How to Build an AI Chatbot: A Complete Step-by-Step Guide
So, you're ready to build an AI chatbot. It’s a fun and rewarding journey that actually begins long before you write a single line of code. It all starts with a clear idea of what you want your bot to do. This guide will walk you through the whole process, from that first spark of an idea to picking the right tools and training your bot to have genuinely helpful chats.
Why Building an AI Chatbot Is Worth Your Time
Before we dive into the nuts and bolts, let's chat about why this is such a great skill to learn right now. This isn't just about following a trend; it's about understanding a massive shift in how businesses and people connect.
Think of this as your motivation. Whether you're a developer adding a new tool to your belt, a marketer looking for better ways to engage customers, or just a curious creator, understanding the "why" will power you through the "how." Chatbots are becoming the new front door for customer interaction, and they're getting smarter every day.
The Real-World Impact of Chatbots
At their core, AI chatbots solve a universal problem: the need for instant, scalable communication. Companies are using them to completely rethink how they talk to their customers, offering support that literally never sleeps.
- Automated Customer Support: Imagine instead of a customer waiting on hold, a bot instantly answers common questions like, "Where's my package?" or "How do I reset my password?" This frees up your human team to handle the really complex, high-touch problems.
- Around-the-Clock Lead Generation: A friendly chatbot on your website can greet a visitor at 2 AM, ask a few simple questions to see if they're a good fit, and even book a demo with your sales team for the next morning.
- Instant Information Access: Internally, bots can act as a company search engine. An employee can ask, "What's our vacation policy?" and get an instant answer instead of digging through documents or interrupting a colleague in HR.
This isn't just a minor convenience—it's a huge market shift. The global AI chatbot market has seen explosive growth, jumping from $8.3 billion in 2023 and is on track to hit nearly $47 billion by 2029. This boom is all thanks to incredible progress in Natural Language Processing (NLP), which helps bots feel less like clunky robots and more like real conversational partners. You can explore more chatbot market statistics to see the full picture of this growth.
To give you a clearer picture of the moving parts, here’s a quick breakdown of the core components we’ll be dealing with.
Core Components of a Modern AI Chatbot
| Component | What It Does | Why It's Important |
|---|---|---|
| Natural Language Processing (NLP) | Allows the bot to read, understand, and interpret human language. | This is the "brain." It's what separates a smart bot from a simple, keyword-based one. |
| Intent Recognition | Identifies the user's goal or what they are trying to accomplish. | Crucial for giving the right answer. "Book a flight" and "check flight status" are very different intents. |
| Entity Extraction | Pulls out key pieces of information from the user's message, like dates, names, or locations. | This is how the bot grabs the details it needs to take action (e.g., booking a flight to Boston on Tuesday). |
| Dialogue Management | Manages the flow of the conversation, keeping track of the context from one message to the next. | Without this, the bot would have no memory and couldn't handle multi-step conversations. |
| Knowledge Base | The source of truth for the bot, containing all the information it can provide. | This is where the answers live. It can be a simple FAQ document or a complex database. |
Understanding how these pieces fit together is the first step to building a bot that actually works the way you want it to.
Expert Opinion: "I’ve been in this space for a while, and the biggest game-changer isn't just that bots can answer questions. It's that they can finally understand context and intent. A user can type 'my order is busted,' and a modern bot gets that they mean 'I need help with a damaged delivery,' which then kicks off the right process. That's a huge leap from old-school bots that would just get stuck on the word 'busted'."
That ability to read between the lines is what makes building an AI chatbot so powerful today. You're not just scripting canned responses anymore; you're truly architecting a conversation. And this guide will show you exactly how to do it.
Laying the Groundwork for a Great Chatbot

Before you ever touch a piece of software, the best chatbots begin on a whiteboard or a simple notepad. This initial planning phase is your blueprint. Honestly, it's the most critical step and often determines whether your bot becomes a helpful assistant or just another frustrating roadblock for your users.
