Machine Learning Use Cases: Transforming Industries in 2025
Ever wonder how Netflix knows exactly what show you'll want to binge next? Or how your bank can text you about a weird-looking charge moments after it happens? That’s not magic; it's machine learning, and it's quietly running the world behind the scenes. Forget the sci-fi stuff about robot overlords—the real AI revolution is already here, helping businesses work smarter, not harder.
This guide is your friendly tour of the most practical and powerful machine learning use cases out there today. We're skipping the dense jargon and diving straight into 12 real-world examples that are making a huge difference. Think of this as a playbook, not a textbook. We'll break down how these systems work, why they're so effective, and what you can learn from them.
You’ll get the inside scoop on how factories predict when a machine will break down, how your favorite shopping site seems to read your mind, and how AI is helping doctors spot diseases earlier than ever. Whether you're a business owner thinking about your first AI project, a tech enthusiast curious about what’s next, or just someone who wants to understand how all this AI stuff actually works, you’re in the right place. Let's explore how machine learning is already making our world more efficient and intelligent.
1. Predictive Maintenance in Manufacturing
Predictive maintenance is a game-changer for anyone who works with heavy machinery. Instead of waiting for a critical piece of equipment to break down (and cause a massive headache), this approach uses machine learning to spot trouble before it starts. How? By listening to the machine. Sensors on the equipment constantly feed data—like temperature, vibration, and energy use—into an ML model. The model learns what "normal" looks like and flags tiny changes that signal a future failure.
This lets companies schedule repairs exactly when needed, avoiding costly surprise shutdowns. As an industry veteran, Maintenance Supervisor Tom Connell, often says, "It's the difference between your mechanic calling you to say your tire tread is getting low and you blowing a tire on the freeway at rush hour. One is a calm appointment; the other is a crisis."
Strategic Breakdown
- Business Impact: The ROI is huge. Preventing just one major shutdown can save a company millions. It also makes equipment last longer, cuts repair costs, and keeps workers safer by avoiding dangerous breakdowns.
- Data & Models: It’s all about time-series sensor data. Common models include Random Forest and Gradient Boosting, with more advanced LSTMs (Long Short-Term Memory) networks being used to understand sequences of events. For a peek at the future, check out how time-series foundation models can act as few-shot learners.
- Maturity Level: This is a tried-and-true application. Big players like General Electric (with their Predix platform) and Siemens (with MindSphere) have proven its value for years.
Actionable Takeaways
Want to try this? Start small. Pick one crucial machine where a failure would be a disaster. Gather at least six months of sensor data, making sure you have examples of both normal operations and past failures. This data is what you'll use to teach your model what to look for.
2. Recommendation Systems for E-commerce
Ever felt like your favorite online store just gets you? That's a recommendation engine at work, and it's one of the most profitable machine learning use cases ever created. These systems are the ultimate personal shoppers. They analyze everything you do on a site—what you buy, what you look at, what you add to your cart and then abandon—to predict what you'll want next.
The goal is to stop shouting generic ads at everyone and start whispering helpful suggestions to each individual. As retail analyst Sarah Chen puts it, "A good recommendation feels like a friend who knows your style, not a pushy salesperson. It builds trust and loyalty because the customer feels understood." That's how Amazon, Netflix, and Spotify keep you coming back for more.
Strategic Breakdown
- Business Impact: It’s massive. Recommendations directly increase how much people buy and how often they return. Amazon famously reported that up to 35% of its sales come from its recommendation engine. It’s not just a feature; it’s a core part of their business model.
- Data & Models: The key ingredients are user interaction logs (clicks, views, purchases) and product details. The techniques range from collaborative filtering (finding people with similar tastes) to more complex deep learning models that can pick up on subtle preferences.
- Maturity Level: This is a very mature field, but it's still evolving. The latest trend is generative AI shopping assistants that can have a natural conversation with you about what you’re looking for.
Actionable Takeaways
If you're just starting, focus on the data you already have, like what people click on. This "implicit feedback" is way more common than explicit star ratings. Start with a simple model to see what works, and don't forget to test where you put the recommendations—on the homepage, a product page, or at checkout?
