Your Guide to AI Terms and Definitions
It's easy to feel like you're learning a whole new language when you first dip your toes into the world of Artificial Intelligence. All the technical ai terms and definitions can be a bit much. So, think of this guide as your personal translator, here to break down that complex jargon into simple, clear concepts. Our mission is to make AI understandable for everyone, whether you're just starting out or a business leader looking to get up to speed.
A Beginner's Guide to Understanding AI
Welcome! If you've ever found yourself lost in a sea of technical AI terms, you've come to the right place. We built this glossary for beginners, entrepreneurs, and any professional who wants to get a solid handle on the language of AI without needing a degree in computer science.
We're going to pull back the curtain on what AI really is and explain why knowing its core terms is so important today. This is your decoder ring for the future of technology, helping you speak the language of innovation with confidence. By using simple, real-world examples, we'll make AI feel a lot less intimidating and a lot more accessible.
Why AI Terminology Matters Now
Let's be clear: understanding AI isn't just for techies anymore. It’s becoming a crucial skill for navigating modern business and daily life. The global AI market is expanding at an incredible pace, with projections showing it could hit a staggering $3.5 trillion by 2033. That kind of growth isn't just a trend; it's a fundamental shift in how companies work and invest.
"To be successful with AI, you need a baseline understanding of the terminology. For AI to be successfully adopted across an organization, everyone needs a fundamental understanding of how it works."
—Lisa Lee, AI expert
Building Your Foundation
A great way to start is by seeing how different AI pieces fit together. For example, when you're learning the basic components of AI, it helps to look at something tangible like conversational AI and how it functions. Those chatbots you see on your favorite shopping sites are perfect, real-world applications of core AI principles at work.
This guide will walk you through the key areas to build a solid foundation of knowledge, including:
- Foundational Concepts: What are the real differences between AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning?
- How AI Learns: We'll look at the building blocks like algorithms, neural networks, and different training methods.
- Language and Generation: A dive into how AI processes human language and creates original text and images.
Ready to jump in? For a more thorough introduction, take a look at our complete guide on the basics of artificial intelligence for beginners.
Exploring Foundational AI Concepts
To really get a handle on the world of AI, you have to start with the big three: Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning. People often throw these terms around as if they mean the same thing, but they actually describe distinct layers of a much bigger field. A great way to think about it is like a set of Russian nesting dolls—each one fits neatly inside the next.
