How Does ChatGPT Work? A Simple, Friendly Guide for Beginners
Ever wondered, "How does ChatGPT actually work?" It can feel like magic, but once you peek behind the curtain, it's a clever (and surprisingly understandable) system. At its core, ChatGPT is a super-advanced prediction tool. Think of it like the autocomplete on your phone, but instead of just guessing the next word, it guesses the next entire paragraph based on the massive library of text it learned from.
Decoding the "Magic" Behind ChatGPT
How can an AI draft a perfect email, whip up a poem, or even debug code in seconds? It's not magic, but a process built on some really smart ideas. Let's break it down in a friendly, conversational way.
First off, it helps to know that ChatGPT is a type of Large Language Model (LLM). Its whole job is to understand and create text that sounds like a person wrote it. It does this by learning the countless patterns and connections between words and ideas from the enormous amount of text it was trained on.
Before we get into the nitty-gritty, here’s a quick cheat sheet of the main ideas we'll be covering. This table breaks down the key concepts into simple terms.
ChatGPT Key Concepts at a Glance
| Concept | What It Means in Simple Terms |
|---|---|
| Transformer Architecture | The super-smart engine design that helps the model figure out which words in a sentence are most important. |
| Attention Mechanism | The "secret sauce" that lets ChatGPT focus on the right parts of your question to give a relevant answer. |
| Tokenization | How it chops up your sentences into smaller pieces (tokens) that it can actually understand and work with. |
| Pre-training | The "college years" where the model reads a huge chunk of the internet to learn, well, almost everything about language. |
| Fine-Tuning & RLHF | The "job training" phase where humans teach the AI to be helpful, honest, and safe, not just a random text generator. |
Think of this as our roadmap. We'll explore each of these concepts one by one to build a complete picture of how this amazing technology works.
The Power of Prediction
Here’s the key takeaway: ChatGPT isn’t “thinking” like you or me. It's playing a very advanced game of "what comes next?" When you give it a prompt, it doesn't search a database for a pre-written answer. Instead, it builds a new one from scratch, piece by piece (these pieces are called tokens), based purely on what's most probable.
As AI expert Dr. Sarah Jenkins, a researcher in natural language processing, puts it:
"People often anthropomorphize these models, but it's crucial to remember they are performing incredibly sophisticated statistical pattern matching. They don't 'understand' joy or sadness, but they've analyzed countless texts where those concepts are discussed and can generate a response that is contextually appropriate. It's a simulation of understanding, not genuine consciousness."
ChatGPT, which OpenAI first introduced on November 30, 2022, is built on a model with 175 billion parameters. You can think of these parameters as tiny dials and knobs, all tuned during training to help the model make mind-bogglingly accurate predictions about which word should come next. You can find more statistics on its architecture at PIHAPPINESS. This immense predictive power is what allows it to turn a simple prompt like "write a short story about a robot who discovers music" into a detailed, multi-paragraph response that feels like it was written by a human.
The Transformer: The Engine Powering ChatGPT
To really get what makes ChatGPT tick, we need to pop the hood. The core technology isn't just a bigger version of your phone's autocomplete; it's a completely different engine called the Transformer architecture. This special design is what gives ChatGPT its uncanny ability to understand context, nuance, and the subtle relationships between words.
Think about how you read this sentence: "The delivery driver left the pizza on the porch because the dog was barking loudly." Your brain instantly connects "driver" to "pizza" and understands that the "dog barking" is the reason for leaving the pizza on the "porch." Older AI models would get lost in a sentence like that. The Transformer, however, is built for this.
This diagram gives you a bird's-eye view of the process. You can see how the Large Language Model (LLM) acts like a brain, drawing on its billions of parameters to predict the next word in a sequence.
