The Difference Between AI and Automation Explained
Hey there! If you've ever felt like the terms AI and automation are used interchangeably, you're not alone. It's super common to hear them thrown around in the same conversation, and it makes sense—both are about making work easier and more efficient. But when you peek under the hood, they're actually quite different.
The simplest way I like to think about it is rules versus reason. Automation is fantastic at following a strict set of pre-programmed rules. Think of it as a flawless instruction-follower. AI, on the other hand, is designed to reason, learn, and make its own decisions. It's more of a problem-solver.
AI vs Automation: Uncovering the Core Difference
Let's imagine automation as a highly dependable workhorse. You give it a script—a defined workflow with clear, unchanging steps—and it will execute that script perfectly, thousands of times over without getting tired or making a single mistake. It's all about consistency and reliability for predictable tasks.
AI is a different beast entirely. It's built to mimic human-like thinking. Instead of just following a script, it analyzes data, recognizes patterns, and learns from what happens. This lets it handle unpredictable situations and tackle problems that don’t have a simple, rule-based answer.
For example, think about your email inbox. An automation rule can file every email from your boss into a "Priority" folder. It's a simple, fixed command. But an AI-powered spam filter analyzes the content, sender, and links in an incoming email to decide if it's junk. It learned what spam looks like and makes a judgment call. That adaptability is the real game-changer. For a deeper dive, you can find the latest automation industry data and insights on thunderbit.com.
Quick Look: AI vs Automation at a Glance
To really nail down the differences, a side-by-side comparison can be super helpful. This table cuts through the noise and lays out the core distinctions between these two powerful technologies.
| Attribute | Automation | Artificial Intelligence (AI) |
|---|---|---|
| Core Function | Executes pre-programmed, repetitive tasks | Simulates human intelligence and makes decisions |
| Decision-Making | Follows strict "if-then" rules | Uses data to make predictions and judgments |
| Learning Ability | Static; requires manual updates to change | Dynamic; learns and adapts from new data over time |
| Task Complexity | Best for simple, predictable, routine tasks | Can handle complex, variable, and nuanced tasks |
| Primary Goal | To increase efficiency and ensure consistency | To solve problems and perform human-like tasks |
So, what's the takeaway? Automation is about doing things faster and more reliably. AI is about doing things smarter. They aren’t mutually exclusive, either. In fact, some of the most powerful systems today are born when automation’s consistency meets AI’s intelligence, but we'll get into that a bit later. For now, just having this foundational difference clear is the most important step.
Breaking Down Automation: What It Really Means

So, what are we really talking about when we say "automation"? At its heart, automation is all about using technology to handle predictable, repetitive tasks that follow a clear set of rules. It's the ultimate workhorse, designed to follow instructions with perfect speed and consistency.
You’re surrounded by automation every day, even if you don't notice it. That order confirmation email that hits your inbox moments after you buy something? That’s automation. The tool that schedules and publishes your social media posts at just the right time? Also automation.
It runs on a very straightforward, powerful principle: if this happens, then do that. There's no thinking, learning, or judgment involved. The system is just executing a script it's been given, and it does it flawlessly every single time. This is precisely why it's so valuable for any job where repetition and precision are non-negotiable.
The Heart of Automation: Rule-Based Execution
The critical distinction here is that automation can't "think" for itself. It can’t adapt to unexpected situations or learn from new data. If something comes up that isn't covered by its pre-programmed rules, the system will either grind to a halt or throw an error.
For instance, an automated billing system is great at sending invoices on the first of every month because that's a simple, clear rule. But it can’t analyze spending habits to flag a potentially fraudulent charge—that kind of pattern recognition is simply beyond its scope.
Expert Opinion: According to tech analyst Sarah Carter, "Automation boils down to getting robots to follow orders. We, the humans, define the rules, and the software or machinery performs them. That's the essence of automation—predictable execution at scale."
This makes it a perfect fit for high-volume, low-complexity work. Think about tasks like:
- Data Entry: Copying information from a spreadsheet into a CRM system.