This diagram helps visualize how these core concepts relate. AI is the all-encompassing field, Machine Learning is a crucial subset of AI, and Deep Learning is an even more specialized technique within Machine Learning.
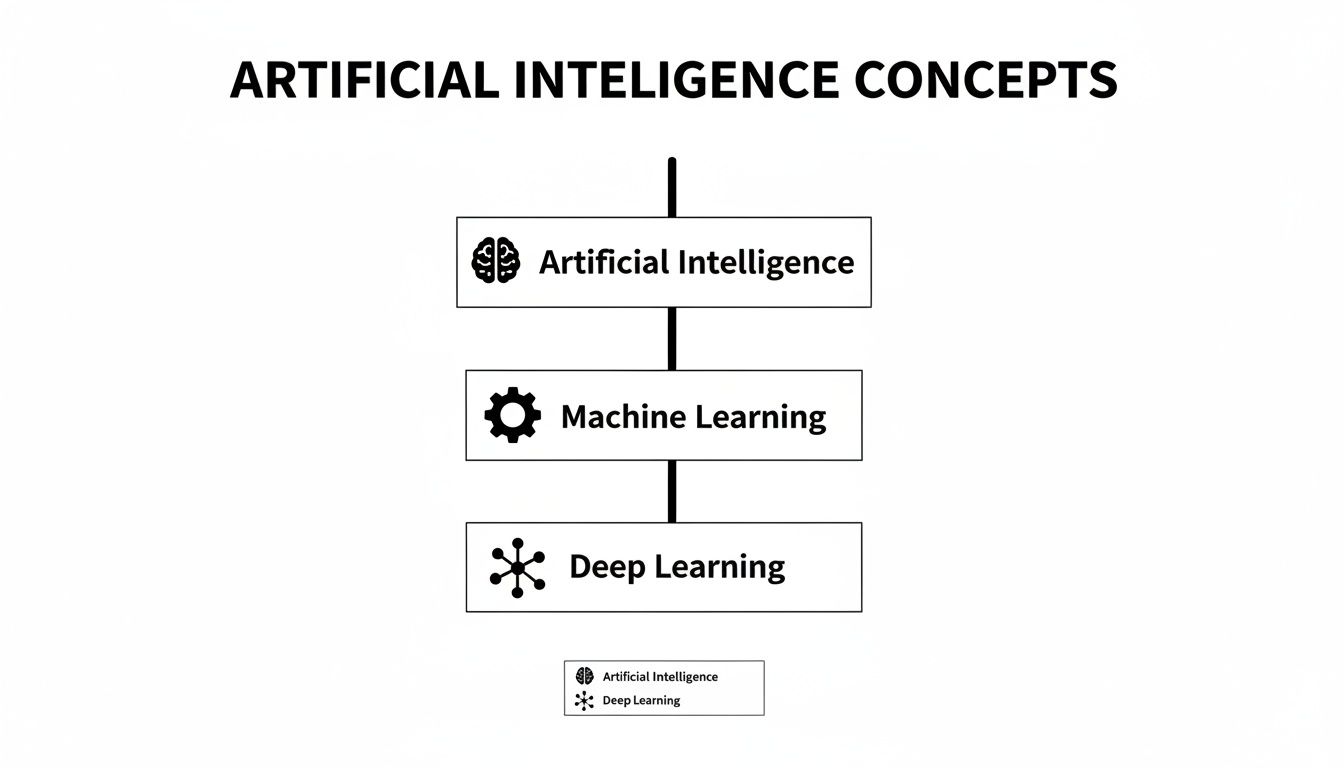
Keeping this hierarchy in mind is key. All deep learning is a form of machine learning, but not all machine learning is deep learning. Grasping this simple structure is the first real step toward building a solid AI vocabulary.
Artificial Intelligence: The Big Picture
At the very top of the hierarchy sits Artificial Intelligence (AI). This is the broadest term of the three, referring to any technology that lets a computer simulate human-like intelligence. It’s the entire discipline focused on building smart machines that can solve problems, reason through information, and understand language.
AI isn't a single thing; it’s a vast collection of different methods and tools working together. When you ask a smart speaker for the weather or use a navigation app to find the quickest route, you're tapping into a form of AI.
Practical Example: Think of a modern video game where an enemy character learns your play style. It stops falling for the same old tricks and adapts its strategy to beat you. That's a classic example of AI—it's not just following a script; it's actively adapting.
Machine Learning: The Engine of AI
Drilling down a level, we find Machine Learning (ML), a specific branch of AI. The key difference here is that instead of being programmed with explicit instructions for every task, an ML system is designed to learn from data. It finds patterns and makes decisions on its own, with very little human hand-holding.
At its core, ML gives AI the ability to get "smarter" over time. The process is fueled by algorithms that are fed huge datasets. The more information the system crunches, the more accurate it becomes at its job, whether that’s recognizing faces in photos or forecasting market trends.
"An AI model is a computer program that is built to work like a human brain. You give it some input (i.e. a prompt), it does some processing, and it generates a response. Like a child, a model ‘learns’ by being exposed to many examples."
- Lenny Rachitsky, AI Expert
Practical Example: Netflix’s recommendation engine is pure machine learning at work. It doesn't need a programmer to tell it you might like a certain show. It just analyzes your viewing history, your ratings, and the behavior of millions of other users to figure out what you'll probably want to watch next.
Deep Learning: The Advanced Brain
Finally, we get to Deep Learning (DL), a highly specialized subfield of machine learning. The magic behind deep learning is its use of artificial neural networks—complex structures inspired by the network of neurons in the human brain. These networks are built with many layers, which allows them to process information in a much more nuanced and sophisticated way.
This multi-layered approach is what allows deep learning to identify incredibly complex patterns in text, images, and audio. It's the powerhouse behind many of today's most impressive AI breakthroughs, from self-driving cars to cutting-edge medical diagnostics. A good way to see how these principles are applied is to compare the performance of different LLM models, which are built on deep learning foundations.
