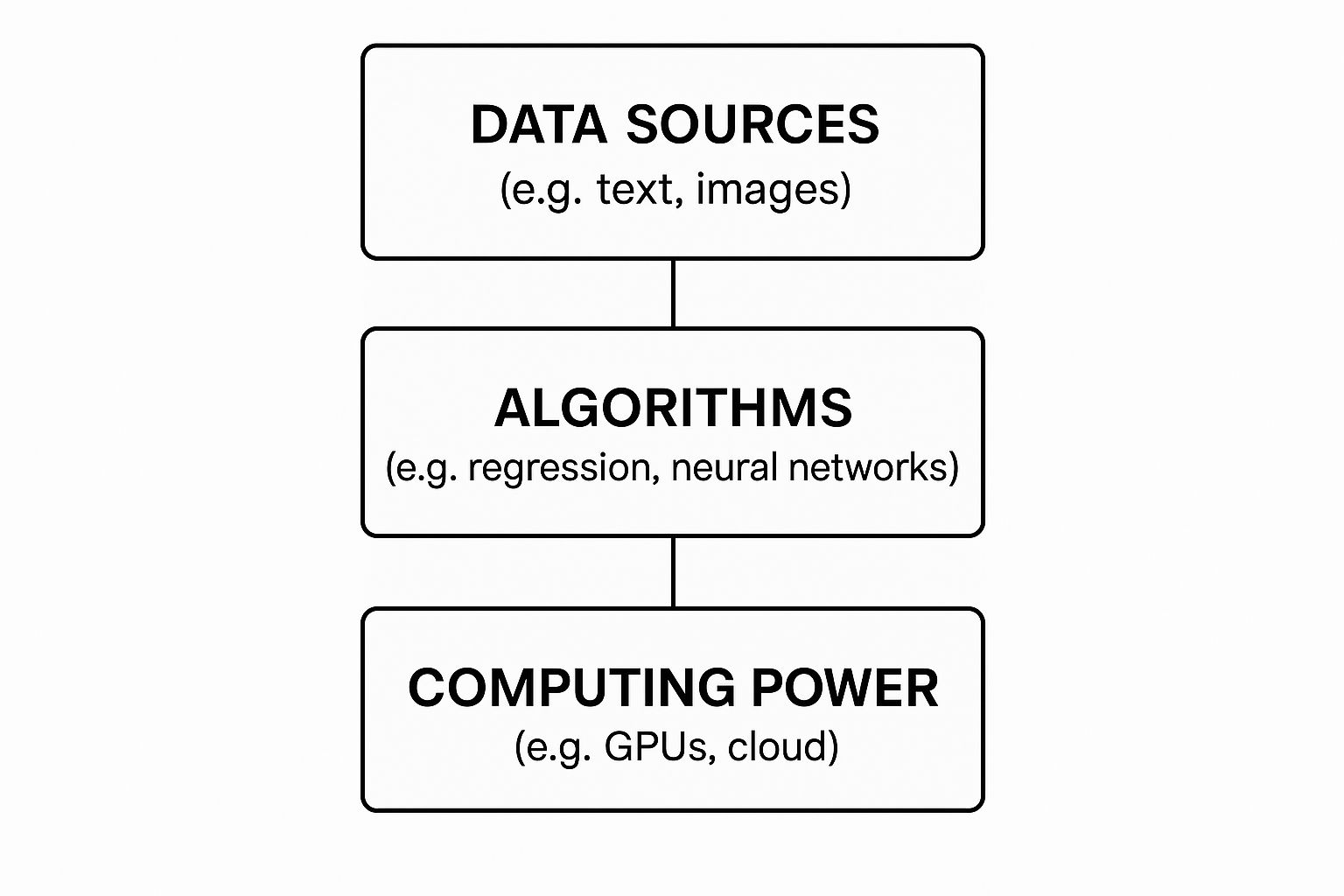
As you can see, every AI starts with raw data. Algorithms then process that data, running on powerful hardware, to produce what we see as an intelligent outcome.