Jumping straight into development without a clear plan is like trying to build a house without architectural drawings. You might get something standing, but I guarantee it won't be a pleasant or functional place to be.
Define Your Chatbot’s Core Purpose
First things first: what is this chatbot's one true job? A bot without a crystal-clear purpose will inevitably fail because it tries to be everything to everyone. Your goal here is to give it a primary mission that will guide every single decision you make from here on out.
Is it a sales assistant meant to qualify leads and book demos? Or maybe you need a 24/7 support agent that can handle common issues like order tracking and password resets. It could even just be an information hub that helps people navigate a complex website.
Let's use a practical example. Imagine you run an e-commerce store selling custom sneakers. Your chatbot’s core purpose could be to "help customers find their perfect sneaker and answer post-purchase questions."
That one sentence gives you immediate focus. You now know its key tasks must include:
- Guiding users through size and style options.
- Answering questions about shipping times.
- Processing return requests.
- Checking on order statuses.
Just as importantly, this clarifies what the bot shouldn't do. It’s not there to give a company history lesson or discuss sneaker design philosophy. Pinpointing this purpose is the foundation for building an AI chatbot that actually adds value instead of creating noise.
Designing a Personality That Fits Your Brand
Once you’ve figured out the bot's job, it's time to decide on its personality. This isn't just a fun little extra; it's a core part of the user experience. The bot's tone has to feel like it belongs to your brand.
A chatbot for a bank, for example, should probably be professional, precise, and reassuring. On the other hand, a bot for a gaming company can be witty, use slang, and crack a few jokes. A personality mismatch feels strange and can seriously erode a user's trust.
Think about these kinds of traits:
- Tone: Formal vs. Casual, Humorous vs. Serious.
- Language: Simple vs. Technical, use of emojis or slang.
- Demeanor: Proactive and bubbly vs. Straightforward and to the point.
For our sneaker store, a friendly, enthusiastic, and slightly informal personality would be a perfect fit. It could use emojis and say things like, "Awesome choice! Those kicks are 🔥. Ready to check out?" This creates an experience that feels authentic to the brand and its customers.
Expert Opinion: "The biggest mistake I see beginners make is neglecting the bot's persona. They focus so much on the logic that they forget they're designing a conversation. A well-defined personality makes the interaction feel natural and builds a connection, which is crucial for getting people to actually use it."
Mapping the User Conversation Flow
With a purpose and personality in place, it’s time to start mapping out the actual conversations. This process, often called conversation design, is all about anticipating what users will need and creating logical paths to solve their problems.
Start by brainstorming the most common questions your users will have. For our sneaker bot, that list would definitely include "Where is my order?", "Do you have these in size 10?", and "What is your return policy?"
Next, sketch out a simple flowchart for each query. For "Where is my order?", the flow might look something like this:
- User: "Where's my stuff?"
- Bot: "I can help with that! What's your order number?"
- User: Provides the order number.
- Bot: (After checking the database) "Looks like your order is out for delivery and should arrive today! Here's the tracking link."
This mapping process is invaluable because it helps you spot potential dead ends and confusing loops long before you start building. It ensures every conversation is productive and, most importantly, leads the user to a successful outcome. At the end of the day, that’s the whole point of a great chatbot.
Choosing the Right Tools for Your Project
With a solid plan in hand, it’s time to pick your toolkit. This is one of the most important decisions you'll make, as it directly shapes how fast you can build, how much you can customize, and how your chatbot will grow. Think of it like deciding whether to build a custom race car from scratch or modify a high-performance street car—both can be incredibly fast, but they offer vastly different levels of control and require different kinds of effort.
Your choice really comes down to two main paths: using an established chatbot platform or building your own solution with programming libraries. Neither is inherently "better." The right call depends entirely on your project's needs, your budget, and how comfortable you are with code.
Chatbot Platforms: Your Fast Track to a Functional Bot
Chatbot platforms are designed to get you up and running quickly, often with very little coding. They give you a visual interface where you can map out conversation flows, define what users are trying to do (their "intent"), and train your bot on that data.