3. Fraud Detection in Financial Services
Fraud detection is one of the most important behind-the-scenes machine learning use cases. Old systems used simple rules, like "flag any transaction over $1,000 from a foreign country." But criminals quickly learned how to get around those. Modern ML models are like super-smart detectives. They analyze thousands of data points in real time—the amount, the location, the time of day, your usual spending habits—to spot anything that looks fishy.
It's all about catching fraud before the money is gone. As one FinTech analyst put it, "Imagine trying to spot a single fake bill in a mountain of cash. Machine learning gives you the superpower to feel the texture of every single one instantly." This is the tech that powers the fraud alerts for companies like Visa, Mastercard, and PayPal, protecting billions of us every day.
Strategic Breakdown
- Business Impact: The main benefit is saving a ton of money that would otherwise be lost to fraud. It also builds trust with customers and cuts down on the time and money spent on manual investigations.
- Data & Models: It’s all about transaction data. Models like Logistic Regression and Random Forest are common, but Gradient Boosting Machines (like XGBoost) are a favorite for their high accuracy.
- Maturity Level: This is a highly mature and essential ML application. If you're in finance, you're either using it or you're falling behind.
Actionable Takeaways
To build a good fraud system, you need a tight feedback loop. When a transaction is flagged, a human analyst should review it. Their decision—"yes, this was fraud" or "no, this was fine"—is priceless data for retraining and improving the model. It’s also wise to combine several different models to get the most accurate result and avoid annoying legitimate customers with false alarms.
4. Medical Image Analysis and Diagnosis
In healthcare, machine learning is literally saving lives. One of the most incredible machine learning use cases is teaching AI to read medical scans like X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans. Deep learning models, especially Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), are trained on thousands of images to learn how to spot signs of diseases like cancer, pneumonia, or diabetic eye disease, sometimes with accuracy matching or even exceeding human experts.
This isn't about replacing doctors. It's about giving them a powerful assistant. The AI can quickly scan an image, highlight areas of concern, and essentially say, "Hey, you might want to take a closer look at this." As one radiologist explained, "AI helps us find the needle in the haystack much faster. I can focus my energy on the toughest cases, which means better care for everyone."
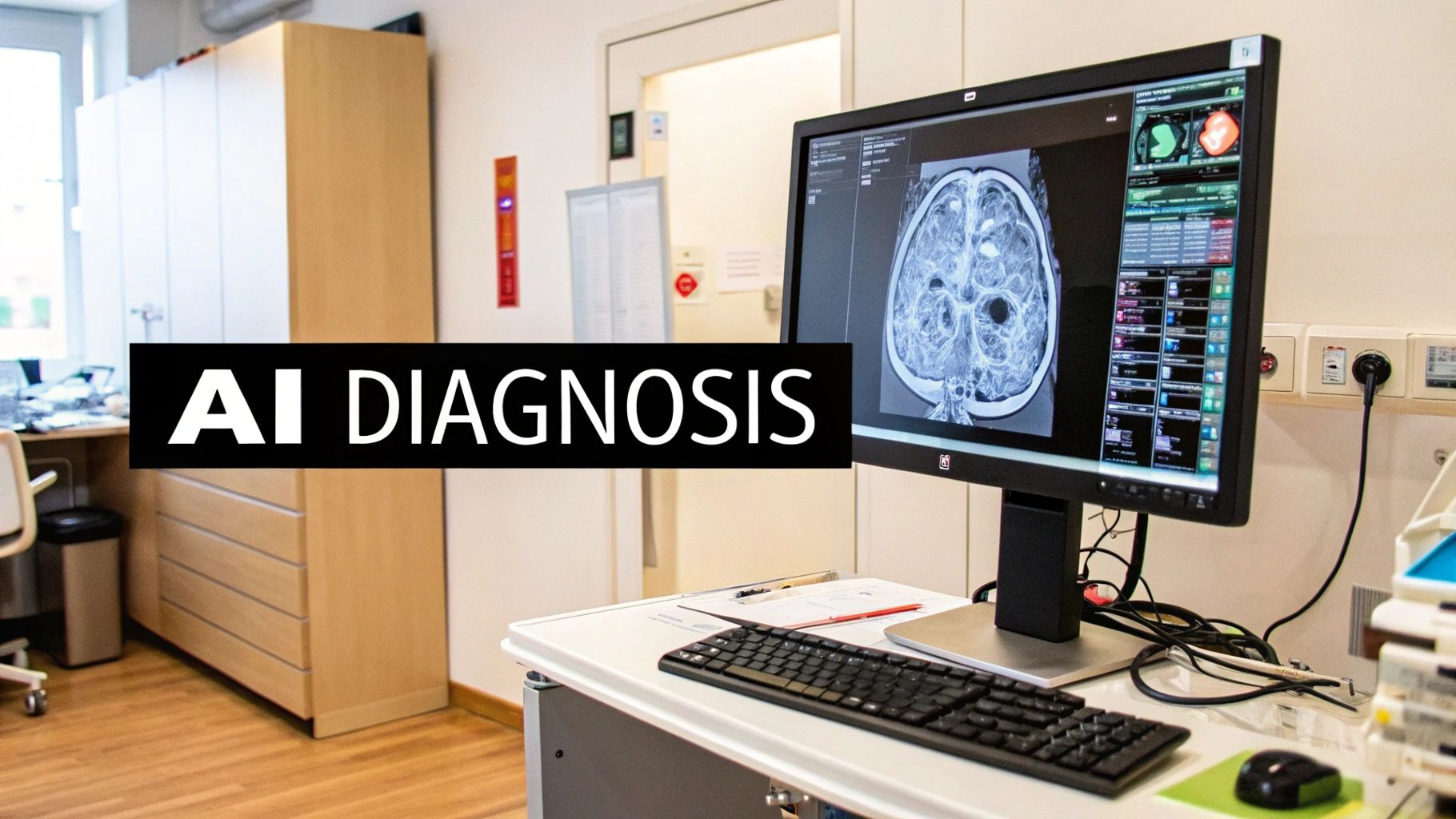
Strategic Breakdown
- Business Impact: Better patient outcomes through earlier, more accurate diagnoses. For hospitals, it means more efficiency, less burnout for radiologists, and fewer costly misdiagnoses.