A Quick Guide to the Types of AI
To help you quickly tell these AI types apart, here's a simple breakdown. This table compares the different kinds of AI based on their capabilities, real-world examples, and limitations, helping you understand their distinct roles.
| AI Type | Key Capability | Everyday Example | Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reactive Machine | Acts in the present; no memory | IBM's Deep Blue (chess program) | Can't learn from past experiences |
| Limited Memory | Uses recent past to make decisions | Self-driving cars avoiding traffic | Memory is temporary and short-term |
| Theory of Mind | Understands human thoughts/emotions | Currently theoretical | Does not yet exist; highly complex |
| Self-Aware | Possesses consciousness, self-identity | Purely science fiction | Raises profound ethical questions |
This table shows the progression from what we have today (Reactive and Limited Memory) to what researchers are still working toward.
Different AI Brains for Different Tasks
Beyond just capability, we can also group AI by its functionality—basically, how it "thinks" and interacts with the world. Think of these as different operating systems for intelligence.
-
Reactive Machines: This is the most fundamental type of AI. It sees the world and reacts, but it has zero memory of the past. IBM's Deep Blue, the chess computer that beat grandmaster Garry Kasparov, is the classic example. It analyzed the board and made the best move for that exact moment, but it never learned from past games.
-
Limited Memory: This is where nearly all modern AI lives. These systems can look into the immediate past to inform their next move. A self-driving car is a perfect example. It's constantly tracking the speed and direction of nearby cars, using that very recent history to navigate safely. Its memory is crucial but fleeting.
-
Theory of Mind: Now we're heading into the future. This is a more advanced class of AI that researchers are actively working on. A "Theory of Mind" AI would be able to understand that people have beliefs, intentions, and emotions, which would allow for far more natural and empathetic human-machine interaction.
-
Self-Aware AI: The final, and most speculative, stage is a self-aware AI. This is a machine that would have its own consciousness, self-awareness, and maybe even feelings. For now, this concept is purely theoretical and belongs more to philosophy and sci-fi than it does to computer science.
By keeping these different categories in mind, you're better equipped to understand the strengths, limits, and true nature of the AI systems that are already changing our world.
You Use AI More Than You Think—It's Part of Your Daily Life

If you think artificial intelligence is something reserved for sci-fi movies or Silicon Valley labs, you might be surprised to learn you’re already using it every single day. AI isn't some far-off concept; it’s the invisible engine running in the background, making your life easier, safer, and more connected.
From the moment you pick up your phone in the morning until you stream a movie at night, AI is quietly working for you. Let's pull back the curtain and see just how deeply this technology is already woven into your daily routine.
Your Morning Routine, Powered by AI
Your day probably starts with your smartphone, a device that's absolutely packed with AI. When you ask a smart assistant like Siri or Google Assistant for the weather, it's using natural language processing to understand your words and give you a conversational answer.
Even snapping a quick photo is an AI-powered event. Your phone's camera uses sophisticated AI to:
- Spot faces in a group photo to make sure everyone stays in focus.
- Tweak lighting and color on the fly, giving you the best possible shot.
- Pick the sharpest image from a quick burst, so you don't have to scroll through blurry duds.
This isn't just simple programming. It’s AI making split-second decisions—acting as a tiny photographer and photo editor right in your pocket.
Navigating Your World and Your Wallet
When you head out the door, AI is right there with you. Fire up a navigation app like Google Maps or Waze, and you're tapping into a powerful AI that crunches live traffic data, accident reports, and road closures to find you the fastest route. It learns and adjusts in real time.
That same helpful technology is also keeping an eye on your finances. Ever gotten a fraud alert from your bank for a weird charge? You can thank an AI for that.
Banks and credit card companies use machine learning algorithms to learn your typical spending habits. If a transaction suddenly pops up that doesn't fit your pattern—like a big purchase in a different country—the AI flags it instantly to protect you from fraud.
This kind of monitoring happens faster and more accurately than any human team could manage, highlighting a massive benefit of AI in modern security.