These platforms are a fantastic starting point if you're new to this or working against a tight deadline. They handle a lot of the heavy lifting on the backend, like server management and the core natural language processing, so you can focus on making the user experience great.
A few popular options I've worked with are:
- Google's Dialogflow: A powerful, widely used platform that plugs right into other Google services. It’s a great choice for building bots for websites, mobile apps, and smart speakers.
- Rasa: This is an open-source favorite that gives you much more control and customization than most cloud-based platforms. It's a fantastic middle ground for teams who want flexibility without starting completely from scratch.
- Microsoft Bot Framework: A comprehensive framework for building and deploying bots across a ton of channels, from Slack and email to Microsoft Teams.
My Take: For a quick prototype or an internal tool, a platform is a no-brainer. But if the chatbot is a core part of your product and needs a unique feel, I'd go custom every time. A platform gets you 80% of the way there fast, but that last 20%—the unique features and brand personality—is where custom code really shines.
Custom Code: The Path to Ultimate Flexibility
The other route is to build your chatbot from the ground up using programming languages and machine learning libraries. This approach gives you almost limitless control over every single piece of your bot, from the AI model itself to the final user interface. Python is the undisputed king here, mostly because of its incredible ecosystem of AI and ML libraries.
The key tools in this stack usually include:
- TensorFlow & PyTorch: These are the two giants in the deep learning world. You’d use one of them to build and train the core NLP models that help your bot understand what people are saying.
- Natural Language Toolkit (NLTK) & spaCy: These libraries are your go-to for processing human language. They handle fundamental tasks like breaking sentences into words (tokenization) and identifying important entities like names or dates.
This path definitely requires stronger programming skills and a good grasp of machine learning concepts. But it's the only way to go if you're building a highly specialized bot, need to keep all your data in-house, or want to create a truly one-of-a-kind conversational experience.
This infographic does a great job of breaking down the key differences between a few platforms, especially when you look at customization, how easy they are to implement, and cost.
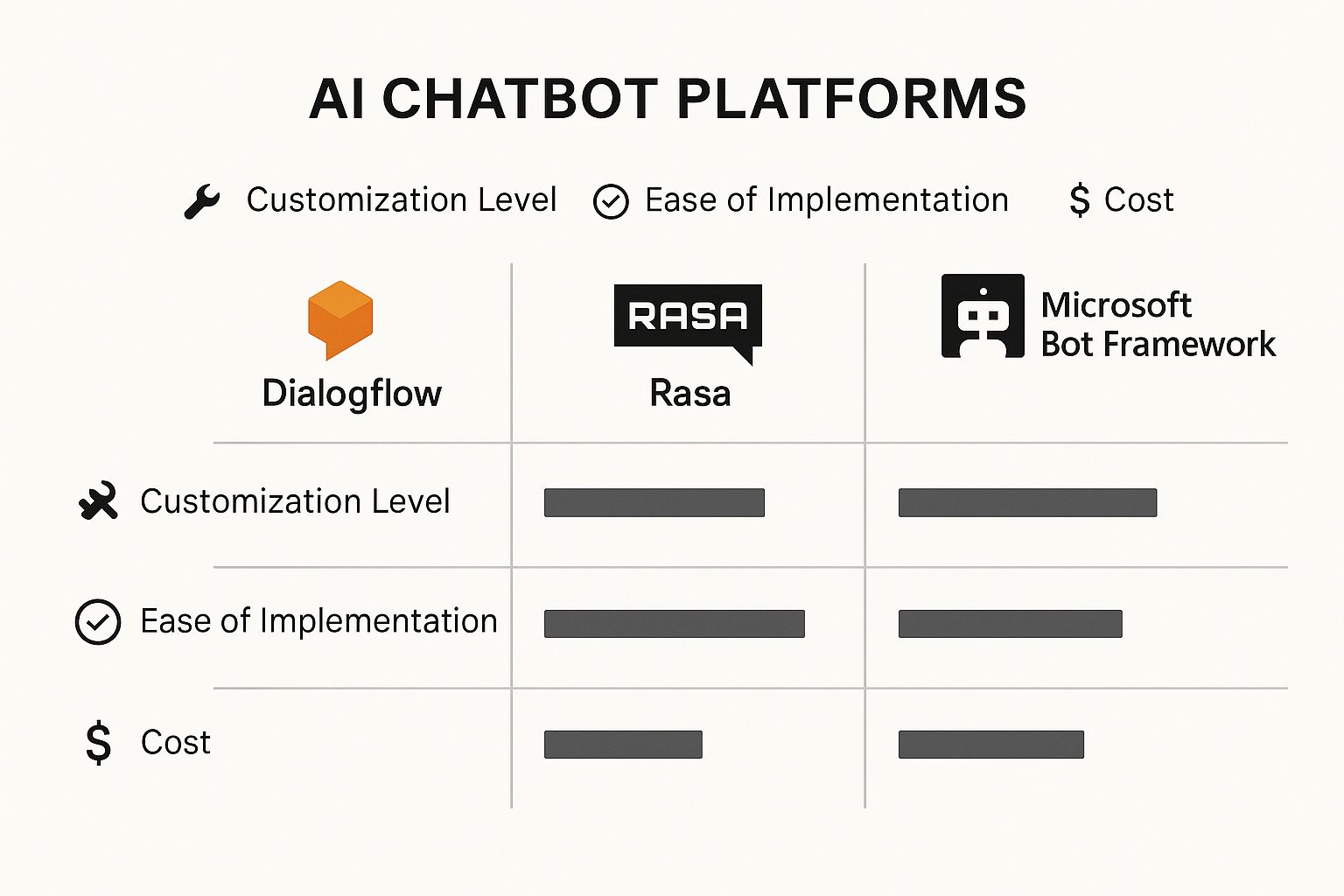