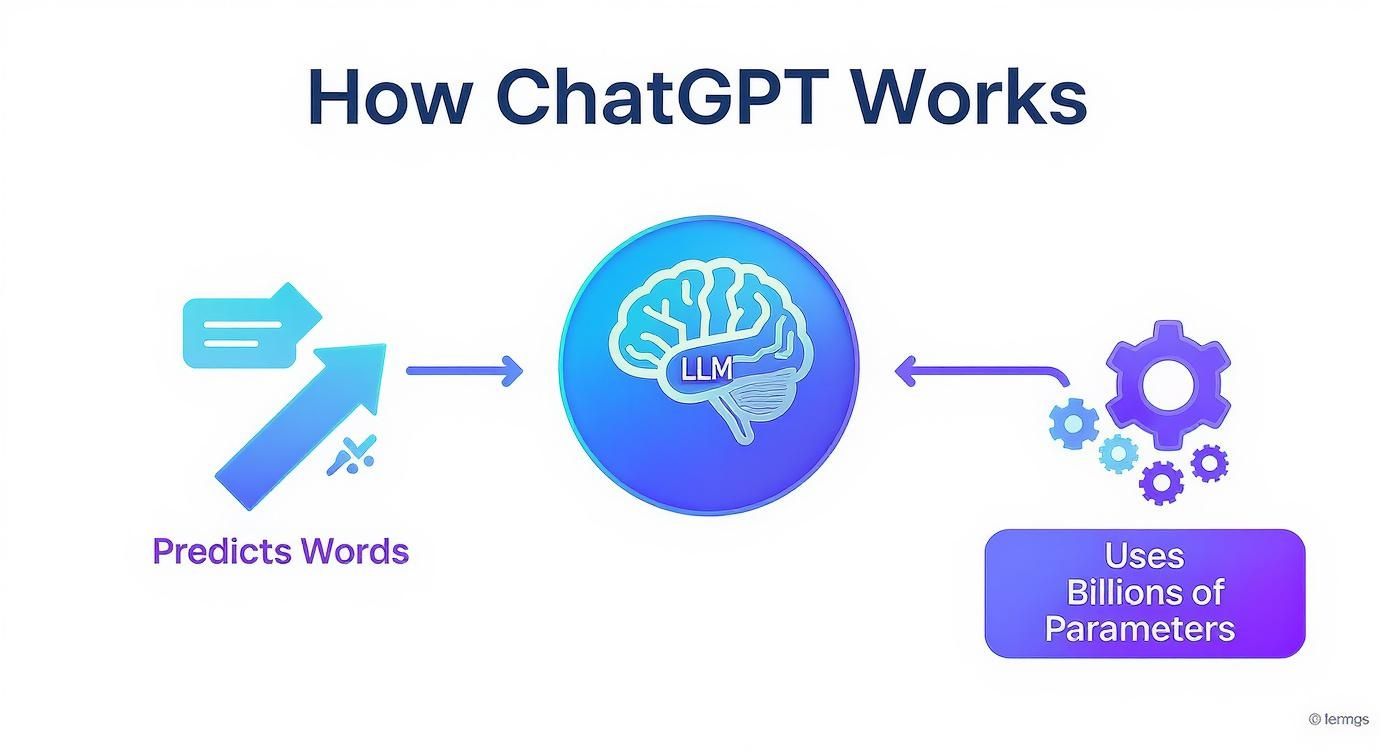
While this is a simplification, it nails the core function: a massive model using its scale to perform sophisticated word prediction. This foundational skill is what enables the complex conversational abilities we see on the surface.
The Self-Attention Secret Sauce
The Transformer’s big trick is a mechanism called self-attention. This is the real magic, the "secret sauce" that lets the model weigh the importance of every word in your prompt relative to all the other words—just like you did with the pizza delivery example.
In technical terms, self-attention allows the model to dynamically assign importance scores to different words in the input, figuring out how they relate to each other.
