Machine Learning Data Analytics: A Beginner’s Guide to Smarter Trends
Ever felt like you're drowning in data but starving for real insights? You're not alone. Machine learning data analytics is the game-changer that helps you stop guessing and start knowing. It’s all about teaching computers to learn from your data, spot hidden patterns, predict what’s coming next, and even suggest your next best move. Think of it as upgrading from a simple calculator to a super-smart strategic partner.
What Is Machine Learning Data Analytics, Really?

Let's break it down with a simple analogy. Imagine you're the manager of a coffee shop. Traditional data analytics is like looking at last month's sales report. You can see you sold a lot of lattes and that Tuesday was your busiest day. That's useful information, for sure.
Now, what if you had a brilliant assistant who could analyze not just your sales, but also local weather patterns, nearby events, and even social media trends? This assistant doesn't just tell you what happened; they tell you, "Hey, a big conference is happening downtown next week, and the weather is going to be chilly. You should stock up on extra pumpkin spice syrup and expect a 30% jump in morning sales." That super-smart assistant is machine learning data analytics.
Moving from Hindsight to Foresight
At its core, machine learning teaches computers to find patterns and make decisions without being explicitly programmed for every single scenario. While traditional business intelligence is fantastic at descriptive analytics (what happened), machine learning pushes us into the exciting worlds of predictive and prescriptive analytics.
- Descriptive Analytics: "We sold 1,000 widgets last quarter." (Looking in the rearview mirror)
- Predictive Analytics: "Based on current trends, we'll probably sell 1,200 widgets next quarter." (Looking at the road ahead)
- Prescriptive Analytics: "To sell 1,500 widgets, we should boost our ad spend by 15% in these specific regions." (Your GPS giving you the best route)
This shift is a huge deal. It allows your business to move from being reactive to proactive. You stop just analyzing past performance and start anticipating customer needs, forecasting inventory, and spotting risks before they become problems.
"Your job won't be taken by AI. It will be taken by someone who knows how to use AI. For anyone in business, understanding the basics of how machine learning can supercharge analytics isn't just a good idea—it's becoming essential for staying competitive." – Christina Inge, Marketing Expert
So, How Does It Actually Work?
Don't worry, you don't need to be a coding genius to get the gist. The process starts by feeding a machine learning algorithm a ton of historical data. The algorithm "trains" on this data, figuring out the relationships between different factors all on its own. It might discover, for example, that customers who buy product A and live in a certain zip code are 80% more likely to purchase product B within the next 30 days.
Once trained, the model can take brand-new data and make surprisingly accurate predictions. This isn't about giving a computer a giant list of "if-then" rules. It's about letting the machine discover the rules for itself, often finding subtle connections a human analyst would completely miss. This self-learning ability is what makes machine learning data analytics such a powerful tool for any business, from a tiny startup to a global giant.
How Machine Learning Transforms Traditional Analytics
Think of traditional data analytics as your car's rearview mirror. It’s absolutely essential for understanding where you’ve been and what’s happened behind you. Machine learning, on the other hand, is the real-time, predictive GPS showing you the best route forward. It doesn't just report on the past; it helps you actively shape the future.
This is the core shift—moving from simply reacting to what has already occurred to anticipating what comes next.
Traditional methods are fantastic for summarizing historical data into neat, digestible reports. You get those clean dashboards showing last quarter’s sales figures, website traffic, or customer demographics. This is descriptive analytics, and its job is to answer the fundamental question, "What happened?" While critical, it often stops there, leaving you to connect the dots and figure out what to do next on your own.
Machine learning supercharges this entire process by adding powerful new layers of insight.
From Looking Back to Seeing Ahead
The first major leap forward is into predictive analytics, which seeks to answer, "What will likely happen?" Instead of just reviewing past sales, a well-trained ML model can forecast future demand with startling accuracy. It learns from all your historical data—sales numbers, seasonal trends, marketing campaigns, and even external factors like holidays or economic shifts—to build a dynamic, forward-looking picture.
This move from descriptive to predictive is a massive deal for businesses. The fusion of machine learning and data analytics is redefining how companies operate, with the ML market projected to rocket from $68.88 billion in 2024 to an incredible $309.68 billion by 2032. In 2023 alone, over 90% of organizations reported a positive return on their data analytics investments. Some firms even boosted sales by 10% and slashed customer churn by 20% simply by swapping older statistical methods for modern machine learning. You can learn more about the market's rapid growth and its incredible business impact.
