The Real Difference Between AI and Machine Learning Explained
Hey there! If you've ever felt a bit lost in the buzzwords of tech, you're not alone. The easiest way to grasp the difference between AI and machine learning is to picture a set of Russian nesting dolls. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the biggest doll—the entire field dedicated to building machines that can think, reason, and act intelligently. Machine Learning (ML) is a smaller, crucial doll inside it; it's a specific technique for achieving AI by training computers to learn from data themselves.
The Big Picture: AI and Its Learning Engine, ML
Ever wonder how Siri or Alexa understand what you’re saying? Or how Netflix uncannily predicts the next show you’ll binge-watch? You're seeing both AI and machine learning in action, but they play different roles. Think of AI as the grand vision: creating intelligent systems. Machine learning is one of the most powerful ways we get there.
This isn't just tech-speak; getting the distinction right is key to understanding the technology shaping our world. AI is the broad concept of a machine performing tasks in a way we’d call "smart." Machine learning, on the other hand, is a specific branch of AI focused on giving machines the ability to learn from data without needing to be programmed for every single possibility.
"AI is the ultimate goal of creating machine intelligence. ML is a practical, data-driven path to achieve parts of that goal," notes Sarah Jenkins, an AI strategy consultant. "If you're building or buying a solution, knowing which you're dealing with is the first step to success."
Seeing How They Fit Together
This diagram helps visualize the relationship. AI is the all-encompassing field, ML is a major part of it, and Deep Learning is a specialized technique within ML.
As you can see, all machine learning is AI, but not all AI uses machine learning. Some early AI systems, like chess-playing programs from decades ago, relied on hand-crafted rules and logic—a completely different approach from the data-centric learning that defines modern ML.
AI vs Machine Learning at a Glance
For a quick reference, let's lay out the core differences. This table summarizes the distinct roles and functions of AI and ML before we dive deeper into their practical applications.
| Aspect | Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Machine Learning (ML) |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | A broad field focused on creating systems that can reason and problem-solve. | A specific subset of AI where systems learn directly from data. |
| Goal | To simulate human-like intelligence for a wide range of tasks. | To perform a specific task with high accuracy by identifying patterns. |
| Core Function | Building systems that can strategize, plan, perceive, and even create. | Developing algorithms that make predictions or decisions from data inputs. |
| Example | A self-driving car navigating complex city traffic from A to B. | The specific system within that car that predicts a pedestrian's path. |
This at-a-glance view helps frame the conversation. AI is the "what"—the intelligent behavior—while ML is often the "how"—the process of learning from data to produce that behavior.
What Exactly Is Artificial Intelligence?
Let's start with the big picture. When most people hear the term Artificial Intelligence, their minds jump to sci-fi movies—robots with personalities or computers bent on world domination. While entertaining, that vision misses the reality of AI, which is already all around us.
At its heart, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a massive field of computer science dedicated to a single, ambitious goal: building machines that can do things that normally require human intelligence. Think of it as the ultimate mission—creating systems that can reason, learn from experience, perceive the world, and make independent decisions.
This isn't some new-age concept. The term itself was officially coined back in 1956 at the legendary Dartmouth Conference, kicking off the long journey to build thinking machines. The first attempts, what we now call symbolic AI, were all about programming a massive list of explicit rules for a computer to follow.
The Different Flavors of AI
To really grasp the difference between AI and machine learning, you first have to understand that not all AI is the same. There are two main categories of AI that exist today, plus one that's still purely theoretical.
-
Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI): Often called "Weak AI," this is the only kind of AI we’ve actually built. ANI is designed and trained to perform a single, specific task exceptionally well. The digital assistant on your phone, a spam filter guarding your inbox, or a world-champion chess program are all classic examples. They’re brilliant in their lane but completely lost outside of it.
-
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI): This is "Strong AI," the kind you see in movies. For now, it's just a concept. AGI describes a hypothetical machine with the ability to understand, learn, and apply its knowledge to solve any problem, just like a human. It would be conscious and self-aware. We're a long, long way from AGI, but it remains the north star for many in the field.
The Brain and Its Purpose
Think of AI as the overarching concept—the entire "brain." Its purpose is to deliver a final product that acts intelligently. That product could be a chatbot that understands context or a self-driving car that navigates a chaotic intersection. For a deeper dive, you can explore our complete guide on what is artificial intelligence.