Entertainment and Shopping, Curated for You
When it’s time to unwind, AI is working to personalize your experience. Streaming giants like Netflix and Spotify have perfected AI-driven recommendations. Their algorithms analyze what you watch and listen to, then cross-reference it with millions of other users' tastes to suggest something you'll almost definitely enjoy. In fact, an incredible 75% of what people watch on Netflix is driven by its recommendation engine.
Online shopping operates on the same principle. When Amazon suggests a product, it's not a shot in the dark. Its AI has learned what you like from your past purchases and browsing history, creating a shopping feed that feels like it was made just for you. This kind of personalization is a huge part of e-commerce, and you can learn more about how businesses use it in our guide on how to use AI for marketing.
The truth is, AI is already a massive part of our lives. An estimated 78% of organizations use AI in some capacity, and it actively engages around 378 million users across the globe. As this Netguru report on AI adoption shows, the technology is everywhere, even if we don't always notice it.
The Promise and Problems of AI Technology

Like any powerful new tool, artificial intelligence is a double-edged sword. To truly grasp what we're dealing with, we need an honest look at both its incredible potential and the serious questions it raises. It promises to help solve some of our biggest problems, but it also brings a host of challenges we have to face head-on.
On one side, the upsides are enormous. AI is already becoming a crucial ally in tackling complex global issues. In medicine, for example, AI algorithms can analyze medical scans with a speed and accuracy that can help doctors spot diseases like cancer much earlier. The goal isn't to replace doctors, but to give them super-powered tools to save lives.
Beyond the hospital, AI is boosting efficiency everywhere you look. It’s helping create smarter energy grids that cut waste, optimizing supply chains to move goods faster, and powering scientific research by finding patterns in data that would take a person decades to see.
A Look at the Opportunities
The positive impact of AI is already showing up across countless industries, creating entirely new ways to work and live. Its potential to improve our world is genuinely far-reaching.
- Accelerating Discovery: AI can sift through massive datasets to speed up research in everything from climate change to developing new materials. A practical example is Google's DeepMind, which used AI to predict the structure of over 200 million proteins, a task that would have taken centuries with old methods.
- Boosting Accessibility: Tools powered by AI, like real-time captioning and voice assistants, are breaking down barriers for people with disabilities.
- Enhancing Safety: AI systems can monitor dangerous work environments, predict when equipment might fail, and even assist in disaster relief efforts.
But these amazing opportunities don't come for free. They bring some significant hurdles and ethical dilemmas to the table.
Navigating the Critical Concerns
As AI becomes more woven into the fabric of our society, we have to confront its downsides. The most talked-about issue is, of course, jobs. While AI certainly creates new roles, it also automates tasks once done by people, sparking real concern about job displacement and the need for new skills. Many routine tasks can now be handled far more efficiently, as detailed in our article about what is robotic process automation.
Another huge problem is algorithmic bias. If you train an AI on biased data, you're going to get biased results. This isn't just a theoretical problem—it has led to hiring tools that unfairly favor certain candidates and facial recognition systems that are less accurate for women and people of color.
Finally, there’s the question of privacy. AI systems often need huge amounts of personal data to work effectively, raising serious concerns about how that information is collected, used, and protected. Striking the right balance between innovation and our right to privacy is one of the defining challenges of our time.
As AI ethicist Kate Crawford wisely noted, "AI is neither artificial nor intelligent. It is made from natural resources, fuel, human labor, infrastructures, logistics, histories, and classifications… it is not autonomous, rational, or able to discern things without extensive, computationally intensive training with large data sets."
This perspective is everything. It reminds us that technical power must always be guided by human values. A thoughtful approach ensures that as we build smarter machines, we're also building a better, fairer, and more equitable future for everyone. It’s a conversation we all need to be a part of.
What Does The Future Hold For AI?
We've covered how AI works and what it's doing today, but where is this all headed? The future of artificial intelligence isn't just a sci-fi movie plot; it's being built right now in research labs and development teams around the world. We're on a path toward AI that is smarter, more understandable, and deeply integrated into our lives.
One of the biggest shifts happening is the push for Explainable AI (XAI). As we hand over more critical decisions to AI—in fields like medicine or finance—just getting the right output isn't good enough. We need to understand the "why" behind its conclusions.