Let’s see how this works in the real world.
Practical Example: An Online Retail Store
-
Traditional Approach: An analyst at an online clothing store pulls a report showing that blue sweaters were the top-selling item last winter. Based on this historical fact, the marketing team plans a "Blue Sweater Sale" for the upcoming season. It’s a solid, data-informed decision.
-
Machine Learning Approach: An ML model digs deeper. It analyzes not just sweater sales but thousands of other data points: which customers bought them, what else was in their carts, their browsing history, geographic location, and even local weather patterns. It uncovers a subtle insight a human analyst would almost certainly miss: customers who buy blue sweaters in October are highly likely to purchase hiking boots in November.
The ML-powered store doesn't just run a generic sweater sale. It launches a highly targeted campaign, showing personalized ads for hiking boots to the specific customers predicted to want them next month. That’s the leap from a broad, reactive strategy to a precise, proactive one.
Beyond Predictions to Proactive Actions
The final frontier is prescriptive analytics, which takes things a step further and tells you, "What actions should we take?" This is where the machine doesn't just predict the future; it recommends specific, concrete actions to achieve a desired outcome.
"Machine learning allows us to move from being data historians to business prophets. It's no longer just about understanding the past; it's about algorithmically discovering the optimal path to a better future. This isn't a luxury anymore—it's the core engine for staying competitive." – AI Strategy Consultant
Prescriptive models can simulate thousands of potential scenarios to find the best possible move. For our online store, it might answer questions like:
- What's the optimal discount for the blue sweaters to maximize profit without devaluing the brand?
- Which marketing channel will give us the highest return on ad spend for our new hiking boot campaign?
- Which five products should we recommend on the checkout page to increase the average order value by 15%?
By automating this incredibly complex analysis and scaling insights across millions of data points, machine learning turns your data from a static historical record into a dynamic, strategic roadmap for growth.
To really nail down the differences, let's compare the two approaches side-by-side.
Traditional Analytics vs Machine Learning Analytics
The table below breaks down exactly where machine learning elevates the practice of data analytics, moving it from a backward-looking reporting function to a forward-looking strategic powerhouse.
| Aspect | Traditional Data Analytics | Machine Learning Data Analytics |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | To describe and summarize past events (What happened?). | To predict future outcomes and prescribe actions (What will happen? What should we do?). |
| Data Handling | Works best with structured data from databases and data warehouses. | Excels at handling massive, complex, and unstructured data (text, images, streaming data). |
| Methodology | Relies on predefined statistical models and human-driven queries. | Uses algorithms that learn and improve from data autonomously, without explicit programming. |
| Focus | Reactive. Provides reports on historical performance. | Proactive. Generates forward-looking insights and recommendations. |
| Scalability | Manual analysis can be time-consuming and difficult to scale. | Highly scalable; models can process vast datasets and make real-time decisions automatically. |
| Example | Creating a Q4 sales report that breaks down revenue by region. | Building a model that forecasts Q1 sales for each region and recommends inventory levels. |
As you can see, it's not about replacing traditional analytics entirely. Instead, machine learning builds upon it, creating a much more powerful and intelligent system for making decisions.
The Core Models Powering Your Analytics
Diving into machine learning can feel like stepping into a workshop full of specialized tools. You see all sorts of interesting gadgets, but the key is knowing which one to grab for the job at hand. Think of machine learning models in the same way—each is a specific instrument designed to solve a different kind of business problem.
You don't need a Ph.D. in mathematics to get started. The real goal is to understand what each model does and where it really shines. Let's walk through the three main types of models you'll encounter, using some everyday examples to make sense of it all.
Regression: Predicting the Next Number
Think about your car's GPS. It's not just showing you where you are; it's constantly predicting your arrival time. It factors in your current speed, traffic jams ahead, and the remaining distance to estimate a specific number. That's a perfect analogy for regression models.
At its heart, regression is all about forecasting a continuous numerical value. It works by finding the relationship between what you know (like ad spend and seasonality) and what you want to predict (like future sales). A business might use this to forecast that next month's revenue will be $1.2 million.
A Real-World Scenario:
An e-commerce company is struggling with inventory. They either have too much stock gathering dust or not enough to meet demand. They can build a regression model that looks at past sales, website traffic, recent ad campaigns, and even the time of year. The model's output isn't a vague guess; it's a specific prediction: "We'll likely sell 850 units of this product next month." This gives them the confidence to order the right amount of stock, keeping costs down and customers happy.