- Data & Models: High-quality, carefully labeled medical images are the key. CNNs like U-Net and ResNet are the industry standard. For more on what's next, see how generative AI is creating new possibilities in healthcare.
- Maturity Level: This is quickly moving from the research lab to the real world. Several AI systems have already been approved by the FDA, and big names like Google and Siemens are leading the charge.
Actionable Takeaways
Getting into this space requires a strong partnership with hospitals to get access to good data. It’s also critical to make sure the AI is "explainable"—it needs to show doctors why it made a recommendation. Trust is everything in medicine.
5. Natural Language Processing for Chatbots and Virtual Assistants
If you've ever asked Siri for the weather or used a website's chat window to ask a question, you've interacted with Natural Language Processing (NLP). This is one of the most common machine learning use cases, and it's all about teaching computers to understand and speak our language. The latest generation of chatbots, powered by Large Language Models (LLMs) like those behind ChatGPT, are incredibly good at it.
They can understand the intent behind your words, remember the context of the conversation, and provide genuinely helpful answers. As AI researcher Dr. Alistair Finch notes, "We've graduated from clunky, scripted bots that only understood keywords. Modern assistants can have a real conversation, making them powerful tools for customer support, education, and more."
Strategic Breakdown
- Business Impact: Happier customers and lower costs. Chatbots can answer common questions instantly, 24/7, freeing up human agents to handle the really tricky problems. This means shorter wait times and more efficient support teams.
- Data & Models: These models are trained on massive amounts of text from the internet. The state-of-the-art models are transformer-based LLMs like the GPT series from OpenAI and Google's Gemini.
- Maturity Level: While simple chatbots have been around for a while, the technology behind advanced virtual assistants is evolving at lightning speed. It's an exciting and competitive space.
Actionable Takeaways
If you want to build a chatbot, start with a clear goal. Don't try to make it do everything at once. Maybe it just answers the top five customer questions. And always, always have an easy way for a user to say, "I need to talk to a human," when the bot gets stuck.
6. Computer Vision for Autonomous Vehicles
Computer vision is what allows self-driving cars to "see" the world. It’s easily one of the most ambitious and high-stakes machine learning use cases. Cameras all around the car feed a constant stream of video into deep learning models. These models are trained to identify everything in real-time: other cars, pedestrians, cyclists, traffic lights, and lane markings.