- Email Marketing: Automatically sending a welcome email to every new subscriber.
- Manufacturing: A robotic arm on an assembly line that puts the same four screws into a car door, over and over.
These kinds of digital tasks are often handled by a specific type of software called RPA. If you're curious, you can dig deeper into what robotic process automation is and how businesses use it. At the end of the day, automation is about efficiency—not intelligence.
Getting Real About Artificial Intelligence

Now, let's chat about Artificial Intelligence. The term "AI" often conjures images of science fiction, but its real-world application is far more grounded and already part of your daily routine. At its heart, AI is about building systems that can mimic human thought processes to navigate complex, often unpredictable, scenarios.
Where automation follows a rigid, pre-programmed script, AI is built to learn, reason, and adapt on its own. It chews through vast datasets to spot patterns, forecast what might happen next, and improve its performance over time—all without a human needing to step in and rewrite its code for every new variable.
You're already using it, probably without thinking. When Netflix serves up a movie you actually want to watch, that's AI. When your phone unlocks with just a glance, that's AI-driven computer vision doing the work. Even when you use ChatGPT to brainstorm ideas, that’s a perfect example of interacting with AI.
The Power of Learning and Adapting
The engine driving most of what we call AI today is machine learning, a method where systems learn directly from data instead of being explicitly programmed for every task. This is the fundamental split between AI and automation. Automation is static; AI is dynamic.
Expert Opinion: As Dr. Fei-Fei Li, a leading AI researcher, puts it, "AI is not about building a smarter machine, it's about amplifying human intelligence." It's designed to perform tasks by observing patterns and past outcomes, much like we do.
This learning ability unlocks capabilities that are simply out of reach for rule-based automation. For instance, AI can:
- Analyze sentiment: It can read a customer review and grasp the nuance of language to figure out if the feedback is positive, negative, or mixed.
- Predict outcomes: By sifting through historical sales data and market indicators, it can forecast future trends with surprising accuracy.
- Recognize anomalies: In a sea of financial transactions, it can flag a single unusual activity that might indicate fraud.
Each of these examples requires judgment and context—something a basic 'if-this-then-that' command can't deliver. To dig deeper into how these models are built, our guide on deep learning vs machine learning is a great place to start. In essence, AI doesn't just perform a task; it works to understand it, making it the right tool for a world that never sits still.
A Detailed Comparison of Key Capabilities
To really get a feel for the difference between AI and automation, we need to move past the textbook definitions and see how they actually behave in the real world. Instead of a simple pro/con list, let's look at them through four critical lenses: their approach to decision-making, their ability to learn, the complexity of tasks they can handle, and the ultimate goal behind each technology. This will show you not just what they are, but how they operate differently.
Decision Making: Rules vs. Judgement
Automation is all about rules. Its decision-making process is straightforward and completely rigid, running on a strict "if this, then that" logic. Every single action is triggered by a pre-programmed condition, leaving zero room for interpretation. If condition 'A' happens, it executes action 'B'. No questions asked.
A perfect example is an automated payroll system. The rule is simple and clear: on the last Friday of the month, calculate hours worked and send the payment. It doesn't need to think; it just has to follow its commands with absolute precision.
Artificial Intelligence, on the other hand, makes decisions using data-driven judgment. It sifts through patterns, probabilities, and context to reach a conclusion, much like a person would. AI doesn't just follow a script—it actually evaluates the situation.
Think about an AI-powered fraud detection system at a credit card company. It doesn't rely on a simple rule like "block all purchases over $1,000." Instead, it analyzes thousands of data points in real-time—your location, purchase history, the merchant, even the time of day—to decide if a transaction looks fraudulent. Its decision is a calculated judgment, not a rigid command.
Learning Ability: Static vs. Dynamic
Automation is fundamentally static. A system set up to perform a task will do it the exact same way every time until a human developer steps in and manually updates its programming. It doesn't learn from its actions or adapt to new information on its own.
