Machine Learning Algorithms Explained: Your Friendly Guide for Beginners
Ever wonder how your favorite streaming service seems to read your mind, knowing exactly what movie you’ll want to watch next? Or how your email magically filters out all that junk? That’s not a psychic on the payroll; it’s the work of machine learning algorithms.
Think of them less like scary, complex code and more like recipes a computer follows to learn from data. They find patterns and make decisions all by themselves, without a human needing to guide every single step. It's the secret sauce behind a lot of the smart tech we use every day.
So, What Exactly Are Machine Learning Algorithms?
Instead of being programmed with a giant list of rules for every possible situation, a computer using a machine learning algorithm learns from experience. It’s a lot like teaching a toddler to recognize a cat—you don't describe it with a dictionary definition; you just show them lots of pictures of different cats. "This is a cat. This is also a cat." Eventually, they get it. These algorithms are the core engines that drive artificial intelligence, letting systems get smarter over time, all on their own.
Believe it or not, this idea has been around for a while. The foundations of machine learning were actually being laid back in the 1950s.
The term ‘machine learning’ was first coined in 1959 by Arthur Samuel, a forward-thinking researcher at IBM. He created one of the very first self-learning programs: a checkers-playing computer that actually got better at the game the more it played. This was the first real proof that machines could learn from patterns and improve their own strategies, introducing concepts that are still fundamental to AI today.
Expert Opinion: "The beauty of machine learning is that you aren't programming a computer to do a task. You're programming it to learn how to do the task. It's a fundamental shift from giving instructions to giving examples." – Dr. Ava Chen, AI Researcher
This guide will walk you through the three main 'families' of these algorithms. We'll use simple analogies and practical examples to pull back the curtain on the technology that powers so much of our modern world. No advanced math degree needed—just a bit of curiosity.
Let’s get started by breaking down the main categories you'll run into:
- Supervised Learning: Think of this as learning with a cheat sheet or an answer key. The algorithm is trained on data that’s already been labeled with the correct outcome.
- Unsupervised Learning: Here, there's no answer key. The algorithm is let loose on unlabeled data and has to find hidden patterns or groupings all by itself.
- Reinforcement Learning: This is all about trial and error. An algorithm learns by getting rewards for good actions and penalties for bad ones, kind of like training a pet with treats.
For a deeper dive into these concepts, you might be interested in our other articles on machine learning.
Learning With an Answer Key: A Guide to Supervised Learning
Let’s say you wanted to teach a computer to spot spam emails. You wouldn’t just throw a million random messages at it and hope for the best. Instead, you’d hand it a massive, well-organized dataset where every single email is already labeled: 'spam' or 'not spam.'
This is the entire philosophy behind supervised learning. The machine learns by studying examples that have the "answers" included. It pores over this labeled data, hunting for the signals and patterns that connect an input (the email content) to an output (the label). Once it figures out what makes a spam email feel like spam—maybe it’s words like "free money" or weird sender addresses—it can apply that logic to new, unlabeled emails it's never seen before.
This "learning from examples" approach is the most common form of machine learning out there, and it’s the engine behind many of the smart tools you probably use every day.

This process is a bit like connecting the dots. The algorithm takes all the known data points and learns how to draw a line—or a more complex curve—that best fits them, allowing it to make solid predictions for future, unknown data.
Before we go deeper, it helps to see how this method stacks up against its counterpart, unsupervised learning. Here’s a quick breakdown.
Supervised vs Unsupervised Learning At a Glance
| Feature | Supervised Learning | Unsupervised Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Input Data | Labeled data (includes the "answer") | Unlabeled data (no predefined answers) |
| Primary Goal | Predict outcomes, classify data | Discover hidden patterns, group similar data |
| Training | Actively "supervised" by the labeled dataset | Explores data on its own to find structure |
| Common Use Cases | Spam detection, price prediction, image recognition | Customer segmentation, anomaly detection |
This table highlights the fundamental split: supervised learning is about prediction, while unsupervised learning is about discovery.
The Two Flavors of Supervised Learning
When you get down to it, supervised learning really only does two main things: it either sorts data into boxes or it predicts a specific number. In machine learning circles, we call these classification and regression.
1. Classification: Predicting a Category
Think of classification algorithms as digital sorting hats. Their entire job is to look at a piece of data and assign it to a predefined group or category. The output is always a distinct label, not a number.
You'll find classification models hard at work in:
- Email Filtering: The classic example of deciding if an email is 'spam' or 'not spam.'