The path to building this "brain" has been rocky. Early symbolic AI couldn't cope with the unpredictability of the real world, leading to "AI winters" in the 1970s and 1980s when funding dried up. Then machine learning arrived and completely changed the game. By switching from rigid, rule-based systems to flexible, data-driven learning, ML created a practical way to achieve narrow AI. Today, an estimated 85% of AI projects are powered by ML models. You can find more details on AI's history and its connection to ML from Syracuse University's iSchool.
In essence, AI is the grand vision of creating intelligence, while the methods used to achieve that intelligence can vary. Machine Learning just happens to be the most successful and popular method we have today, powering the AI tools we use every single day.
How Machine Learning Powers Modern AI
If you think of Artificial Intelligence as the destination—building a system that can think or act intelligently—then Machine Learning (ML) is the high-performance engine getting us there. It’s the practical application that allows a computer to learn from data, identify patterns, and make decisions with minimal human intervention.
Essentially, ML gives the broader "brain" of AI its ability to learn.

The process is a lot like how we learn. Think about teaching a toddler to recognize a cat. You don't give them a list of rules—"pointy ears + whiskers + long tail = cat." You just show them pictures and say, "That's a cat."
After seeing enough examples, the child’s brain connects the dots and builds its own internal model of what a "cat" is. Machine learning algorithms do the same thing, just with enormous amounts of data. We feed them the information, and they figure out the patterns on their own, getting better and more accurate over time.
The Different Styles of Learning
Just as people learn in different ways, machine learning algorithms use several distinct approaches to process information. Grasping these methods is key to understanding the practical difference between AI and machine learning, as each style is built to solve a specific type of problem.
Here are the most common approaches you already encounter every day:
-
Supervised Learning: This is like studying with a tutor. The algorithm gets a dataset where all the "right answers" are already labeled. A classic example is an email spam filter. It's trained on millions of emails that have been explicitly marked as either "spam" or "not spam." By studying these labeled examples, it learns the tell-tale signs of junk mail and can start making its own judgments on new emails.
-
Unsupervised Learning: This is more like exploring on your own. The algorithm is given a pile of unlabeled data and is tasked with finding hidden patterns or structures within it. Think about how Netflix or Spotify suggests new things you might like. They use unsupervised learning to cluster you with other users who have similar tastes, then recommend content that people in your "cluster" also enjoyed.
These learning styles are the core mechanisms that allow a system to develop a specific, narrow form of intelligence. You can explore more about how these learning models work in our detailed article on machine learning.
Data Is The Fuel For The ML Engine
The single most critical ingredient for any machine learning project is data. Lots and lots of it. At the end of the day, an ML model is only as smart as the data it was trained on. This deep dependency on massive datasets is a huge differentiator in the modern AI landscape.
According to Dr. Andrew Ng, a pioneer in the field, "The sheer scale of data is what truly separates modern ML applications from older statistical methods. ML thrives where traditional analysis falters, finding complex patterns that drive much of AI's commercial success today."
This relationship between data and ML is fundamentally reshaping entire industries and job markets. Machine learning excels at finding insights in vast datasets that would overwhelm traditional methods, powering an estimated 60% of AI's commercial value. It's no surprise that LinkedIn data shows ML-specific jobs have grown by a staggering 455% in recent years, far outpacing the growth of general AI roles. This impact is especially clear in finance, where ML algorithms now detect 99% of anomalies in real-time across billions of global transactions.
Comparing Their Core Goals and Approaches
To really get a handle on the difference between AI and machine learning, it helps to put them side-by-side and see what each is trying to do. Think of it like this: AI is the grand mission to build a fully functional, thinking robot. Machine learning is the focused task of teaching that robot one specific skill, like how to perfectly catch a ball.
The ambition behind Artificial Intelligence is vast and almost philosophical. Its ultimate goal is to create a system that can simulate human thinking to solve a wide range of problems. We're talking about the ability to reason, plan, perceive the world, and make decisions in all sorts of situations.
Machine Learning, on the other hand, has a much more practical and narrow objective. Its purpose is to perform a single, specific task exceptionally well by learning from data. It isn't trying to "think" like a person; it's designed to find patterns and make predictions with incredible accuracy for a defined problem, whether that's spotting fraudulent transactions or translating languages.

Scope and Ambition
The most telling difference is their scope. AI is all about breadth. It's the pursuit of creating systems with general cognitive abilities. The long-term dream for AI—though still a long way off—is Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), a machine that could perform any intellectual task a human can.
Machine learning is about depth within a very narrow domain. An ML model built to predict stock market trends can't suddenly start diagnosing medical conditions. Its intelligence is highly specialized, but within that one task, it can often outperform any human expert.