An automated email responder is a great illustration. If you program it to send a "Thank you for your message" reply, that's what it will send forever. It won’t notice that 70% of incoming emails are about shipping and proactively suggest adding tracking information to its response.
The core operational difference is that automation is programmed to do, while AI is designed to learn. Automation delivers consistency based on existing rules; AI delivers evolving performance based on new data.
AI is the complete opposite; it’s built to be dynamic. Through processes like machine learning, AI systems constantly analyze new data to refine their performance and get better over time. The more information an AI model is fed, the smarter and more accurate it becomes.
A streaming service's recommendation engine is a prime example. It doesn't just show you movies from a fixed list. It learns from every show you watch, rate, or even skip, constantly updating its understanding of your tastes to offer better suggestions. The AI literally evolves along with your viewing habits.
Now that we've covered the core operational differences, let's break down how these two technologies stack up across a few key business functions. This table provides a quick, at-a-glance comparison.
Comparing Automation and AI Across Key Functions
| Function | Automation | Artificial Intelligence (AI) |
|---|---|---|
| Task Execution | Follows a predefined, static set of rules and instructions. | Adapts its approach based on real-time data and past outcomes. |
| Data Handling | Processes structured data based on explicit commands (e.g., copy-paste). | Interprets both structured and unstructured data to find patterns and insights. |
| Problem Solving | Handles predictable, repetitive problems with a known solution. | Tackles complex, ambiguous problems that require cognitive judgment. |
| Learning & Improvement | Requires manual updates by a developer to change its behavior. | Learns independently from new data to improve its accuracy and performance. |
| Human Interaction | Executes tasks in the background with minimal direct interaction. | Can engage in natural language conversations, understand intent, and personalize responses. |
| Long-Term Goal | Efficiency: To execute simple tasks faster and more reliably than a human. | Effectiveness: To provide insights, make predictions, and solve complex problems. |
As you can see, automation is the reliable workhorse for consistent, high-volume tasks, while AI is the strategic thinker that tackles complexity and uncertainty.
Task Complexity and Ultimate Goal
Finally, let’s talk about what each technology is truly built for. Automation is designed to handle high-volume, low-complexity tasks. Its ultimate goal is efficiency—performing simple, repetitive jobs faster and more accurately than a human ever could.
This is where technologies like Robotic Process Automation (RPA) shine, delivering returns between 30% and 200% in the first year by taking over routine back-office work. By offloading these predictable tasks, automation can reduce operational costs by an average of 22%. You can find more insights on this in reports about AI in the industrial automation market.
In contrast, AI is built to handle complex, nuanced, and often unpredictable tasks that demand cognitive abilities. Its ultimate goal is effectiveness—solving tricky problems, generating valuable insights, and managing situations where the rules aren't black and white. It opens the door to things like predictive maintenance, real-time data analysis, and autonomous decision-making that provide a level of operational flexibility far beyond what traditional automation can offer.
When AI and Automation Work Together
It’s easy to get caught up in an "AI versus automation" debate, but the real magic happens when they team up. Their true potential isn’t unlocked in opposition but in partnership. This powerful combination is what we often call intelligent automation, where raw efficiency gets a major intelligence boost.
Think of it like this: automation is the tireless assembly line worker, performing the same task perfectly every time. AI is the experienced supervisor who watches the line, spots potential problems, and adjusts the process on the fly. Automation handles the high-volume, repetitive work with speed, while AI adds the ability to think, learn, and make smart decisions.
This partnership transforms a basic, rule-following process into a dynamic, self-improving system that can actually handle the messiness of the real world. It’s at this point that the conversation shifts from comparing AI and automation to celebrating their synergy.
Real-World Examples of Intelligent Automation
To bring this out of the clouds and into reality, let's look at how this plays out in actual business operations. This isn't science fiction; it's happening today.
- Smarter Customer Service: A support chatbot first uses automation to instantly pull up your order history. That's the straightforward, rule-based part. But then, AI kicks in. It analyzes your messages, understands the frustration in your tone, and empowers the bot to offer a personalized discount to turn a bad experience around.