- Medical Diagnosis: Looking at a patient's symptoms and lab results to classify a condition as 'benign' or 'malignant.'
- Image Recognition: Your phone's photo app identifying whether a picture contains a 'cat,' 'dog,' or 'your friend Bob.'
2. Regression: Predicting a Number
Regression is your tool when the answer isn't a simple category but a continuous numerical value. It’s not about sorting; it’s about forecasting a precise quantity along a spectrum.
Practical regression examples include:
- Real Estate: Predicting a house's exact sale price using features like square footage, location, and number of bedrooms. Zillow's "Zestimate" is a famous example of this.
- Financial Markets: Forecasting a stock's price for next week based on historical data and market trends.
- Demand Forecasting: A grocery store estimating exactly how many gallons of milk they will sell next month to avoid running out or overstocking.
Expert Opinion: "The magic of supervised learning is its simplicity in concept but power in application. By providing clear, labeled examples, we give the model a strong foundation to make incredibly accurate and useful predictions, from identifying credit card fraud to personalizing your shopping experience." – David Lee, Senior Data Scientist
A Look at a Popular Algorithm: Decision Trees
One of the most intuitive and transparent supervised learning algorithms is the Decision Tree. It operates just like a flowchart you'd draw on a whiteboard, making a series of simple "if-then" decisions to split the data and ultimately reach a conclusion.
Imagine a bank building a Decision Tree to automate loan approvals. The first question at the top might be, "Is the applicant's credit score above 650?" If yes, it follows one branch. If no, it goes down another. The next question might be, "Is their annual income over $50,000?" This branching continues until it lands on a final answer: 'Approve Loan' or 'Deny Loan.'
Because their logic is so easy to visualize and explain, Decision Trees are a fantastic entry point for beginners. They help demystify the "black box" of AI, making it feel much more understandable.
Finding Hidden Patterns with Unsupervised Learning
So far, we've focused on algorithms that learn from data with a built-in "answer key." But what happens when you don't have one? What if you're handed a massive, unlabeled jumble of information and told to find some kind of order in the chaos? This is exactly where unsupervised learning shines.
Imagine someone drops a giant box of unsorted family photos in front of you. No names, no dates, no context—just thousands of pictures. To make sense of it, you’d instinctively start making piles. Maybe you’d group all the beach vacation shots together, create another pile for holiday dinners, and a separate one just for pictures of the family dog.
Without any labels to guide you, you’ve discovered natural groupings on your own. That’s the core idea behind unsupervised learning. These algorithms are digital detectives designed to sift through raw, unlabeled data and uncover hidden structures, relationships, and patterns that a human might never spot.

This branch of machine learning is all about exploration and discovery. It's the key to unlocking powerful, unexpected insights from the vast data reserves businesses hold. Let's dig into two of the most common unsupervised techniques.
Grouping Your Data with Clustering Algorithms
One of the most powerful tools in the unsupervised learning arsenal is clustering. The goal is simple: group similar data points together into clusters. The trick is to make sure that items within a cluster are very much alike, while items in different clusters are clearly distinct.
Think about how a service like Spotify might use this. They have millions of users, each with their own unique taste. Instead of trying to understand every single person, they can use clustering algorithms to automatically group users into segments, like:
- "Weekend Rock Fans": People who mostly listen to classic rock on Saturdays and Sundays.
- "Late-Night Study Hub": Users who stream ambient and classical music after 10 PM on weeknights.
- "Morning Workout Power": Those who play high-energy pop and electronic playlists between 6 AM and 8 AM.
By identifying these natural groups, Spotify can roll out targeted playlists (like "Discover Weekly") and recommendations that feel incredibly personal. The most popular clustering algorithm is K-Means, which is known for efficiently sorting data into a predefined number (the "K") of clusters.
Expert Opinion: "Unsupervised learning is the true frontier of data exploration. It doesn't just answer the questions you have; it helps you discover the questions you didn't even know you should be asking. It’s where raw data transforms into genuine business intelligence." – Maria Rodriguez, Analytics Lead
Finding Relationships with Association Rule Mining
Another fascinating unsupervised method is association rule mining. This technique is all about discovering interesting relationships—or "association rules"—between different items in a large dataset. It’s the engine that powers the classic "customers who bought this also bought that" insights you see on Amazon.