You can see the clear trade-off: a platform like Dialogflow is all about ease of use, while a tool like Rasa gives you a much higher degree of freedom to build what you want.
Before we go further, it's helpful to see a side-by-side comparison of these two approaches.
Chatbot Platforms vs Custom Code: A Comparison
The table below lays out the key trade-offs between using a no-code/low-code platform and writing your chatbot from scratch.
| Factor | Chatbot Platforms (e.g., Dialogflow) | Custom Code (e.g., Python & TensorFlow) |
|---|---|---|
| Speed to Market | Very Fast. Can build a functional prototype in hours or days. | Slower. Requires significant development time for architecture, coding, and training. |
| Technical Skill | Low. Accessible to non-developers and product managers. | High. Requires expertise in programming, ML frameworks, and NLP. |
| Customization | Limited. You're confined to the platform's features and integrations. | Nearly Unlimited. You can build any feature or logic you can imagine. |
| Scalability | Managed by Platform. Scaling is handled for you but can get expensive. | Developer-Managed. You have full control but are responsible for infrastructure. |
| Cost | Pay-as-you-go. Often priced per interaction, which can grow quickly. | Upfront Investment. Primarily developer salaries and infrastructure costs. |
| Data Ownership | Platform-Dependent. Your data is often stored on third-party servers. | Full Ownership. You have complete control and privacy over your data. |
Ultimately, the choice isn't about which is "best" overall, but which is best for your specific project. Platforms excel at speed and simplicity, while custom code delivers unmatched power and control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
So, how do you decide? The global chatbot market was valued at around $7.76 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit $27.29 billion by 2030. This explosive growth is happening in both platform-based solutions and custom development. What's driving it? A huge demand for specialized, industry-specific bots, which often require more tailored development. You can dive deeper into these chatbot market growth and trends to see where things are headed.
To help you land on the right path, just ask yourself these questions:
- What's our team's technical skill level? If you don’t have seasoned developers on hand, a platform is the much safer bet.
- How quickly do we need to launch? Platforms will always win the race to get a first version out the door.
- How unique does this bot need to be? If you’re building a core product feature that has to stand out, custom code is the way to go.