This technology is the heart of systems like Tesla's Autopilot and Waymo's self-driving taxis. The goal is to create a driver with superhuman perception that never gets tired or distracted. As one industry expert explained, "We're teaching cars to see and understand the road like an expert driver, but with 360-degree vision and lightning-fast reflexes."

Strategic Breakdown
- Business Impact: The ultimate goal is to make our roads dramatically safer by eliminating accidents caused by human error. It also has the potential to completely change logistics and public transportation.
- Data & Models: The secret sauce is massive amounts of labeled video data from millions of miles of driving in all sorts of conditions. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are the workhorses for this kind of image recognition.
- Maturity Level: This field is advancing quickly but is still emerging. While we have cars with impressive driver-assist features, achieving full self-driving (where no human is needed at all) is still a huge technical challenge.
Actionable Takeaways
Developing this tech requires an obsession with safety and data. You need data from every imaginable "edge case"—a deer jumping onto the road, a sudden snowstorm, a confusing construction zone. Testing starts in computer simulations before ever hitting the road, and even then, safety drivers are crucial.
7. Personalized Marketing and Customer Segmentation
Personalized marketing is about moving beyond one-size-fits-all ad campaigns and talking to customers as individuals. This is one of the most valuable machine learning use cases for any business. ML algorithms sift through customer data—purchase history, browsing behavior, demographics—to group people into specific segments. For example, it can identify a group of "high-value customers who love running shoes and usually buy on weekends."
This allows companies to send the perfect message to the right person at the right time. As marketing strategist Amelia Chen says, "Good personalization feels helpful, not creepy. The algorithm spots the pattern, which allows the marketer to build a genuine relationship." It's the technology that powers the tailored emails and ads you get from brands that seem to know exactly what you need.
Strategic Breakdown
- Business Impact: A much better return on investment (ROI) for your marketing dollars. Personalized campaigns get more clicks, more conversions, and build stronger customer loyalty.
- Data & Models: The fuel is customer data from your CRM, website analytics, and sales records. K-Means Clustering is a popular algorithm for creating segments, while models like Logistic Regression can predict which customers are likely to churn.
- Maturity Level: This is a very mature field. Tools from companies like HubSpot, Salesforce, and Adobe have made this technology accessible to businesses of all sizes.
Actionable Takeaways
To get started, combine what people do (behavioral data) with who they are (demographic data). This gives you a much richer picture. And always remember the golden rule: be transparent about how you use data and respect customer privacy.
8. Sentiment Analysis for Brand Monitoring and Social Media
Sentiment analysis is like having a superpower that lets you know what the entire internet is feeling about your brand in real time. It’s one of the most practical machine learning use cases, using NLP to read through thousands of social media posts, news articles, and product reviews, automatically labeling each one as positive, negative, or neutral.
This gives you an instant snapshot of public opinion. Did your new ad campaign land well? Are people complaining about a bug in your latest software update? As social media strategist Maria Flores puts it, "Sentiment analysis is your early warning system. It tells you whether you've got a viral hit or a PR crisis on your hands, often before you see it in the sales numbers."
Strategic Breakdown
- Business Impact: It helps you protect your brand's reputation, find and help unhappy customers, and get honest feedback on your products. For example, a sudden spike in negative sentiment around "battery life" tells your product team exactly what to fix.
- Data & Models: The data is all the text you can find online about your brand. Simple models like Naive Bayes can work, but more advanced models like BERT are much better at understanding the nuances of human language, like sarcasm.
- Maturity Level: This is a very mature technology. There are plenty of ready-to-use tools like Brandwatch and Sprout Social that can get you started in minutes.
Actionable Takeaways
Don't just look at the overall sentiment. Dig deeper. Is the sentiment negative about your pricing but positive about your customer service? This level of detail is where the real insights are. Set up alerts for big swings in sentiment so you can react quickly.
9. Credit Risk Assessment and Loan Approval
For banks and lenders, one of the most important machine learning use cases is figuring out who is likely to pay back a loan. Old-school credit scores look at a few basic factors. But ML models can analyze hundreds of different variables—from your transaction history to your employment stability—to create a much more accurate and holistic picture of your creditworthiness.