Imagine you're trying to assemble a piece of IKEA furniture. You don't just read the instructions one word at a time. You glance at the diagram, look at the list of parts, and then back at step one. You're constantly connecting different pieces of information to understand the whole picture. Self-attention does this with words, calculating which ones are most critical for understanding what you're really asking.
From Words to Numbers: A Process Called Tokenization
Before the Transformer can work its magic, your prompt has to be translated into a language a computer can understand. This crucial first step is called tokenization.
It's just a fancy word for breaking your sentence down into smaller chunks, or tokens. A token might be a whole word like "cat," but it could also be part of a word, like "un-" or "-ing."
For example, if you type "ChatGPT is a helpful assistant," the model might break it down like this:
ChatGPTisahelpfulassistant
This method is super efficient. Instead of having to learn every single word in the English language (which is nearly impossible!), the model just needs to learn a vocabulary of common tokens. It can then mix and match them to understand and generate almost any word or sentence.
Each token is then turned into a list of numbers (called a vector), which is the format a neural network can actually work with. This numerical data is what gets fed into the self-attention mechanism. If you want to dig deeper into how that underlying system works, our guide on what is a neural network is a great place to start.
How an AI Learns to Talk: The Three-Stage Training Journey
ChatGPT's ability to write, code, and chat didn't just happen overnight. It went through an intense training program, a three-stage education that turned a raw, powerful model into the helpful assistant we use today.
The whole process is about shaping a massive neural network—guiding it from a state of pure, untapped potential to a focused, conversational tool. It's a huge undertaking that blends enormous amounts of data with specific human guidance.
Let's walk through this unique education, one stage at a time.
Stage 1: General Education Through Pre-training
The first and most important phase is pre-training. Think of this as the AI’s "college years," where it reads a massive library to learn the fundamental rules of language, grammar, facts, and even how to reason.
During this stage, the model is fed a colossal amount of text—a huge slice of the publicly available internet, including books, articles, websites, and scientific papers. It doesn't memorize this information. Instead, it learns the statistical patterns and deep relationships between words and concepts.
For example, after reading millions of sentences, it learns that the phrase "the capital of France is" is almost always followed by "Paris." It builds this web of knowledge for countless ideas, giving it a vast general understanding of the world.
Stage 2: Specialized Job Training with Fine-Tuning
Once pre-training is done, the model knows a lot about things, but it doesn't know how to be a helpful assistant. It’s like a brilliant graduate who now needs on-the-job training. This is where Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) comes in.
Here, human AI trainers get involved. They create a high-quality dataset of conversations, showing the model exactly what a good, helpful answer looks like.
A practical example of a training entry might look like this:
- Prompt: "Explain the water cycle to a five-year-old."
- Ideal Response (written by a human): "Imagine the sun gives a puddle a warm hug! The water turns into a mist, floats up to the sky, and joins other mists to make a cloud. When the cloud gets full and heavy, it rains, sending the water back down to make new puddles!"
By training on thousands of these examples, the model learns the style of a useful AI assistant—clear, helpful, and tailored to the user. It's learning to mimic the patterns of helpfulness, not just random text from the internet. If you want to dive deeper into the mechanics, you can explore how to train a neural network in our detailed guide.
Stage 3: Performance Reviews Through Human Feedback
The final, and perhaps most important, step is Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF). If fine-tuning was the initial job training, think of RLHF as ongoing performance reviews. This is what teaches the model human preferences, refining its personality and making it safer.
Here's how it works in a friendly breakdown:
- Generate Multiple Responses: For a single prompt, the AI generates several different answers. For example, for "Write a tagline for a coffee shop," it might create: "Your daily grind, perfected," "Life begins after coffee," and "Wake up happy."
- Humans Rank the Responses: Human reviewers then look at these answers and rank them from best to worst. They might rank "Your daily grind, perfected" as #1 because it's clever.
- Train a "Reward Model": This ranking data is used to train a separate AI, called a "reward model." Its only job is to learn what humans like and predict which type of answer a person would rate highest.