Classification: Sorting into Buckets
Now, picture your email inbox. Somehow, it knows how to filter out junk, sending some messages to the spam folder while letting important ones through. That automatic sorting is the work of a classification model. Its entire job is to look at a new piece of data and assign it to a predefined category.
While regression predicts a number, classification predicts a label. The questions it answers are usually binary (Yes/No, Fraud/Not Fraud) or multi-class (High/Medium/Low Priority). This is easily one of the most common techniques in analytics, driving everything from medical diagnoses to predicting which customers might leave your service.
A Real-World Scenario:
A bank needs to spot fraudulent credit card transactions the moment they happen. They train a classification model on millions of past transactions, each labeled as either 'legitimate' or 'fraudulent'. The model learns the subtle tells of fraud—like strange purchase amounts, unusual locations, or odd times. When a new transaction happens, the model classifies it in milliseconds, flagging suspicious activity before the customer loses thousands of dollars.
"Machine learning models aren't magic. They are powerful pattern-recognition engines trained on historical data. Their strength is in seeing connections that are far too complex or subtle for a human to catch on their own. Think of it as giving your business a superpower." – Industry Expert
Clustering: Finding the Hidden Groups
Imagine a librarian gets a donation of a thousand unsorted books. No labels, no genres. How would they start organizing? They’d probably start making piles based on similarities—books with similar covers, page counts, or writing styles would go together. Without knowing the genres beforehand, they are discovering the natural structure in the collection. This is exactly what clustering does.
Clustering is a form of unsupervised learning, which is a fancy way of saying you don't give the model pre-labeled data. You just hand it a dataset and ask it to find the natural groups on its own. It's a fantastic tool for exploration, helping you uncover customer segments or patterns you never knew existed.
A company might think it has three types of customers, but after a clustering model analyzes their purchasing behavior, it might reveal five completely distinct groups, each with its own unique habits.
A Real-World Scenario:
A marketing team at a streaming service wants to stop sending generic emails and create campaigns people actually care about. They use a clustering algorithm on their user data—what people watch, when they watch, and what genres they prefer. The model might uncover segments like:
- Cluster 1: "Weekend Binge-Watchers" who burn through entire seasons on Saturdays.
- Cluster 2: "Documentary Buffs" who stream non-fiction content on weekday nights.
- Cluster 3: "Classic Film Fans" who almost exclusively watch movies made before 1990.
Armed with these insights, the marketing team can craft hyper-targeted promotions that speak directly to what each group loves, leading to a huge boost in engagement.
Your Roadmap To Implementing ML Analytics
It’s one thing to understand the theory behind machine learning analytics, but putting it into practice is where you really start seeing results. Diving in headfirst without a plan can be a recipe for disaster, so let's walk through a practical, step-by-step roadmap for getting your first project off the ground.
Think of this less as a technical manual and more as a straightforward playbook. It’s designed to guide you from a simple idea all the way to a live, working model that adds real value.
Step 1: Start with a Clear Business Question
This is the single most common place where projects go wrong. People get excited by the technology and forget to ask the most important question: What problem are we actually trying to solve? The best ML analytics projects don’t start with an algorithm; they start with a painful, well-defined business problem.
Forget vague goals like "we want to use AI." You need to frame your objective with a specific, measurable outcome in mind. It makes all the difference.
- Weak Goal: "Let's use ML to understand our customers better."
- Strong Goal: "How can we reduce customer churn by 15% in the next quarter?"
- Weak Goal: "We need to optimize our marketing."
- Strong Goal: "How can we identify our top 5% most valuable leads within 24 hours of their first contact?"
Starting with a sharp, focused question gives your entire project a north star and makes it infinitely easier to measure success down the line.
"The biggest failure I see in ML adoption is starting with a cool algorithm instead of a painful business problem. If you can’t articulate the 'why' in simple business terms, you’re setting yourself up for an expensive science experiment with no real ROI." – AI Strategy Consultant
Step 2: Gather and Clean Your Data
Once your question is locked in, it’s all about the data. This stage is easily the most time-consuming part of any ML project—often 80% of the work—but it's absolutely non-negotiable. There's a classic saying in this field for a reason: "garbage in, garbage out." A model is only ever as good as the data it learns from.
This process breaks down into a few key activities:
- Data Collection: Pulling information from all your relevant sources—your CRM, sales databases, website analytics, customer support logs, you name it.