This leads to faster, fairer, and more accurate lending decisions. Dave Girouard, the CEO of the fintech company Upstart, often points out that AI can find creditworthy people that traditional systems might overlook, opening up access to affordable credit for more people. For example, a young person with a thin credit file but a high-earning degree and stable job might be approved by an ML model but rejected by a standard score.
Strategic Breakdown
- Business Impact: Lenders can approve more loans while taking on less risk. This means more revenue and happier customers who get instant decisions instead of waiting for days.
- Data & Models: The core data includes loan applications and credit reports. Gradient Boosting models (like XGBoost) are the industry standard because they are powerful and can be made "explainable."
- Maturity Level: This is a very mature application that forms the backbone of the modern fintech industry.
Actionable Takeaways
When you're using AI to make important decisions about people's lives, you have to be able to explain why the model made its decision. This is a huge focus for regulators. It's also smart to have a "human-in-the-loop" system where a person reviews any borderline cases the AI isn't sure about.
10. Demand Forecasting and Inventory Optimization
For any business that sells physical products, demand forecasting is crucial. It’s one of the most profitable machine learning use cases because it helps you have exactly the right amount of stuff in stock. Too much, and you're wasting money on storage. Too little, and you're losing sales. ML models are great at this because they can look at past sales, seasonality, current promotions, and even external factors like weather or holidays to predict what customers will buy next week, next month, and next quarter.
It's the difference between guessing and knowing. As supply chain analyst Sarah Jenkins says, "Good forecasting lets you move from a 'just in case' inventory strategy to a much more efficient 'just in time' one. It’s the secret weapon of retail giants like Walmart and Amazon."
Strategic Breakdown
- Business Impact: Lower storage costs, fewer lost sales due to stockouts, and happier customers. It directly improves your bottom line.
- Data & Models: It’s all about time-series data (your sales history) combined with other useful information (like your marketing calendar). Algorithms like ARIMA and Prophet are common, but XGBoost is great for including lots of different factors.
- Maturity Level: This is a very mature field with lots of proven tools and techniques available.
Actionable Takeaways
If you want to get started, pick one product category to focus on first. Combine your sales data with information about past promotions. Did sales for ice cream go up during last July's heatwave? That’s the kind of pattern the model can learn and use to make better predictions in the future.
11. Email Spam and Phishing Detection
Every day, a silent battle is fought in your inbox, and machine learning is your best defense. Email spam and phishing detection is one of the most widespread machine learning use cases, protecting billions of people from scams and malware. Instead of relying on simple rules that scammers can easily get around, ML models learn what spam looks like. They analyze thousands of signals—the sender's reputation, the words used in the subject line, whether the links are suspicious—to make an intelligent guess.
This is why your spam filter is so good at catching new and tricky scams. As security analyst Jane Foster explains, "Modern phishing attacks are designed to fool people. Machine learning provides a predictive shield, spotting threats it's never seen before by recognizing the tell-tale signs of malicious intent." It’s the technology that powers Gmail's filter, which is more than 99.9% accurate.
Strategic Breakdown
- Business Impact: It dramatically reduces the risk of costly data breaches, financial theft, and ransomware attacks. It also saves everyone a lot of time by keeping our inboxes clean.
- Data & Models: Models are trained on gigantic datasets of emails that have been labeled as "spam" or "not spam." Classic models like Naive Bayes are still used, but deep learning is better at understanding the content and context of an email.
- Maturity Level: This is a highly mature field, but it's a constant cat-and-mouse game. As spammers get smarter, the models have to keep learning.
Actionable Takeaways
For businesses, the best approach is a layered defense. Use a professional email security service that is powered by machine learning. And most importantly, create a culture where employees are encouraged to report suspicious emails. Every reported phish is a new piece of data that can make your defenses stronger.
12. Energy Consumption Prediction and Smart Grid Optimization
Balancing the supply and demand of electricity is a massive challenge, and it's one of the most important machine learning use cases for our planet's future. ML models can predict how much energy a city or region will need with incredible accuracy. They analyze historical usage data, weather forecasts (a hot day means more AC!), holiday schedules, and other factors to forecast demand. This allows utility companies to generate just the right amount of power, which is more efficient and less expensive.