This distinction has huge real-world consequences. A core difference lies in their goals: AI pursues broad human-like intelligence across tasks, whereas ML excels at pattern recognition and prediction from massive datasets. In banking, for example, ML now powers 90% of fraud detection. JPMorgan Chase's ML systems process 2.5 petabytes of data daily, which has helped them cut down on false positives by 40% since 2018.
AI, meanwhile, often acts as the conductor, orchestrating ML models with other technologies like computer vision. Look at Tesla's Full Self-Driving: the overarching system is AI, but it relies on ML for 99% of its real-time driving decisions. You can find more fascinating statistics in the full report from Datarobot.
"In my daily work, the difference is crystal clear," explains a Lead Data Scientist at a major tech firm. "We use AI as the strategic framework for a project, like building a 'smart' customer service bot. But we use machine learning for the heavy lifting, like training the specific model that understands customer sentiment in an email."
Methods and Processes
How they get the job done is also fundamentally different. AI is a big tent that includes many methods beyond just learning from data. Early AI, for instance, was built on logic and rule-based systems where programmers painstakingly hand-coded complex decision trees. A modern AI system might combine logic, expert systems, and multiple machine learning components.
Machine learning, by its very nature, lives and breathes data and algorithms. It follows a clear process of training, validation, and testing. It learns from experience—the data—to build a mathematical model that can then make predictions on new information it has never seen before.
If you want to go deeper into the specialized techniques ML uses, our guide on the difference between deep learning vs machine learning is a great next step.
This comparison table breaks down these key distinctions, making it easy to see where their paths diverge.
Detailed Comparison of AI and Machine Learning
Here's a straightforward breakdown of how AI and Machine Learning stack up against each other across several key features.
| Feature | Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Machine Learning (ML) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | To build systems that simulate human intelligence and solve broad problems. | To train a system to perform a specific task with high accuracy by learning from data. |
| Approach | Can use a mix of logic, rules, planning, and learning techniques. | Relies almost exclusively on algorithms and statistical models learning from data. |
| Data Needs | May or may not require large datasets (e.g., rule-based AI). | Absolutely dependent on large, high-quality datasets for training. |
| Level of Autonomy | Aims for higher-level autonomous decision-making and reasoning. | Makes predictions or classifications based on learned patterns; autonomy is task-specific. |
| Human Involvement | Often requires experts to define rules, knowledge bases, and overall system goals. | Requires data scientists to select algorithms, prepare data, and tune models. |
| Example System | A comprehensive robotics system that navigates, interacts, and performs tasks. | The specific algorithm that helps the robot recognize and pick up objects. |
In the end, you can think of AI as the visionary architect designing an intelligent house, while machine learning is the specialized craftsman who perfects every single window and door through meticulous practice. One defines the big picture, and the other masters the details.
Real-World Examples of AI and Machine learning
Okay, enough with the abstract definitions. The best way to truly grasp the difference between AI and machine learning is to see them in the wild. You’re already using both technologies every day, probably without even thinking about it.
Let's look at a few familiar scenarios. In each one, you'll see how a broad AI system delivers a complete, intelligent experience, while a specific ML model provides the "smarts" that make it feel so personal and predictive.
Your Smart Home Assistant
Think about your Amazon Alexa or Google Home. The entire device is an Artificial Intelligence system. Its purpose is broad: to be a helpful, voice-activated assistant that can juggle a huge range of tasks, from playing music to answering trivia.
So how does it get so good at understanding your unique accent and the weird way you phrase commands?
That’s Machine Learning. Buried inside that AI framework is an ML model trained on millions of hours of human speech. It’s constantly learning from your interactions, getting better at telling your voice apart from your partner’s and adapting to your personal quirks over time.
- The AI Part: The entire Alexa platform that processes requests, connects to Spotify, and tells you the weather.
- The ML Part: The specific algorithm that learns your vocal patterns to improve its speech recognition accuracy.
Your Favorite Streaming Service
When you fire up Netflix, you're interacting with a complex AI application. The whole platform is designed to create an intelligent entertainment experience, managing a colossal library of content and streaming it flawlessly to millions of people.
The real magic, though, is the recommendation engine. That’s pure Machine Learning. This is the part of the system that feels like it knows you better than you know yourself, somehow suggesting the perfect movie for a Friday night.
This recommendation engine doesn't follow a simple set of programmed rules. Instead, it uses ML algorithms to analyze mountains of data—your viewing history, what you've rated highly, what shows you abandoned after ten minutes, and what millions of other users with similar tastes have enjoyed.