- Data Cleaning: This is the real grunt work. It means fixing errors, dealing with missing values (either by filling them in or removing them), and standardizing inconsistencies, like when "New York," "NY," and "N.Y.C." all mean the same city.
- Data Transformation: You also have to get your data into a shape the model can actually work with. This often involves turning raw data into meaningful predictors, a critical process known as feature engineering. To get a serious performance boost, you'll want to dive into the fundamentals of feature engineering for machine learning.
Step 3: Choose and Train the Right Model
With clean, prepped data in hand, you can finally pick the right tool for the job. As we've covered, different models are built to solve different problems, and your business question from Step 1 will point you in the right direction.
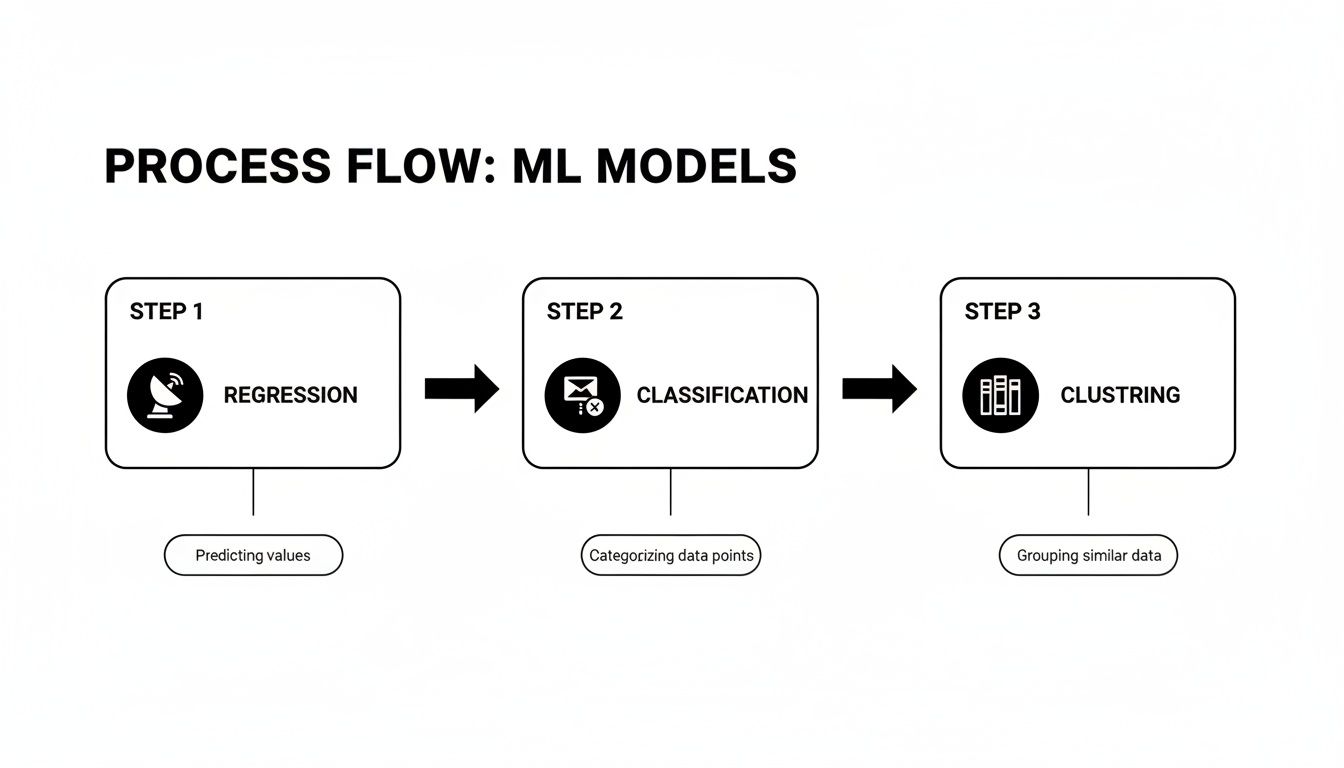
This visual is a great cheat sheet: predicting a number? Use regression. Sorting things into categories? That's a job for classification. Finding natural groupings? You need clustering.
Once you’ve chosen your model type, you "train" it by feeding it your historical data. During this training phase, the algorithm crunches through the information, learning the patterns and relationships hidden inside.