It's the brain of the "smart grid." As energy analyst Sarah Jenkins notes, "Machine learning turns our power grid from a one-way street into a dynamic, intelligent network. It helps integrate renewable sources like solar and wind, and ultimately leads to a more stable and efficient energy system for everyone."
Strategic Breakdown
- Business Impact: Lower operating costs for utility companies, a more stable power grid with fewer blackouts, and the ability to better integrate clean energy. It can even lead to lower bills for consumers.
- Data & Models: The key data comes from smart meters and weather forecasts. Time-series models like ARIMA, Prophet, and LSTMs are perfect for this kind of forecasting. You can even see how Google DeepMind has reduced energy consumption in its own data centers using similar technology.
- Maturity Level: This field is maturing quickly. While it used to be the domain of huge utility companies, the technology is becoming more accessible.
Actionable Takeaways
When getting started, it’s often best to focus on a specific area, like residential energy use. High-quality weather data is absolutely essential—it's often the biggest factor in short-term energy demand. Good models will also provide a range of likely outcomes, not just a single number, which helps grid operators prepare for the unexpected.
Comparison of 12 Machine Learning Use Cases
| Use case | Implementation complexity 🔄 | Resource requirements ⚡ | Expected outcomes 📊 | Ideal use cases 💡 | Key advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Predictive Maintenance in Manufacturing | High 🔄 — data + domain expertise, anomaly pipelines | High ⚡ — sensors, IoT, storage, real-time compute | 📊 Reduces unplanned downtime 35–45%; maintenance costs −20–30% | 💡 Heavy industry equipment with high failure cost | ⭐ Proactive repairs, longer equipment life |
| Recommendation Systems for E‑commerce | Medium‑High 🔄 — algorithm tuning, cold‑start solutions | High ⚡ — user/product data, real‑time inference, compute | 📊 Increases AOV 20–30%; boosts retention & conversions | 💡 Online retail, streaming, marketplaces | ⭐ Personalized experience, higher revenue |
| Fraud Detection in Financial Services | High 🔄 — real‑time pipelines, imbalance & explainability | High ⚡ — streaming data, low‑latency scoring, labeled fraud data | 📊 Detects fraud in milliseconds; reduces losses 50–70% | 💡 Payments, card networks, online banking | ⭐ Fast detection at scale, adapts to new tactics |
| Medical Image Analysis and Diagnosis | High 🔄 — large labeled sets, clinical validation, regs | High ⚡ — annotated images, GPUs, clinical partnerships | 📊 Comparable/superior accuracy to clinicians; faster reads | 💡 Radiology triage, screening, diagnostic support | ⭐ Consistent detection, supports early diagnosis (regulatory dependent) |
| NLP for Chatbots & Virtual Assistants | Medium 🔄 — dialog design + ongoing model updates | Medium‑High ⚡ — hosting, annotations, integration | 📊 Handles 50–80% inquiries; reduces support costs 30–40% | 💡 Customer support, FAQs, standard workflows | ⭐ 24/7 scalable support, improves over time |
| Computer Vision for Autonomous Vehicles | Very High 🔄 — safety‑critical, multi‑sensor fusion, edge cases | Very High ⚡ — massive labeled data, specialized hardware | 📊 Potential to reduce accidents; still challenged by rare scenarios | 💡 Self‑driving, advanced driver assistance systems | ⭐ Real‑time perception enabling autonomy (safety dependent) |
| Personalized Marketing & Customer Segmentation | Medium 🔄 — data pipelines, feature engineering | Medium ⚡ — CRM data, analytics platforms, retraining | 📊 ↑ Marketing ROI 20–50%; campaign lift 15–40% | 💡 Targeted campaigns, retention and upsell programs | ⭐ Better ROI, targeted spend allocation |
| Sentiment Analysis for Brand Monitoring | Medium 🔄 — domain adaptation, sarcasm handling | Medium ⚡ — social data, NLP models, monitoring tools | 📊 Real‑time brand insights; accuracy 75–90% (domain dependent) | 💡 Social listening, PR monitoring, campaign tracking | ⭐ Scales sentiment tracking; early issue detection |
| Credit Risk Assessment & Loan Approval | Medium‑High 🔄 — explainability, fairness, regulatory checks | Medium ⚡ — financial data, explainability tools, audits | 📊 Faster decisions (minutes); typical accuracy 75–85% | 💡 Loan underwriting, credit scoring, alternative lending | ⭐ Faster, scalable risk decisions with explainability |