XAI is all about cracking open that black box. The goal is to make an AI's thought process transparent, so a doctor can see exactly why an AI model flagged a medical scan, or a bank customer can understand the specific factors that led to their loan being denied. Trust is everything, and explainability is the key.
The Rise of Creative and Hyper-Personalized AI
The boom in Generative AI is only just beginning. We're moving way beyond just creating text and images. Think about AI composing original soundtracks for indie films or designing dynamic lesson plans for students that adjust on the fly based on their individual learning pace. This isn't about replacing human creativity; it's about amplifying it.
This level of sophistication opens the door to a future where hyper-personalization is everywhere. Healthcare could move from treatment to prevention, with AI analyzing your unique genetic data and daily habits to recommend lifestyle tweaks before a problem ever starts. From education to entertainment, our experiences will become far more tailored to who we are.
As Demis Hassabis, CEO of Google DeepMind, puts it, "The goal is to build general-purpose learning systems that can learn to solve any problem. I think of AI as a meta-solution. It’s a tool that will help us solve all sorts of other problems."
The economic force behind this shift is massive. Projections suggest AI could pump over $15 trillion into the global economy by 2030. The market is expected to grow at a compound annual rate of nearly 36% between 2025 and 2030.
This explosive growth also means a huge demand for talent. It's estimated that 97 million skilled professionals will be needed by 2025 to keep up. You can discover more insights about AI's economic future and see just how fast this market is expanding.
Of course, the ultimate moonshot for many researchers is still achieving a truly human-like intelligence. While that remains a distant destination, every step we take today in building more transparent, creative, and personalized AI is getting us closer.
If these future trends spark your imagination, a great next step is to look into some forward-thinking artificial intelligence startup ideas. After all, the future isn't just something to watch unfold—it's something we're all helping to build.
Answering Your Top Questions About AI
As you get more familiar with AI, some questions always seem to come up. Let's dig into a few of the most common ones to help clear the air and lock in the concepts we’ve covered.
Is AI the Same as Machine Learning?
This is a fantastic question, and it really comes down to scope. The simplest way to think about it is to picture Artificial Intelligence as the entire, sprawling field of making machines smart. Machine Learning (ML) is one of the most important and powerful subsets within that field.
So, while all machine learning is definitely a form of AI, not all AI involves machine learning. For example, some early AI systems were based purely on hard-coded rules—a massive list of "if-then" statements—with zero ability to learn on their own. ML is the game-changer that gives modern AI the power to actually learn from data and get better over time.
Will AI Take Away All Our Jobs?
This is probably the biggest question on everyone's mind. And while it's true that AI is getting incredibly good at handling routine and repetitive tasks, history has shown us that new technology tends to transform jobs rather than erase them entirely. Think about it—the internet created whole new industries and careers that no one could have imagined. AI is poised to do the same.
In fact, a recent PwC analysis predicts a need for 97 million people by 2025 just to keep up with the demand for AI skills. The real shift will be away from tasks that can be automated and toward roles that lean on uniquely human skills like creativity, strategic thinking, and emotional intelligence. Adapting and learning how to work with AI will be the name of the game.
Can AI Actually Think and Feel?
For now, that’s a hard "no." The AI we use every day, from chatbots to recommendation engines, has no consciousness, self-awareness, or genuine emotions. It's just incredibly sophisticated pattern-matching. It analyzes vast amounts of data and generates outputs that mimic intelligence or empathy.
An AI can write a heartbreaking poem, but it doesn't feel the heartbreak. It's just masterfully arranging words in a sequence that it has learned humans associate with sadness.
The kind of AI that could truly think for itself, often called Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), is still purely theoretical. The systems we have today are incredibly powerful tools, but they aren't sentient beings. Keeping that distinction in mind is crucial for having a realistic view of what today's AI can and can't do.
Ready to stay ahead of the AI curve? At YourAI2Day, we provide the latest news, tools, and insights to help you make sense of this fast-moving field. Visit https://www.yourai2day.com to explore more.