Practical Example: When you use an app like Google Translate to instantly translate spoken words, you're witnessing deep learning in real-time. The neural network has been trained on a massive library of audio clips and corresponding text, enabling it to grasp the subtle complexities of human speech and deliver an accurate translation.
Understanding How AI Models Learn
If you think of basic AI concepts as the "what," then the learning processes are definitely the "how." It's one thing to know AI can learn, but it's far more interesting to dig into the methods it uses to actually get smart. This is where we pop the hood and see how the engine of intelligence really works.
At the core of any AI is an algorithm. In the simplest terms, an algorithm is just a set of instructions a computer follows to solve a problem. It’s the recipe that tells the AI precisely what to do to transform raw data into a useful insight, a prediction, or a new decision.
These algorithms are the driving force behind the learning process, and they can get incredibly sophisticated. One of the most powerful structures for AI learning is the Neural Network.
The Brain Behind the Operation: Neural Networks
A Neural Network is a complex type of algorithm designed to mimic the structure of the human brain. It's built from interconnected nodes, often called "neurons," which are organized into layers. Each neuron processes a tiny piece of information before passing it along to the next layer.
This layered design allows the network to spot incredibly complex patterns in data—from identifying a specific face in a photo to understanding the subtle nuances of human language. This is the technology that powers many of the most advanced AI applications we use every day. If you want a deeper dive into the mechanics, our guide explains in detail how neural networks learn.
Now, let's break down the three main ways these models are taught to think.
Supervised Learning: Teaching with an Answer Key
Supervised Learning is a lot like studying with flashcards that have both the question and the answer. In this approach, we feed the AI a massive dataset where all the information has already been labeled with the correct outcomes. For instance, you could show it thousands of images, each one tagged as either "dog" or "cat."
The algorithm’s job is to figure out the patterns that link the input data (the image) to the correct label ("dog" or "cat"). Over time, it gets so good at this that it can identify those patterns all by itself on new, unseen data.
- Practical Example: Spam filtering is a classic business use case. Your email provider trained its model on millions of emails that were already marked as "spam" or "not spam." It learned the telltale signs of junk mail and now uses that knowledge to keep your inbox clean.
Unsupervised Learning: Finding Patterns on Its Own
With Unsupervised Learning, we take away the answer key. The AI gets a dataset with no labels and is simply asked to find interesting structures or patterns on its own. It's like giving someone a giant, mixed-up box of LEGOs and asking them to sort the bricks into logical groups without any instructions.
This technique is perfect for exploring huge datasets where you might not even know what you're looking for. It’s fantastic at uncovering hidden relationships and segmenting information.
- Practical Example: Companies often use unsupervised learning for customer segmentation. An e-commerce site can feed all its customer purchase data into a model, which might then automatically cluster customers into groups like "frequent high-spenders," "weekend shoppers," or "discount hunters"—all without being told what to look for.
Reinforcement Learning: Learning from Trial and Error
Reinforcement Learning is all about learning through consequences, much like how you might train a pet. When the pet does the right trick, it gets a treat (a reward). When it does the wrong thing, it doesn't.
In this model, an AI "agent" operates in an environment and gets positive or negative feedback for its actions. Through countless iterations of trial and error, it learns which sequence of actions leads to the biggest reward.
- Practical Example: A self-driving car uses reinforcement learning to get better at driving. It receives a reward for safe actions like staying in its lane and a penalty for unsafe ones like getting too close to another vehicle.
To make these distinctions clearer, here’s a quick-reference table that compares the three main machine learning methods.
Comparing Machine Learning Methods
| Learning Type | How It Learns | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Supervised | Learns from labeled data with correct answers provided. | Email spam detection, predicting house prices. |
| Unsupervised | Finds hidden patterns in unlabeled data on its own. | Customer segmentation, anomaly detection. |
| Reinforcement | Learns through trial-and-error, guided by rewards. | Game-playing bots, self-driving car navigation. |
Each of these methods has its own strengths and is chosen based on the problem you're trying to solve and the kind of data you have available.
Decoding Natural Language Processing
So, we've covered how AI models learn from data. Now, let's dive into one of the most fascinating applications of that learning: teaching computers to understand and speak our language. This branch of AI is all about closing the communication gap between humans and machines, making our technology feel less like a tool and more like a partner.