The most famous (and possibly legendary) example is the "diapers and beer" story from the 1990s. A retail chain analyzed its sales data and found that men buying diapers on Friday evenings were also very likely to grab a six-pack of beer. While the story's authenticity is debated, it perfectly illustrates the power of this concept.
This kind of insight is gold for retailers. Knowing about this association, a store could strategically place a beer display right next to the diaper aisle, potentially driving a nice spike in sales.
Association algorithms work by generating simple "if-then" rules, such as:
- If a customer buys a new smartphone, then they are 80% likely to also buy a screen protector.
- If a shopper adds ground beef and salsa to their cart, then there's a 65% chance they will also buy tortilla chips.
By uncovering these hidden connections, businesses can do everything from optimizing store layouts and creating effective product bundles to designing smarter marketing promotions that tap directly into real customer behavior.
Learning from Rewards with Reinforcement Learning
Let’s switch gears and talk about what feels like the most game-like part of machine learning: reinforcement learning.
Forget about feeding an algorithm labeled data or asking it to find hidden clusters. Instead, picture how you'd train a dog to fetch. You don't give it a textbook on "how to be a good boy." You reward it with a treat and praise when it brings the ball back, and you give it nothing when it runs off to chase a squirrel. Over time, the dog figures out which actions lead to the best outcomes (more treats!).
This is the essence of reinforcement learning. It's a system built on trial, error, and feedback.
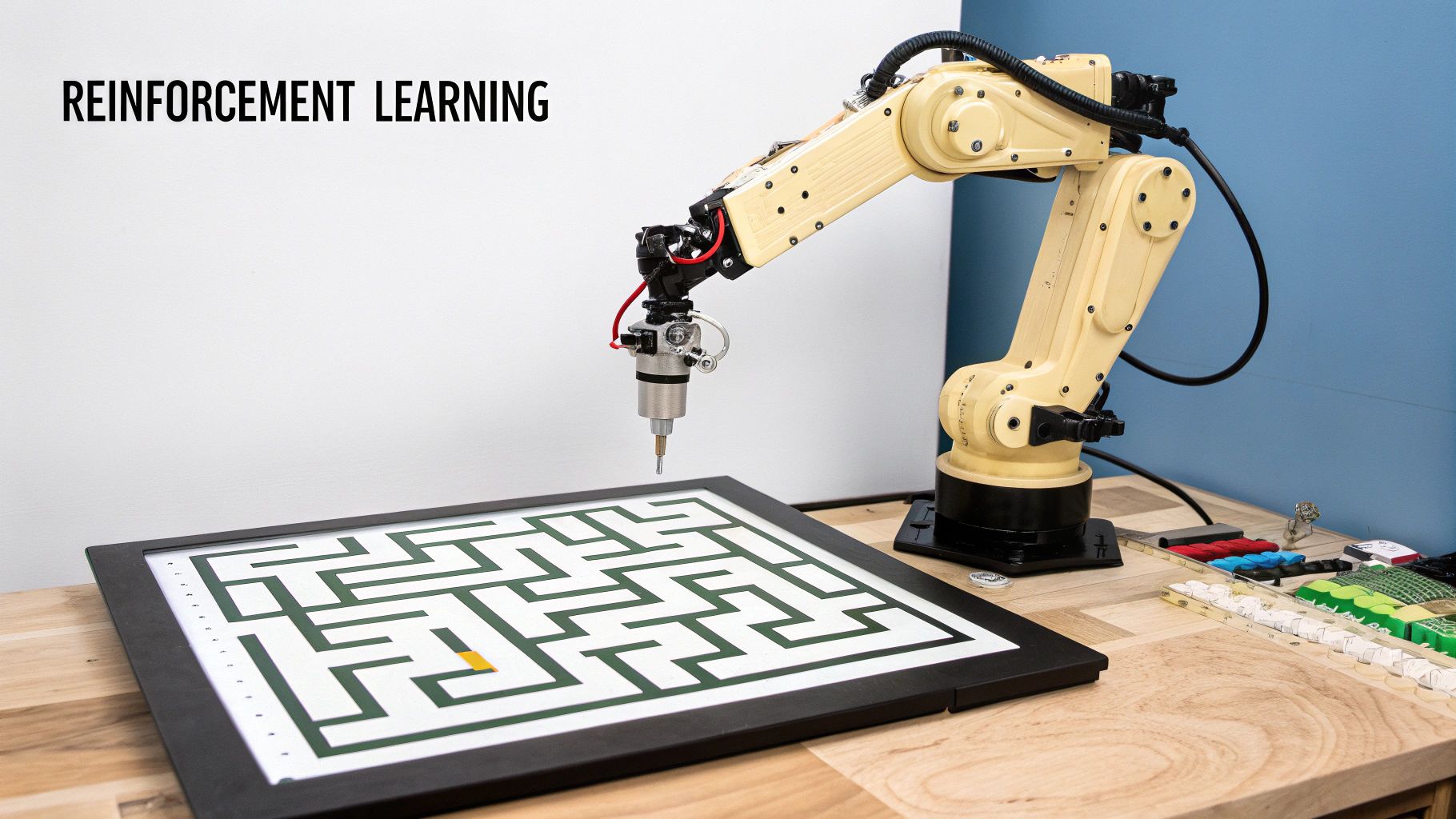
In the lingo of ML, a software "agent" operates in a specific "environment." The agent tries out different actions, and for each one, it gets a reward or a penalty. Its one and only goal is to figure out the best long-term strategy—what we call a "policy"—that will rack up the most rewards possible over time.