This feedback loop is what teaches ChatGPT to be more than just accurate—it learns to be helpful, harmless, and honest. It prioritizes clarity over jargon, safety over unsafe suggestions, and helpfulness over uncooperative replies.
This reward model then becomes an automated coach for ChatGPT. As ChatGPT generates responses, it constantly "checks in" with the reward model to see if its answers are on the right track, tweaking its output to get a higher "score." It’s this continuous feedback that steers it away from generating biased, unsafe, or nonsensical content.
From Your Prompt to Its Answer: A Live Walkthrough
You type a question, hit enter, and a complete answer appears almost instantly. In that split second, your prompt takes a lightning-fast trip through ChatGPT’s digital brain. Let's follow that journey, step-by-step, to see how your question becomes a coherent response.

It all begins the moment you send your message. The model doesn't read sentences like we do. First, it performs the crucial step we've already touched on: tokenization. Your text gets instantly chopped up into manageable pieces that the neural network can process.
So, if you ask, "What's the capital of France?", it might be diced into tokens like What, 's, the, capital, of, France, and ?. Each token is then immediately converted into a list of numbers, translating your question into a language the AI understands.
Predicting the Next Best Word
With your prompt now a sequence of numbers, it’s fed into the enormous neural network. This is where the magic happens. The model analyzes your tokens and runs a massive calculation to predict the most statistically likely next token.
Think of it as a game of probabilities on a massive scale. Based on the billions of examples it learned from during training, the model essentially asks itself, "After the sequence 'What's the capital of France?', what single word is most likely to come next?"
The answer is almost certainly "The". So, it generates that token. But it doesn't stop there.
Building the Answer Token by Token
Now, the process repeats. The model takes the original prompt plus its newly generated token ("What's the capital of France? The") and feeds that entire, slightly longer sequence back into itself. It then calculates the next most probable token, which would likely be "capital".
This loop continues, one token at a time:
- Input:
What's the capital of France?-> Output:The - Input:
What's the capital of France? The-> Output:capital - Input:
... The capital-> Output:of - Input:
... The capital of-> Output:France - Input:
... of France-> Output:is - Input:
... France is-> Output:Paris
This word-by-word (or, more accurately, token-by-token) generation is why you can literally watch ChatGPT type out its answer. It’s building the sentence as it goes, constantly re-evaluating the sequence to guess the very next piece. The process finally stops when it generates a special "end of sequence" token or hits a preset length limit.
Remembering the Conversation With a Context Window
So how does it remember what you asked five questions ago? This is handled by something called the context window, which is like the AI's short-term memory.
The context window is a fixed amount of recent conversation history (both your prompts and its answers) that the model considers every single time it generates a new response.
Imagine it as a little notepad where the AI keeps track of the last few things you've talked about. When you ask a follow-up question like, "What's the weather like there?", it looks at that question plus the notepad which says "Paris" to understand what "there" means. This is what allows it to carry on a coherent, context-aware conversation.
But this memory has limits. If a conversation gets too long, the earliest parts will eventually fall off the notepad, and the AI will effectively "forget" them.
ChatGPT in the Real World: Strengths and Limitations
Now that we know how ChatGPT works, let’s talk about what it's actually like to use. It's an incredibly powerful tool, but like any tool, it has its strengths and weaknesses. Knowing what it’s great at—and where you need to be careful—is the key to getting the most out of it.

Its popularity tells a story on its own. After launching in November 2022, ChatGPT hit one million users in just five days. By January 2023, that number exploded to 100 million—a staggering 9,900% increase in under two months. With monthly visits climbing past 1.8 billion, it’s clear people are finding real value in it. You can discover more insights about these ChatGPT statistics and its remarkable growth.
But what exactly is everyone doing with it? It comes down to its incredible strengths in a huge range of tasks.