Step 4: Test and Evaluate Your Model
After training, you have to figure out if your model is any good. To do this, you test it on a separate chunk of data it has never seen before. It’s like giving a student a final exam with questions they weren't explicitly prepped for—it’s the true test of knowledge.
You'll use specific metrics to grade its performance. For a classification model trying to spot fraud, for example, you'd measure its accuracy (what percentage of its predictions were right?) and precision (of the transactions it flagged, how many were actually fraudulent?).
If the model doesn't hit the mark, it's back to the drawing board. You might tweak your data, try a new algorithm, or adjust some parameters and train it again. This cycle of training, testing, and refining is the heart of building a robust model.
Step 5: Deploy and Monitor the Results
At the end of the day, a model that isn't being used is just a science project. Deployment is the step where you integrate your model into a real-world business process. This could be a fraud system flagging live transactions, a recommendation engine personalizing your website, or a dashboard forecasting next month's sales.
But your job isn't done. The world changes, customer behavior shifts, and your model's performance can slowly degrade over time. This phenomenon is called model drift. You have to continuously monitor its accuracy and retrain it with fresh data to make sure it stays sharp and continues to deliver that all-important business value.
Real-World Examples of ML Analytics in Action
All the theory and roadmaps are great, but the real magic happens when machine learning data analytics gets its hands dirty solving actual business problems. Let’s move past the concepts and look at how major companies are using these models to get some truly incredible results.
These stories make the abstract ideas concrete and show the tangible value ML can unlock. And the impact is enormous. The global data analytics market, supercharged by machine learning, hit a staggering $64.99 billion in 2024 and is on a rocket ship trajectory toward $402.70 billion by 2032. This isn't just a tech trend; it's a fundamental business shift. Some European banks have seen up to a 10% sales boost in new products and a 20% drop in customer churn just by swapping old-school stats for ML. You can explore more on this explosive growth on fortunebusinessinsights.com.
Netflix and the Power of Personalization
Ever wonder how Netflix seems to know exactly what you want to watch next? It’s not luck; it's a world-class machine learning system.
- The Business Challenge: With millions of subscribers and an overwhelming library, how do you keep people engaged and prevent them from canceling? The key is helping them find content they’ll love.
- The ML Solution: Netflix built a sophisticated recommendation engine that chews through colossal amounts of data. It looks at your viewing history, what you've rated, the time of day you watch, and even what you’ve searched for. It then compares your behavior to millions of other "taste clusters" to make an eerily accurate prediction about what you'll enjoy.
- The Impressive Result: The company estimates this system saves it over $1 billion every year just by reducing customer churn. It's a textbook example of using predictive analytics to drive retention and growth.
Catching Fraudsters in Milliseconds
Credit card fraud is a constant cat-and-mouse game, but machine learning has become the financial industry’s most powerful weapon. Here, speed and accuracy are everything.
"Data is the new currency, and machine learning is the mint. The companies that learn how to turn their data into predictive insights will not just lead their industries; they will define them." – Data Analytics Lead
A transaction might look perfectly normal to a human, but an ML model can spot the nearly invisible red flags that scream "stolen card."
- The Business Challenge: How do you detect and block fraudulent credit card transactions in real-time without constantly annoying legitimate customers with false alarms?
- The ML Solution: Banks train classification models on billions of past transactions. These models learn the subtle, complex patterns of fraudulent activity—a tiny test purchase followed by a huge one, a purchase from a location inconsistent with the cardholder's history, or a transaction at an unusual time.
- The Impressive Result: These systems can analyze a transaction and return a fraud score in under 50 milliseconds. This allows them to block theft the instant it happens, saving consumers and banks billions. This is one of the most powerful real-world machine learning use cases transforming our daily lives.
Optimizing Logistics for a Global Supply Chain
Finally, let’s look at the incredibly complex world of logistics. For a company like UPS or FedEx, even a tiny improvement in efficiency can save millions.
- The Business Challenge: You need to predict shipping delays before they happen. This allows for optimized delivery routes and lets you manage customer expectations.
- The ML Solution: Logistics firms use regression models that analyze countless variables—weather patterns, real-time traffic data, vehicle maintenance records, and historical delivery times. This system lets them predict the likelihood and length of potential delays for any given route.
- The Impressive Result: By proactively rerouting shipments around predicted bottlenecks, these companies boost on-time delivery rates and slash fuel consumption. As a bonus, they can give customers far more accurate delivery estimates, which drastically improves the overall experience.