This is the world of Natural Language Processing (NLP). At its core, NLP is a field of AI that gives computers the ability to read, interpret, understand, and even generate human language. If you've ever asked Siri for the weather, used Google Translate, or had a chat with a bot on a website, you've seen NLP in action.
The growth here is staggering. The market for natural language processing, which is the engine behind conversational AI, hit $39.79 billion in 2024. It's expected to jump by another $161.7 billion by 2031. This explosive growth shows just how vital NLP has become, turning abstract ai terms and definitions into practical, valuable products. You can read the full research on AI market trends to get a better sense of the scale.
The Powerhouse Behind Conversation: Large Language Models
A huge leap forward in NLP has been the development of Large Language Models (LLMs). Think of these as incredibly sophisticated AI models that have been trained on mind-boggling amounts of text data—we're talking a significant chunk of the internet. By sifting through all this information, they learn the intricate patterns, grammar, context, and subtle nuances that make up human language.
This deep training enables them to do some amazing things, from drafting emails and summarizing dense reports to answering seriously complex questions. When you use tools like ChatGPT or Google's Gemini, you're interacting directly with a powerful LLM.
- Practical Example: You could tell an AI writing assistant, "Write a professional but friendly follow-up email to a potential client." The LLM taps into its vast understanding of language to craft an email that perfectly captures that specific tone and intent.
Chatbots: Your Everyday AI Companions
A Chatbot is a program built to simulate human conversation, either through text or voice. The first chatbots were pretty clunky and mostly relied on simple keywords. Today’s versions are a world apart, powered by advanced NLP and LLMs that allow for far more natural and genuinely helpful conversations.
"An AI model is a computer program that is built to work like a human brain. You give it some input (i.e. a prompt), it does some processing, and it generates a response."
—Lenny Rachitsky, AI Expert
These are the helpful assistants you encounter on shopping sites, banking apps, and customer support portals, ready to field your questions anytime, day or night.
Understanding the Vibe: Sentiment Analysis
Another powerful use of NLP is Sentiment Analysis. This is the process of using AI to figure out the emotional tone behind a piece of text. Is a customer's review positive, negative, or just neutral? What's the general mood on social media after a new product launch?
Sentiment analysis gives businesses a way to measure public opinion and customer satisfaction at a massive scale. It takes unstructured text from reviews, tweets, and surveys and turns it into real, actionable insights.
- Practical Example: A hotel chain might use sentiment analysis to automatically scan thousands of online reviews. The system could flag a pattern of negative comments about "slow check-in," giving management a heads-up to fix the issue before it damages their reputation.
Defining the World of Generative AI
It seems like you can't talk about AI these days without hearing the term Generative AI. This is the creative engine of artificial intelligence. Instead of just analyzing data that already exists, this type of AI actually produces something entirely new. We're talking about original text, images, music, and even computer code, all generated from scratch.
While most AI is busy classifying data or predicting outcomes, generative models are built to create. They digest massive amounts of information, learn the deep-seated patterns and structures within it, and then use that knowledge to produce brand-new content. This leap from analysis to creation is what makes the field so fascinating.

This ability to generate original content is opening up possibilities we could only dream of a few years ago. For a closer look at the mechanics behind it all, check out our guide that really dives into what Generative AI is and how it's shaking up industries.
The Art of the Ask: Prompt Engineering
Getting the most out of generative AI really comes down to Prompt Engineering. You can think of it as the art and science of writing the perfect instructions to get the exact result you're after. A prompt is just the input you give the model—it can be a simple question, a command, or a paragraph of detailed instructions.
How you phrase your prompt makes a world of difference. A vague request will almost always get you a generic, uninspired response. But a clear, detailed prompt gives the AI a solid roadmap to follow.
Practical Example:
- Weak Prompt: "Write about a dog."
- Strong Prompt: "Write a short, heartwarming story from the perspective of an old golden retriever who is spending a quiet afternoon napping in a sunny spot on the living room floor."
The second prompt provides specific context, a point of view, and a desired tone, guiding the AI to produce something far more compelling and focused.
From Words to Worlds: Image Generation
One of the most mind-blowing applications of generative AI is Image Generation. This is where you can describe virtually any scene with words, and an AI model will craft a completely unique image from your text. Tools like Midjourney and DALL-E have brought this incredible technology to the masses.