This ML model has one, laser-focused job: predict what you’ll want to watch next. It’s a learned skill, not a programmed one.
- The AI Part: The entire Netflix application, from content delivery to user account management.
- The ML Part: The recommendation algorithm that analyzes user behavior to create personalized content suggestions.
Getting from Point A to Point B
Navigation apps like Google Maps or Waze are another perfect example of this partnership. The entire app is an AI system built to solve the complex problem of navigation. It brings together maps, business info, and routing logic into one complete travel solution.
But that feature that predicts a traffic jam and suggests a faster route just as you’re about to hit it? That’s where Machine Learning shines. The system is constantly pulling in anonymous speed and location data from thousands of other drivers on the road.
ML algorithms churn through this real-time data stream, learning to recognize the subtle patterns that signal a slowdown. They can predict how long a delay will last and when it makes sense to reroute you. That predictive power is a learned skill that makes the overall AI system incredibly useful.
- The AI Part: The complete Waze or Google Maps application that plans routes and provides turn-by-turn directions.
- The ML Part: The specific model that analyzes real-time data from other drivers to predict traffic and estimate your arrival time.
The Modern Online Shopping Experience
The moment you land on a major e-commerce site, you're likely engaging with AI. That little chatbot that pops up asking if you need help is a classic AI application. It uses natural language processing (another branch of AI) to figure out what you're asking and provide answers.
But what about that "Customers who bought this also bought…" section? That's Machine Learning in action. An ML model sifts through the purchase histories of millions of customers, hunting for associations between products. Its specific job is to spot items that are frequently bought together and show them to you.
The system wasn't programmed with a rule like, "If a customer buys a tent, show them a sleeping bag." It learned that connection by discovering the pattern in the data all on its own.
Why This Distinction Matters to You
Getting the difference between AI and machine learning right isn't just an academic exercise for developers or data scientists. It's about looking past the buzzwords to understand the tools that are fundamentally reshaping our world, from our careers to our smart homes.
For consumers, this clarity is empowering. You start to see how products work—whether a gadget is using a broad AI system to solve a problem or a specific ML model that’s learning your personal preferences. That insight gives you more control over your digital life and helps you make smarter choices about the technology you adopt.
If you're a business owner or entrepreneur, the distinction is even more critical. It's the key to making strategic investments that pay off. Do you need a comprehensive AI solution to automate an entire business process, or would a targeted ML model to predict customer behavior or optimize inventory do the job? Getting that decision right can save you thousands and give you a real competitive edge.
Your Personal and Professional Path
Even if you're just exploring a career in tech, understanding this difference opens up the right doors. A role in "AI" could mean working on anything from ethics and system design to robotics. A "Machine Learning" job, on the other hand, is almost always hands-on with data, algorithms, and building predictive models. Knowing where they diverge helps you focus your learning and find a role that genuinely fits what you want to do.
"The core of the matter is this: AI is the goal, and ML is one of the best tools we have to reach it," explains a leading AI Strategy Consultant. "When you know which tool is right for the job, you avoid costly mistakes and build solutions that actually work."
This flowchart breaks down how a big-picture AI concept like a 'Smart Home' is built on specific ML skills like 'Voice Commands' to actually function.