The Essential Tools to Get You Started

Ready to dive into machine learning data analytics? The good news is you don't need a computer science degree to get your hands dirty. The toolbox available today is massive, with powerful options for everyone—from seasoned developers to business analysts who live in spreadsheets.
Your best starting point really depends on what you want to achieve and your comfort level with code. If you want total control and don't mind writing a few lines, the coding path is incredibly powerful. But if you prefer a visual, drag-and-drop experience, no-code platforms are the perfect entry point.
For Those Who Want to Code
If you’re open to coding, Python is the undisputed king in the machine learning world. It’s famous for its clean, readable syntax, but its real superpower is the incredible ecosystem of free, open-source libraries that do most of the heavy lifting.
- Pandas: Think of this as your Swiss Army knife for data. It's the go-to for cleaning, exploring, and manipulating datasets with ease.
- Scikit-learn: This is your primary library for building models. It offers simple, ready-to-use tools for classification, regression, and clustering, which makes it perfect for getting started.
Seriously, you can run your first predictive model with just a handful of code lines. It's a fantastic way to build both skills and confidence quickly.
For Those Who Prefer a Visual Interface
Not a coder? No problem. The rise of cloud computing has brought us powerful, low-code and no-code platforms that let you build sophisticated models through a visual interface. These tools are all about accessibility.
"The democratization of AI tools is the biggest shift in a decade. You no longer need to be a top-tier programmer to build a useful predictive model. The focus is shifting from coding ability to your understanding of the business problem." – Industry Expert
These platforms allow business analysts and other subject-matter experts to apply their knowledge directly, without getting bogged down in syntax. The three big players here are:
- Google AI Platform (Vertex AI): A standout for its AutoML capabilities, which can automatically build and tune models for you.
- Amazon SageMaker: Offers a huge suite of tools, from no-code interfaces like Canvas to advanced development environments for pros.
- Microsoft Azure Machine Learning: Known for its user-friendly drag-and-drop designer that makes the entire workflow visual and intuitive.
These platforms are gaining ground fast. Globally, ML solutions on Google Cloud alone hit 281 by January 2024, mostly delivered as easy-to-use SaaS and APIs. This is part of a larger trend, with 90% of organizations now using AI regularly, making it easier than ever for newcomers to get started. You can read more about the growth of these accessible solutions.
Whether you choose to code or click, there are countless AI data analysis tools available to help you begin your journey. The best approach is to simply pick a path and start experimenting.
Frequently Asked Questions About ML Data Analytics
It's natural to have a lot of questions when you're first exploring machine learning in analytics. That’s perfectly normal. Let's walk through some of the most common ones to give you a clearer picture.
Do I Need to Be a Coder to Use ML Analytics?
Not necessarily. While knowing a language like Python is incredibly valuable for building custom models from scratch, the game has changed. Today, there's a whole suite of powerful low-code and no-code platforms available.
Tools like Google AutoML or Microsoft Azure Machine Learning Studio have intuitive, drag-and-drop interfaces that let you build and deploy effective models without ever writing a line of code. This means business experts can now directly apply machine learning data analytics to solve their own problems, focusing on the outcome instead of the programming.
How Much Data Do I Actually Need?
This is the classic "it depends" scenario, and for good reason. For a relatively simple task, like forecasting next quarter's sales, you might get a solid result with just a few thousand clean data entries. But for something much more complex, like training a model to recognize specific defects in product images, you'll need a significantly larger dataset.
"The golden rule here is always quality over quantity. A smaller, well-curated, and clean dataset will almost always give you better results than a massive, messy one. It's always better to start with the quality data you have and expand from there." – Data Scientist
What's the Biggest Mistake Beginners Make?
By far, the most common trap is falling in love with the technology before identifying the problem. Too many teams jump in wanting to "do AI" without first defining a clear, measurable business goal. It’s a solution in search of a problem.
The right way to approach it is to work backward. Start with a concrete business question. For example:
- "How can we reduce customer churn by 15% in the next six months?"
- "How can we more accurately identify our most valuable leads at the top of the funnel?"
Once you have a specific objective, you can then select the right ML model and technique to achieve it. This problem-first mindset is the secret to a successful project.
At YourAI2Day, we provide the latest news, research, and tool guides to help you confidently navigate the world of AI. Explore our resources to stay ahead of the curve: https://www.yourai2day.com.