These models are trained on billions of image-and-text pairings, which teaches them the intricate relationships between words and visual ideas. They can generate anything from photorealistic portraits to surreal, abstract art.
Practical Example: You could give a model the prompt, "A vibrant, detailed painting of a futuristic city at sunset, with flying cars and glowing neon signs, in the style of Van Gogh." The AI will then generate a brand-new work of art that captures that exact vision.
When AI Gets It Wrong: Hallucinations
As impressive as these models are, they're far from perfect. A critical term you need to know is Hallucination. This happens when an AI model states something with complete confidence that is factually wrong, nonsensical, or just plain made up. The AI isn't "lying"—it has no intent—it's just generating a plausible-sounding string of words that isn't connected to reality.
"A common source of ‘hallucinations’ is when you don’t give the model the context it needs to answer your question."
—Lenny Rachitsky, AI Expert
Hallucinations occur because the AI is fundamentally a pattern-matching machine, not a fact-checking encyclopedia. It's built to predict the next most probable word in a sequence, and sometimes that path leads it straight into fiction. This is why you should always double-check any critical information an AI gives you, especially when it comes to facts, statistics, or historical events.
Essential AI Terms for Business
If you're in business, getting a handle on AI terminology isn't about impressing people in meetings. It's about recognizing real-world opportunities to grow your company and work more efficiently. The real skill is translating these techy concepts into strategic advantages. Knowing the right AI terms and definitions helps you talk about AI's value with confidence and pinpoint exactly where it can make a difference in your operations.
Let's unpack four of the most important concepts every business leader should get comfortable with.
Big Data: The Fuel for Business AI
You've probably heard the term Big Data. It refers to the enormous, messy datasets that are just too much for standard software to handle. Think about everything from your customer's purchase history and website clicks to social media chatter and supply chain logs. On its own, most of this data is just noise.
But when you feed it to an AI, it becomes one of your most powerful assets. AI algorithms are built to dig through this mountain of information, find patterns a human would miss, and pull out insights you can actually use to make better business decisions.
- Practical Application: Imagine a retail chain analyzing its sales data alongside local weather forecasts and social media trends. This allows them to accurately predict demand for certain products, keeping shelves stocked with what customers want and avoiding costly over-inventory.
Predictive Analytics: Getting a Glimpse of the Future
Predictive Analytics is a fascinating area of AI that uses historical data, statistical models, and machine learning to forecast what's likely to happen next. It’s not a crystal ball, but for strategic planning, it's pretty close.
This capability allows a business to shift from reacting to problems to proactively getting ahead of them. You can start anticipating what your customers will need or how the market will move before it even happens.
- Practical Application: A company with a subscription service, like a streaming platform, can use predictive analytics to spot customers who are showing signs of canceling. By flagging these at-risk accounts, the business can step in with a targeted discount or extra support to convince them to stick around.
Automation: Accomplishing More with Less
In the world of AI, Automation means using technology to handle tasks that used to require a person. This isn't just about assembly-line robots anymore. Modern AI-driven automation can manage complex processes, make informed decisions, and even run customer service chats.
Bringing automation into your workflow frees up your team from the grind of repetitive tasks. This lets them focus their energy on more creative and strategic work that really moves the needle. It's a direct route to improving productivity and trimming operational costs.
"A common misconception about AI and automation is that it will eliminate the need for human employees. The reality is that the most successful companies will learn to use automation to empower their workers to be more effective and efficient."
—Lisa Lee, AI Expert
AI Ethics: Earning Trust and Acting Responsibly
Finally, there's AI Ethics. This is a set of guiding principles to make sure AI systems are built and used in ways that are fair, transparent, and accountable. It tackles tough issues like data privacy, bias baked into algorithms, and the social impact of automation.
Building a solid ethical framework for your AI isn't just about checking a compliance box. It’s fundamental to earning and keeping the trust of your customers and partners. In the long run, businesses that take ethical AI seriously are the ones that will thrive.
AI Terms at a Glance
We've all been there—stuck in a meeting or reading an article when an unfamiliar AI term pops up. You need a quick, no-nonsense definition right now, not a lengthy explanation.