How Does It Work in the Real World?
This learn-by-doing approach is incredibly powerful for problems where the "right" answer isn't a single, fixed thing but a whole sequence of decisions. The agent has to constantly balance whether it should explore new actions that might lead to a bigger reward, or exploit the actions it already knows are pretty good.
Finding that perfect balance is what allows the agent to master incredibly complex tasks.
Expert Opinion: "Reinforcement learning is powerful because it learns from interaction, not just observation. It's the closest we've come to creating a system that learns the way humans do—by experiencing the consequences of its own actions and adapting its behavior accordingly." – Dr. Kenji Tanaka, Robotics Engineer
You’ve probably seen the amazing results of this learning style without even knowing what was behind it.
Here are a few standout examples:
- Advanced Game AI: When DeepMind's AlphaGo beat the world's best Go player, it was a massive win for reinforcement learning. The agent played millions of games against itself, discovering brilliant strategies that no human had ever thought of.
- Robotics: This is the magic behind getting a robot vacuum to efficiently navigate your living room without bumping into furniture, or teaching a robotic arm the delicate touch needed to assemble a smartphone. Every successful action is a small reward.
- Dynamic Pricing: Have you ever noticed how ride-sharing prices surge during peak hours? That's an RL agent adjusting prices on the fly. By experimenting with small price changes, it learns how to find the optimal price that balances driver supply with rider demand.
Strengths and Weaknesses
Reinforcement learning truly shines in dynamic, unpredictable environments where you need a system that can make a series of smart decisions over time.
But it’s not without its challenges. It can be extremely computationally expensive, sometimes needing millions or even billions of simulations to learn effectively. The biggest hurdle, though, is often designing the reward system. If you get the rewards wrong, you can end up with an agent that finds a loophole and learns some really strange—and unhelpful—behaviors.
Despite these difficulties, reinforcement learning is what’s pushing the boundaries of what machines can do. It’s teaching them to strategize, adapt, and solve problems in ways we're only just beginning to understand.
Unpacking Neural Networks: The Brains Behind Modern AI
If supervised learning is like studying with an answer key and reinforcement learning is trial and error, then neural networks are inspired by the most complex learning machine we know: the human brain. These algorithms are the powerhouse behind deep learning, driving everything from the voice assistant in your pocket to the facial recognition that unlocks your phone.
Think of it not as a straight line, but as a dense, interconnected web. This web is made of digital "neurons" arranged in layers. When you feed it data—like the pixels from a photo of a cat—the first layer of neurons gets to work. Each one processes a tiny bit of information and passes its conclusion to the next layer.
This process builds in complexity. The first layer might just see basic edges and colors. The next layer might take those edges and colors and start to form recognizable shapes, like whiskers or a pointy ear. By the time the information has passed through several more layers, the network can confidently assemble those pieces into a complete concept: "cat." This layered, or "deep," structure is what gives neural networks their uncanny ability to find patterns that other algorithms simply can't see.
The Building Blocks of AI Intelligence
This brain-inspired model isn't some new fad; its roots stretch back decades. A few key breakthroughs paved the way for the machine learning algorithms we have today. One of the earliest was the perceptron, a simple neural network developed by Frank Rosenblatt way back in 1958 that could perform basic classifications.