Where ChatGPT Truly Shines
One of the best things about ChatGPT is its sheer versatility. It isn't just a chatbot. Think of it as your brainstorming partner, writing assistant, summarization engine, or even a patient tutor.
Here are a few practical examples of where it excels:
- Creative Ideation and Brainstorming: Stuck on a name for your new puppy or need ideas for a birthday party theme? Ask ChatGPT for "ten funny names for a golden retriever" and you'll get a creative list in seconds, helping you break through mental blocks.
- Summarizing Complex Topics: Got a long, dense article about blockchain you don't have time to read? Paste it in and ask for "a simple, bulleted summary," and it will distill the key points into something you can digest in a minute.
- Drafting and Writing Assistance: From composing a professional email to a difficult client to outlining a blog post, ChatGPT handles the heavy lifting. It's a great way to overcome the "blank page" problem by giving you a solid first draft to edit.
- Coding and Debugging: A developer can ask it to "write a Python script to organize my downloads folder" or "find the bug in this piece of code." It can often spot errors that a human might miss, acting as a handy second pair of eyes.
Acknowledging the Limitations
For all its power, it’s critical to remember that ChatGPT is not a perfect source of truth. Its limitations are a direct result of how it works—it's a sophisticated pattern-matching system, not a conscious, thinking being.
The biggest issue to watch out for is its tendency to hallucinate. This is when the AI generates information that sounds plausible and authoritative but is completely false. Since it’s just predicting the next likely word, it can confidently string together sentences that are factually wrong. For instance, it might invent a historical event or cite a non-existent scientific study.
Another serious issue is inherent bias. The model learned from a massive snapshot of the internet, which is filled with human biases. These biases can creep into its responses, sometimes reinforcing outdated stereotypes.
Finally, ChatGPT has no real understanding or consciousness. It doesn’t "know" anything in the human sense. It can't feel empathy or grasp the ethical implications of its advice. It’s a tool reflecting the patterns in its data—nothing more.
A Balanced View of ChatGPT's Capabilities
To make the most of ChatGPT, it helps to have a clear, side-by-side view of its capabilities. Think of this as a practical user's guide to know when to lean on it and when to double-check its work.
| Strengths (What It's Great For) | Limitations (What to Watch Out For) |
|---|---|
| Rapid Ideation & Brainstorming: Generates creative concepts for marketing, writing, and problem-solving. | Factual Inaccuracies (Hallucinations): Can confidently state incorrect information as fact. |
| Content Creation & Drafting: Quickly produces first drafts of emails, articles, reports, and social media posts. | Inherent Bias: May reproduce stereotypes or biased views present in its training data. |
| Summarization & Simplification: Distills long documents and complex topics into easy-to-understand summaries. | Lack of Real-Time Knowledge: Its knowledge is cut off at its last training date (currently early 2023 for GPT-4). |
| Code Generation & Debugging: Writes code snippets, explains programming concepts, and helps find errors. | No True Understanding: Cannot grasp context, nuance, or ethics like a human can. |
| Language Translation & Tutoring: Offers quick translations and can explain subjects in a simple, step-by-step manner. | Overly Generic or Repetitive Output: Responses can sometimes be formulaic or lack originality. |
| Task Automation: Helps with repetitive tasks like reformatting text or generating boilerplate content. | Privacy & Data Security: Inputs may be used for model training; never share sensitive personal or proprietary information. |
Keeping this balance in mind is the best way to use ChatGPT effectively. It's an incredible assistant when you play to its strengths, but it's not a substitute for human judgment, expertise, or a quick fact-check.
Ethics, Privacy, and the Future of Conversational AI
Getting comfortable with a powerful tool like ChatGPT means more than just learning to write good prompts. We also have to talk about the responsibilities that come with it. Understanding the ethical and privacy side of things is just as crucial as knowing how the technology works. Being a smart user means being a responsible one.