- What’s our budget look like? Platform costs are usually based on usage and can add up over time, while custom work is a bigger upfront investment in developer hours.
Your decision should be a practical one that aligns your team's resources with your project's goals. Choose the toolkit that sets you up for success, not frustration.
Alright, let's get our hands dirty. The theory is great, but the best way to really understand how to build a chatbot is to… well, build one. We're going to walk through the entire process, from a blank slate to a functioning bot, using a classic and practical example: a customer service bot for an e-commerce store.

This isn't just about code. We'll focus on the core building blocks that make a chatbot genuinely intelligent. Our goal is to turn a static script into a dynamic conversational partner that can actually understand and help people.
Figuring Out What Users Want: Defining Intents
First things first, we need to teach the bot to understand why someone is talking to it. In the chatbot world, we call these user goals intents. An intent is just the user's objective—the "what" behind their words.
For our e-commerce bot, some common intents jump out immediately:
- checkOrderStatus: The user wants to know where their package is.
- askForRefund: The user isn't happy and wants to start a return.
- productInquiry: The user has a question about a specific item.
- greeting: It's as simple as the user saying "hi" or "hello."
Getting your intents right is the foundation of everything that follows. You're creating the primary buckets that every single user message will get sorted into.
Spotting the Key Details: Identifying Entities
Once the bot knows what the user wants (the intent), it has to pull out the specific details it needs to get the job done. These little nuggets of information are called entities. Think of them as the important nouns or proper nouns in a user's sentence.
If a user types, "I want to check the status of order #12345," the intent is checkOrderStatus, but the crucial entity is the order number: 12345. Without that entity, the bot is stuck.
Expert Take: "Beginners often get tangled up between intents and entities. Just remember this: Intent is the verb (what they want to do), and entities are the nouns (the specific things they're talking about). Getting this right is 90% of the battle in building a useful bot."
Here’s how entities line up with our intents:
| Intent | Potential Entities | Example User Message |
|---|---|---|
checkOrderStatus |
order_number |
"Where is my order ABC-987?" |
askForRefund |
order_number, product_name |
"I need to return the Red Sneakers from order XYZ-123." |
productInquiry |
product_name, product_feature |
"Do the Trail Runners come in blue?" |
Recognizing entities is what allows your bot to have a truly helpful conversation. It's the difference between knowing a user wants a refund and knowing they want to return the Red Sneakers from order XYZ-123.
Mapping the Conversation: Crafting Dialogue Flows
With our intents and entities defined, we can start mapping out the actual back-and-forth. This is the dialogue flow—the step-by-step logic that guides the user from their first message to a final answer. It’s like creating a flowchart for a conversation, with different branches for different scenarios.
Let's sketch out a simple flow for the checkOrderStatus intent:
- User says: "Where is my order?" (The bot correctly tags this with the
checkOrderStatusintent). - Bot checks for an entity: It scans the message for an
order_numberbut doesn't see one. - Bot asks for the missing info: "I can definitely help with that! What's your order number?"
- User provides the entity: "It's 12345."
- Bot takes action: It pings the company's order database with "12345."
- Bot delivers the answer: "Great news! Your order is out for delivery and should arrive today. You can track it here."
This simple exchange is the heart of your chatbot. By designing these flows, you ensure the conversation stays on track and efficiently gets the information it needs to be useful.
Making It Smart: Training Your Chatbot Model
This is where the real "AI" part happens. All the intents, entities, and flows we've defined are just a blueprint. The training process is what breathes life into it. Training is all about feeding your chatbot model tons of example data so it can learn to spot patterns all on its own.
You don't need a giant, complex database to get started. A simple spreadsheet will do the trick. For each intent, you just need to brainstorm all the different ways a real person might ask for that thing.
Practical Example: Training Data for checkOrderStatus
- "Where's my stuff?"
- "Can I get a shipping update?"
- "track my package"
- "Has my order shipped yet?"
- "Give me the status on order 12345."