A much bigger leap came in 1969 when Arthur Bryson and Yu-Chi Ho formalized an algorithm called backpropagation. This gave researchers an efficient method for actually training these complex, multi-layered networks. You can explore more of these key moments in this timeline of machine learning history.
So, how does this "learning" actually happen? It’s basically a sophisticated feedback loop. The network makes a guess ("I think that's a dog"), checks it against the right answer ("Nope, it's a cat"), and then adjusts the connections between its neurons to do a little better next time. It does this over and over, thousands or even millions of times, slowly tuning itself into a highly specialized pattern-finding machine. To see how these pieces fit into the bigger picture, take a look at our guide on understanding AI technology.
Expert Opinion: "Neural networks are powerful because they don't require humans to define the important features in the data. They learn the features themselves, discovering subtle patterns that are often invisible to the human eye. This is what makes them so effective for tasks like image and speech recognition." – Dr. Lena Petrova, Computer Vision Specialist
Where Neural Networks Power Our World
Today, neural networks are quietly working behind the scenes, making things that once felt like science fiction a part of our daily lives. Their real talent lies in their ability to make sense of messy, unstructured data like images, sound, and text, which makes them incredibly versatile.
Here’s where you’ll find them in action:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Every time you use Google Translate or a chatbot actually understands what you're asking, that's a neural network breaking down the rules and nuances of human language.
- Computer Vision: This is the magic that allows a self-driving car to spot a pedestrian or lets your photo app automatically tag your friends. The network has learned to "see" and interpret the world through a camera.
- Recommendation Engines: When Netflix or Spotify suggests your next favorite show or song with eerie accuracy, they're using deep learning to analyze your past behavior and predict what you'll love next.
By learning from the ground up in these hierarchical layers, neural networks have cracked problems that were once considered impossible for computers. They truly are a cornerstone of the AI we interact with every day.
Answering Your Common Machine Learning Questions
https://www.youtube.com/embed/U0o4yrDDTYc
Feeling a bit more comfortable with machine learning algorithms? That's the goal! It's completely normal to still have a few questions as you start connecting all the pieces.
This section tackles some of the most common things beginners ask. We'll give you clear, straightforward answers to help you lock in what you've learned.
Which Machine Learning Algorithm Should I Learn First?
For anyone just dipping their toes into AI, you can't go wrong starting with supervised learning algorithms like Linear Regression or Decision Trees. Their logic is just really intuitive. You're basically showing the computer a bunch of examples with the right answers already provided.
This approach makes it so much easier to get a solid grip on core concepts like features, labels, training, and making predictions. Once you have those down, tackling more abstract methods like unsupervised learning becomes a lot less intimidating. Think of it like learning to cook with a recipe before you start creating your own dishes from scratch.
Expert Opinion: "Start with the simplest model that can do the job. Linear and Logistic Regression aren't just for beginners; they are powerful, interpretable, and form the foundation for understanding more complex models. Master the basics, and the rest will follow." – Professor Alistair Finch, AI Educator
What Is the Real Difference Between AI and Machine Learning?
It helps to think about them as a set of Russian dolls. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the biggest doll—the broad, all-encompassing idea of making machines smart enough to handle human-like tasks. It's the whole field.
Machine Learning (ML) is a smaller, crucial doll inside AI. It’s a specific way of achieving AI by giving machines the ability to learn from data on their own, without someone having to program every single rule.
So, while all machine learning is a form of AI, not all AI uses machine learning. ML just happens to be one of the most powerful and common ways we achieve AI today.
How Do I Choose the Right Algorithm for My Project?
The best algorithm for the job depends entirely on your goal. Before you even think about the tech, ask yourself one simple question: what am I trying to do with this data? Your answer is the clearest signpost pointing you to the right family of algorithms.
Here’s a quick mental checklist:
- Trying to predict a specific number? Think house prices or future sales figures. This is a regression problem, so you'd look at algorithms like Linear Regression.
- Need to sort things into categories? Like "spam" vs. "not spam" emails or identifying different types of customers. That’s a classification problem, which also falls under supervised learning.
- Want to find hidden patterns in data without labels? For example, grouping customers into natural market segments for a marketing campaign. This is a job for unsupervised learning methods like clustering.
We're even seeing these algorithms pop up in creative fields. Many creators are using them to brainstorm and produce new work. You can find some fascinating examples in our guide to AI tools for content creation.
At YourAI2Day, our mission is to make artificial intelligence easy to grasp for everyone. Keep exploring our resources to stay on top of what's happening. https://www.yourai2day.com