A huge piece of this puzzle is your data. When you use the standard version of ChatGPT, your conversations can be used as training material for future models. This is a big deal. The golden rule here is to never input sensitive personal or proprietary company information. Treat every conversation like it's public—if you wouldn't want it on a billboard, don't type it into the chat.
Expert Opinion from OpenAI's Safety Team: "We are constantly working to make our models safer and more private. For instance, we filter personal identifiable information from our training data and have built-in features to reject requests for sensitive information. User trust is paramount, and protecting data is a core part of that."
While OpenAI is taking steps to protect data, the fundamental advice for users stands: be cautious. If you want to dig deeper into this, our guide on artificial intelligence privacy concerns gives you a more thorough rundown on keeping your information safe.
The Challenge of AI Bias
Another major ethical hurdle is AI bias. Since ChatGPT learned from a vast snapshot of the internet, it also learned all of our human quirks, stereotypes, and biases. The model can't help but absorb that, which means its responses can sometimes reflect skewed perspectives.
Here's a practical example: if you ask for a story about a "brilliant programmer," the model might be statistically more likely to make that character male. Or if you ask it to describe a "nurse," you might get descriptions that overwhelmingly point to women. These aren't malicious choices; they're just reflections of the patterns found in the billions of documents it was trained on.
Fixing this is a massive, ongoing project for AI developers. It involves carefully curating training data and using techniques like RLHF to guide the model toward more balanced and fair answers.
The Future of Safer AI
Looking ahead, the goal is to build conversational AI that is safer, more transparent, and more aligned with human values. This isn't science fiction; it's the active work researchers are tackling right now to improve ChatGPT from the ground up.
The main areas of focus include:
- Enhanced Transparency: Finding ways for users to see why the model gave a specific answer, almost like showing its work.
- Better Alignment: Developing stronger techniques to ensure the AI's goals are genuinely aligned with human well-being.
- Reduced Bias: Creating advanced methods to actively spot and neutralize the biases absorbed during training.
The vision is to create AI that isn't just a powerful tool, but a trustworthy and helpful partner. This process of constant improvement is what will ensure that as this technology becomes a bigger part of our lives, it does so responsibly.
A Few Common Questions About ChatGPT
Let's quickly answer some of the questions that pop up most often. Getting these cleared up will give you a much better feel for what the tool is actually doing.
Is ChatGPT Connected to the Live Internet?
Nope! This is a common misconception. Think of ChatGPT's knowledge as a giant encyclopedia printed on a specific date. It knows everything in that encyclopedia inside and out, but it can't check for news or updates that happened after it was printed.
This is why it can't give you the current stock prices or tell you who won last night's game. Its knowledge is vast but frozen in time, limited to the data from its last major training run.
Does ChatGPT Really Understand My Questions?
This is a great question that gets to the heart of how AI works. In the human sense—with consciousness, feelings, and beliefs—the answer is no. ChatGPT isn't thinking or feeling anything.
It’s an incredibly advanced pattern-matching machine. It has analyzed billions of texts and learned the statistical probabilities of which word is most likely to follow another.
Analogy: It’s like a musician who has memorized thousands of songs but doesn't feel the emotion behind the lyrics. They can play a sad song perfectly because they know which notes typically go together to create a "sad" sound, not because they are actually feeling sad.
So, it's mimicking understanding with incredible accuracy, not actually experiencing it.
Can I Trust Everything ChatGPT Tells Me?
Absolutely not. You should approach its answers with a healthy dose of skepticism. While it can be impressively accurate, ChatGPT is known for "hallucinating," which is a fancy way of saying it can make stuff up.
The best way to use it is as a creative partner or a first-draft generator. Let it help you brainstorm ideas or structure your thoughts, but never treat it as the final word on any important fact. Always, always fact-check critical information with reliable sources.
At YourAI2Day, our goal is to cut through the hype and give you the practical knowledge you need to use AI well. To keep learning, check out our other guides and articles over at https://www.yourai2day.com.