The more varied and realistic your examples, the smarter your bot gets. It begins to learn that "stuff," "package," and "order" are all related in this context. This is the magic of Natural Language Understanding (NLU).
For those curious about the code, here’s a peek at what this data structure might look like in Python, maybe for a framework like Rasa or a custom model. This isn't runnable code, but it shows the concept perfectly.
# This is a simplified example of a training data structure
training_data = [
{"text": "where is my order?", "intent": "checkOrderStatus", "entities": []},
{"text": "check on my package with id 54321", "intent": "checkOrderStatus", "entities": [{"start": 29, "end": 34, "value": "54321", "entity": "order_number"}]},
{"text": "I want a refund for my shoes", "intent": "askForRefund", "entities": [{"start": 25, "end": 30, "value": "shoes", "entity": "product_name"}]}
]
# You would then pass this 'training_data' to your NLU model's training function
# model.train(training_data)
By feeding the model hundreds (or thousands) of these examples, it moves beyond rigid rules. It becomes a flexible, pattern-recognizing machine that can understand human language in all its messy glory. This is what truly makes a chatbot intelligent.
Getting Your AI Chatbot Ready for Primetime
You’ve done the hard work of building and training your chatbot. That’s a huge milestone, but now comes the moment of truth: testing. This isn't just about squashing bugs. It's about ensuring the conversation feels natural, is genuinely helpful, and never leaves a user stranded in a digital dead-end.
Think of it this way: your bot is like a pilot who has aced the flight simulator. It knows the theory, but you need to see how it handles real-world turbulence before you let actual passengers on board. A thoroughly tested chatbot builds trust; a buggy one just creates frustration.
Putting Your Chatbot Through Its Paces
Testing shouldn't be a sterile, predictable process. Your real mission is to simulate the wonderful chaos of human interaction. This means throwing more at it than just the "happy path" where users ask questions exactly how you imagined they would.
A great first step is to grab a few friends or colleagues and challenge them to "break" the bot. Get them to ask bizarre questions, use typos, or be deliberately vague. This kind of adversarial testing is pure gold for finding the weak spots in your NLU model.
Here are a few methods I’ve found work best in practice:
- Unit Testing: This is your technical deep dive. You'll write scripts to verify that individual pieces of your bot work as expected. For instance, does mentioning "shipping update" reliably trigger your
checkOrderStatusintent every single time? - End-to-End Testing: This simulates an entire user journey from start to finish. You’ll build test scripts that mimic a user trying to achieve a complete goal, like navigating the entire process for a product return.
- Regression Testing: Every single time you tweak your bot or feed it new training data, you risk breaking something that was working perfectly before. This is where regression testing saves you—having automated tests run after every update is a lifesaver.
Expert Opinion: "The real goal of testing isn’t to hit a 100% success rate. It's to deeply understand your bot's failure points. Knowing exactly where and why it gets confused is the most valuable feedback you can possibly get before you launch. That's where the real learning happens."
Deploying Your Chatbot to the World
Once you’re confident in how your bot performs, it's time to set it loose. Deployment is simply the technical process of making your chatbot accessible to users on their favorite platforms, whether that's your website, Slack, or Facebook Messenger.
For a website, this is often as straightforward as embedding a small JavaScript snippet into your HTML. That little piece of code is what powers the chat widget your visitors will see and use.
If you’re integrating with messaging apps, the process involves connecting to their APIs. The specifics vary, but the idea is the same:
- Slack: You’ll need to create a Slack App and use its API tokens to grant your bot permission to read and send messages in specific channels.
- Telegram: This starts with registering your bot with the "BotFather" to get an API key. That key is your bot's passport to the Telegram ecosystem.
- Facebook Messenger: You'll set up an application on the Meta for Developers platform, link it to your business's Facebook Page, and use webhooks to handle incoming and outgoing messages.
The push to integrate AI into our daily tools is growing fast. In 2024, nearly 987 million people are using AI chatbots, which shows just how mainstream the technology has become. The market itself was valued at $15.6 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit $46.6 billion by 2029. This growth is fueled by a boom in AI startups, which have increased a staggering 14-fold since the year 2000. For more on this, check out these fascinating chatbot statistics and market trends at Rev.com.