- Intelligent Financial Processing: An automated system rips through thousands of invoices, extracting key data points—a classic automation job. Then, an AI model takes over, analyzing all that data to spot unusual spending patterns and flagging a transaction that looks suspiciously like fraud. The automation did the heavy lifting; the AI provided the crucial insight.
This blend is so effective because automation handles the 'what' (the task itself), while AI addresses the 'why' and the 'what if' (the context and the decision-making). You end up with a system that is both incredibly efficient and genuinely effective.
The Future is a Partnership
The most forward-thinking business solutions are heading in this direction. Instead of being forced to choose one or the other, companies are layering AI capabilities right on top of their existing automation platforms. This strategy allows them to tackle a much broader spectrum of challenges, from simple data entry to complex problem-solving, all within a single, integrated workflow.
This fusion is what elevates a business from just being productive to being truly intelligent and adaptive. If you're looking for more ways to make this happen, our guide on how AI and automation for businesses can drive growth offers more practical insights. Ultimately, the synergy between AI and automation isn’t just a passing trend; it’s the next logical step in building smarter, more resilient companies.
How to Choose the Right Tool for Your Task
Now that we've broken down both technologies, let's get practical. Choosing between AI and automation doesn't need to be a complex debate. In fact, it all comes down to a single, straightforward question about the job at hand: Does this task require learning and adaptation, or just rule-following?
If you're dealing with a repetitive process that follows a strict, unchanging set of instructions, automation is your best bet. It’s the perfect solution for tasks where consistency and speed are the most important outcomes.
But if the task involves sifting through unstructured data, making educated guesses about the future, or adapting to new information on the fly, you need the power of AI. It’s designed to handle complexity and navigate situations where the rules aren't so clear-cut.
Real-World Decision Making
Let’s put this into practice with a couple of common business scenarios.
-
Scenario 1: Automating Appointment Reminders
Imagine a small clinic trying to cut down on no-shows. The goal is to send a text reminder to every patient 24 hours before their appointment. This is a textbook case for automation. The rule is fixed and simple: "If an appointment is 24 hours away, send this exact message." No thinking required, just execution. -
Scenario 2: Predicting Campaign Success