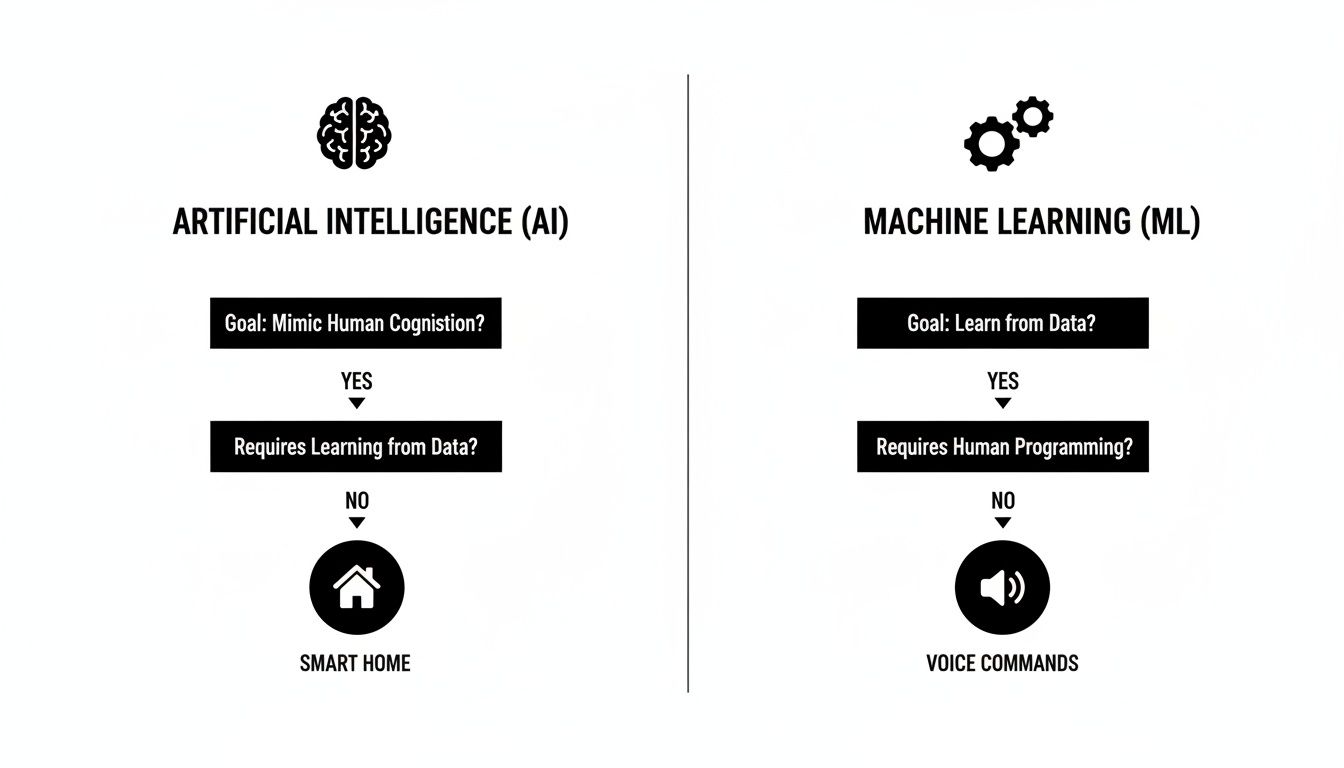
As the visual shows, the broader AI system (the smart home) sets the overall framework. It’s the machine learning component (voice recognition) that provides the specialized, learned capability that makes the system feel intelligent.
At the end of the day, a solid grasp of the AI vs. ML distinction gives you the confidence to discuss these technologies, judge their real-world impact, and decide where they fit into your own life. It’s the first step from being a passive user to becoming an informed participant in the tech world—someone who can cut through the marketing fluff and see what’s truly valuable.
Common Questions About AI and Machine Learning
Even with the core concepts laid out, some questions tend to surface again and again. Let's dig into a few of the most common ones to really cement your understanding of where AI and machine learning stand.
Is AI Harder Than Machine Learning?
That's a fantastic question, and the answer isn't a simple yes or no. In a way, you could say AI is "harder" because its ultimate ambition—to create a machine with genuine, human-like intelligence—is one of the biggest unsolved challenges in science. It’s a massive, philosophical, and technical mountain to climb.
Machine learning, on the other hand, is much more focused. While the work is incredibly complex, an ML practitioner is solving a specific, bounded problem. Their goal is tangible: train a model to master a task, whether it's identifying faces in photos or forecasting sales figures. The math is tough, but the finish line is clear.
Can You Have AI Without Machine Learning?
You absolutely can. In fact, that's how it all started. The early days of artificial intelligence were dominated by what we call "expert systems." Before we had the processing power or the enormous datasets needed for ML, developers built AI by hand-coding intricate webs of if-then rules.
A classic example is an early chess-playing computer. It didn't learn from experience by playing millions of games. Instead, programmers fed it an enormous library of rules and strategies straight from the minds of chess grandmasters. It was a form of AI, but one based entirely on pre-programmed logic, not learning from data.
The big shift came when we figured out it's far more powerful to let the machine discover the best moves from data itself, rather than us trying to explicitly code every single possibility.
Which One Should I Learn First?
If you're looking to build a career in this field right now, start with machine learning. It's the practical, hands-on choice. ML is the engine driving almost every modern AI application you see today, from recommendation systems to self-driving cars.
Mastering the fundamentals of data processing, algorithms, and model training will give you the highly sought-after skills that companies are desperate for. Once you've got a firm handle on ML, you can then zoom out and see how these powerful models plug into the broader architecture of complex AI systems.
Ready to stay ahead of the curve? At YourAI2Day, we break down complex topics and bring you the latest insights into the world of artificial intelligence. Explore our articles and tools today!