That’s exactly what this section is for. Think of it as your rapid-fire glossary for the 15 most common terms you'll encounter. I've boiled each one down to its core meaning so you can get the gist in seconds and get back to your conversation.
| Term | Quick Definition |
|---|---|
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | The big-picture field of making computers that can think, learn, and solve problems like humans. |
| Machine Learning (ML) | A branch of AI where systems learn from data to find patterns and make predictions without being explicitly programmed. |
| Deep Learning (DL) | An advanced type of machine learning that uses complex, multi-layered neural networks to tackle sophisticated tasks like image recognition. |
| Neural Network | A computing system modeled after the human brain's structure, designed to recognize complex relationships in data. |
| Supervised Learning | Training an AI with a "cheat sheet" — a dataset where all the data points are labeled with the correct answers. |
| Unsupervised Learning | Training an AI by letting it discover hidden patterns and structures in a dataset that has no labels. |
| Reinforcement Learning | Teaching an AI agent through trial and error, rewarding it for good decisions and penalizing it for bad ones. |
| Natural Language Processing (NLP) | The technology that allows computers to understand, interpret, and respond to human language, both written and spoken. |
| Large Language Model (LLM) | A massive deep learning model trained on huge amounts of text to generate conversation, write content, and answer questions. |
| Generative AI | A creative class of AI that can produce brand-new content, like images, music, text, or code. |
| Prompt Engineering | The skill of carefully crafting instructions (prompts) to guide a generative AI toward the most accurate and useful output. |
| Hallucination | When an AI confidently states something that is incorrect or completely made-up, presenting it as a fact. |
| Algorithm | A set of rules or instructions that a computer follows to perform a specific task or solve a problem. |
| Big Data | Extremely large and complex datasets that traditional data-processing software can't manage, often used to train powerful AI models. |
| Computer Vision | A field of AI that trains computers to "see" and interpret visual information from the world, like images and videos. |
Hopefully, this table helps clear things up in a pinch. If any of these definitions pique your interest and you want to explore the details, just click the term to jump back to its full explanation in the main glossary.
Frequently Asked Questions About AI Terms
Once you start getting familiar with the basic AI terms and definitions, you'll inevitably run into some practical questions. This section dives into the common queries that pop up as people begin to apply their knowledge, offering clear advice to help you move forward confidently.
What's the Real Difference Between AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning?
It's helpful to think of them like a set of Russian nesting dolls, with each one fitting inside the other.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the biggest doll—the broad, all-encompassing idea of machines that can perform tasks that would normally require human intelligence.
Machine Learning (ML) is the next doll down. It's a specific subset of AI where systems learn directly from data to make predictions or decisions, instead of being explicitly programmed for every possible scenario.
Deep Learning (DL) is the smallest doll, a specialized part of machine learning. It uses complex, multi-layered neural networks (inspired by the human brain) to tackle highly sophisticated problems, like image recognition or generating human-like text.
So, all Deep Learning is a type of Machine Learning, and all Machine Learning is a type of AI. Each is just a more focused version of the last.
Can I Really Use AI in My Small Business Without a Tech Team?
Absolutely. The barrier to entry has dropped dramatically. You don't need a team of data scientists or coders to start making AI work for you.
Today, there's a whole ecosystem of user-friendly AI platforms designed for people without a technical background. These tools can handle everything from drafting social media content and designing marketing visuals to setting up a customer service chatbot. The trick is to identify a specific business problem you need to solve first, then look for a ready-made tool that fits the bill. Don't feel like you have to build something from the ground up.
For AI to be successfully adopted across an organization, everyone needs a fundamental understanding of how it works.
— Lisa Lee, AI Expert
Which AI Terms Should I Know for a Non-Technical Job Interview?
For a non-technical role, interviewers want to see that you grasp the business value of AI, not that you can write the code. Focus on being able to discuss a few core concepts in plain language.
You should be comfortable explaining:
- AI and Machine Learning
- Generative AI
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Automation
The key is to connect each term to a simple, real-world example. Mentioning how Netflix uses machine learning for its recommendation engine shows you understand how the technology translates into a better customer experience and drives business results. That's what really matters.
At YourAI2Day, our mission is to demystify artificial intelligence for everyone. We offer the latest news, detailed guides, and practical tools to keep you informed and ahead of the curve. Continue exploring with us at https://www.yourai2day.com.