Life After Launch: The Real Work Begins
Heads up: launching your chatbot isn't the finish line. It’s the starting line for its real education. The post-launch phase is where you monitor, learn, and improve. This is how a good bot becomes a great one.
Your main job now is to become a student of real user conversations. Dive into the logs and look for patterns:
- Where are conversations breaking down most often?
- What are people asking that your bot has no answer for?
- Are there common phrases that are consistently misinterpreted?
Most chatbot platforms offer analytics dashboards to help you spot these issues. If you’ve built a custom solution, you’ll need to implement your own logging. This feedback loop is the engine that drives improvement: monitor the chats, find the weak points, add new training data, and redeploy. An AI chatbot is never really "finished"—it's a living project that gets smarter with every single conversation.
Common Questions About Building a Chatbot

Jumping into your first chatbot project is exciting, but let's be real—it brings up a ton of questions. As you start turning your great idea into actual code and conversation flows, a few practical concerns always pop up. I've been there, and I've seen these same questions come up time and again.
So, think of this as a quick FAQ for those "wait, how does this actually work?" moments. Let's tackle some of the most common uncertainties I hear from people just starting out.
How Much Does It Really Cost to Build an AI Chatbot?
This is the big one, and the honest answer is: it depends. The price tag for a chatbot can swing from absolutely free to well into the tens of thousands of dollars. It all boils down to how complex your bot needs to be and the tools you choose to build it.
-
The Free-to-Cheap Route: You can get surprisingly far with no-code platforms. Many offer free tiers for basic features and low traffic. Even powerful services like Google's Dialogflow are often pay-as-you-go, meaning a small project might only cost you a few bucks a month.
-
The Expensive Route: If you're imagining a completely custom bot built from scratch, you're looking at a serious investment. This involves salaries for developers, server costs for hosting the model, and ongoing maintenance fees to keep it running smoothly.
For anyone just getting their feet wet, I always recommend starting with a low-cost platform. It’s the smartest way to learn the ropes without a huge financial gamble.
Do I Need to Be an Expert Coder?
Absolutely not. The old idea that you needed a Ph.D. in computer science to even think about building a chatbot is a total myth these days. Modern tools have opened the doors for everyone.
Platforms like Tidio or the aforementioned Dialogflow have fantastic visual, drag-and-drop interfaces. You can literally map out entire conversation flows and train your bot on what to say without writing a single line of code. It’s an incredible way to grasp the core logic behind chatbot design.
That said, if your goal is a highly unique or complex chatbot, knowing a language like Python and its AI libraries (TensorFlow, Rasa) is a game-changer. This guide gives you a solid feel for both paths so you can decide where you feel most comfortable starting.
Expert Opinion: "For most developers just starting out, the biggest challenge is Natural Language Understanding (NLU). This is the 'brain' that has to figure out what a user means, even with typos, slang, or vague questions. Getting enough good training data and constantly improving the NLU model based on how people actually talk to your bot is a tough but essential part of the process."
How Can I Make My Chatbot Sound Less Robotic?
This is where the art comes in. Making a chatbot feel more human is all about sweating the small stuff—a mix of good writing and smart technical choices.
First, give it a consistent personality. Is your bot witty and informal, or straight-laced and professional? Whatever you choose, stick with it. Simple things like using contractions ("you're" instead of "you are") can make a huge difference. You'll also want to vary its greetings and common responses so it doesn't sound like a broken record.
But the real secret? Train it with real conversation examples. Feed it the slang, the shortcuts, and the exact phrases your customers actually use. The more your bot learns from genuine human language, the less robotic it will sound. That’s how you create a bot that people actually enjoy talking to.
Ready to dive deeper into the world of AI and stay ahead of the curve? YourAI2Day is your go-to source for the latest news, tools, and insights in artificial intelligence. Explore our articles and join the conversation at https://www.yourai2day.com.