| Demand Forecasting & Inventory Optimization | Medium‑High 🔄 — time‑series models, hierarchical reconciliation | Medium ⚡ — historical sales, external features, compute | 📊 Reduces inventory costs 10–30%; accuracy varies 70–90% MAPE | 💡 Retail, supply chain, assortment planning | ⭐ Better stock levels, reduced stockouts/overstock |
| Email Spam & Phishing Detection | Medium 🔄 — adversarial updates, feature engineering | Medium ⚡ — high‑throughput scoring, threat intel | 📊 Filters 95%+ spam; precision ~98–99%, recall 95–97% | 💡 Email providers, enterprise security, gateways | ⭐ Strong protection at scale; reduces breaches |
| Energy Consumption Prediction & Smart Grid Optimization | Medium‑High 🔄 — grid integration, external factor modeling | High ⚡ — smart meters, weather data, real‑time systems | 📊 Saves ~5–15% energy; improved grid stability & pricing | 💡 Utilities, microgrids, demand response programs | ⭐ Optimizes operations, enables renewable integration |
Key Takeaways: Making Machine Learning Work for You
So, after looking at all these different machine learning use cases, what's the big takeaway? It's that ML isn't some far-off, futuristic dream. It's a practical tool that is solving real problems and creating real value right now.
From the factory floor to your email inbox, machine learning is making processes smarter, more efficient, and more personal. And while the applications are diverse, the recipe for success is surprisingly consistent.
The Universal Blueprint for ML Success
You don't need the world's most complicated algorithm to succeed. Across all these examples, the winners focus on three key things: the problem, the data, and the execution.
First, know exactly what problem you're trying to solve. A vague goal like "let's use AI" is doomed to fail. A specific goal like "we want to reduce customer support wait times by 30% with a chatbot that can answer our top 10 most common questions" is a clear target you can actually hit.
Second, your data is everything. As we saw in medical imaging and credit scoring, the quality and quantity of your data will make or break your project. A great ML project always starts with a great data strategy. Garbage in, garbage out.
Expert Insight: As data scientist Dr. Alistair Finch notes, "People get obsessed with the fancy models, but 80% of the real work and value comes from preparing the data. Your model can only be as smart as the data you teach it with."
From Theory to Actionable Strategy
Understanding these machine learning use cases is the first step. Turning that knowledge into a real-world project is the next.
Here are a few tips to get you started:
-
Start Small, Think Big: Don't try to boil the ocean. Pick one clear problem where you can get a quick win. A successful pilot project builds momentum and gets everyone excited for what's next. For example, start by predicting demand for just your top-selling product before you try to do it for your entire inventory.
-
Embrace the Human-in-the-Loop: The best AI systems don't replace people; they make them better. In fraud detection, the AI flags a weird transaction, and a human makes the final call. This combination of machine speed and human judgment is almost always the winning formula.
-
Iterate and Measure Everything: Machine learning isn't a one-and-done deal. The world changes, and your model needs to change with it. Constantly monitor its performance, test new ideas, and retrain it with new data to keep it sharp.
The Future is Now: Your Next Move in AI
The huge variety of machine learning use cases shows a fundamental shift in how the world works. The ability to use data to predict the future, automate tasks, and create personal experiences is no longer a luxury—it's a competitive necessity.
Getting started with machine learning can feel intimidating, but it doesn't have to be. By focusing on solving real problems, respecting your data, and taking a smart, iterative approach, you can unlock its incredible power. The tools have never been more accessible, and the opportunities have never been greater. The time to start is now.
Keeping up with the rapid evolution of AI is crucial for making informed decisions. Platforms like YourAI2Day are designed to help you navigate this complex landscape, offering the latest news, in-depth analysis, and practical insights on machine learning use cases and tools. Visit YourAI2Day to stay ahead of the curve and turn AI potential into business reality.