Now, think about a marketing team trying to decide which ad campaign will deliver the best results. This involves digging into past performance data, analyzing current market trends, and understanding customer behavior to forecast outcomes. This is squarely a job for AI, as it demands pattern recognition and predictive insight, not just following a predefined script.
This simple decision tree can help you visualize the difference and guide your choice.
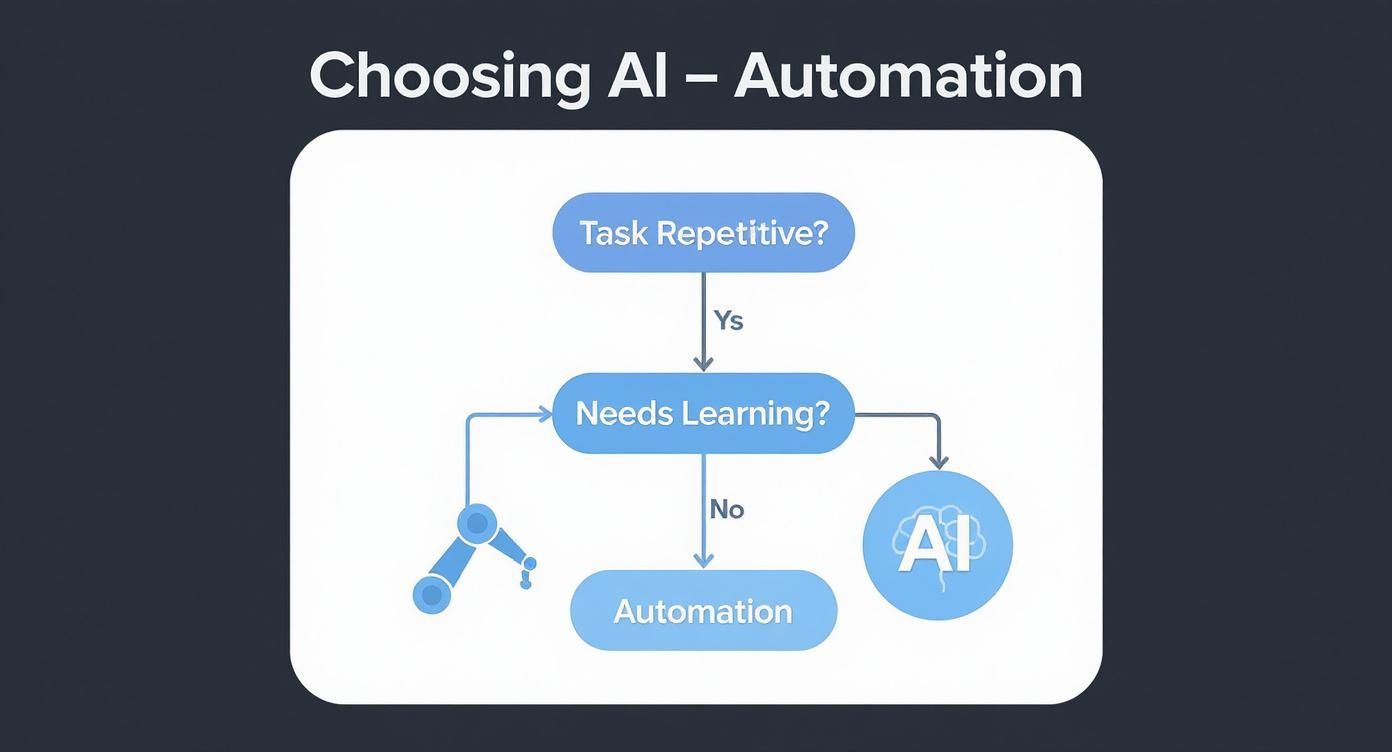
As the infographic highlights, the need for learning is the critical fork in the road. It's the key differentiator that should drive your decision.
The real question isn't which technology is "better." It's about which one truly fits your goal. Automation is for executing flawlessly; AI is for thinking strategically.
By starting with a clear understanding of your task, you can confidently pick the right tool to boost efficiency and solve your most pressing challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions
Alright, let's wrap up by tackling a few common questions that always seem to come up when people talk about AI versus automation. These answers should clear up any final confusion and give you a solid handle on both concepts.
Can You Have AI Without Automation?
You sure can. Think of an AI that exists purely to analyze data and offer insights, without actually taking any action on its own. It's more of a strategic advisor than an automated worker.
For instance, a medical AI could analyze thousands of patient scans to identify potential early signs of a disease. The AI's job is done once it flags a concerning image. It doesn't automatically schedule a follow-up or notify the patient; a doctor uses that insight to decide on the next steps. In this scenario, the AI is all about thinking, not doing.
Will AI Replace Automation?
That's highly unlikely. It’s much more accurate to say that AI will make automation smarter and more capable. There will always be a need for simple, rule-based automation to handle straightforward, repetitive tasks where you just need the same thing done perfectly every time.
Think of it this way: AI gives automation a brain. Basic automation is great at following orders, but AI allows it to start thinking for itself, handling tasks that have more nuance and variability.
Is All Automation a Form of AI?
Nope, and this is a big point of confusion for many. The vast majority of automation out there has nothing to do with AI. Standard automation is just a pre-programmed set of rules: if this happens, do that. It doesn't learn, adapt, or make any real decisions.
AI only enters the equation when the system needs to interpret data, learn from it, and make a judgment call. So, while an AI system automates a task (like thinking or predicting), most automation tools don't contain any AI at all. They are distinct technologies that just happen to work incredibly well together.
Ready to explore how AI can fit into your strategy? The team at YourAI2Day provides the latest news, tools, and insights to help you get started. Visit us to learn more and stay ahead of the curve.