What Is Training Data and Why Is It AI’s Secret Ingredient?
Ever wondered how your favorite AI tool seems to read your mind, suggesting the perfect song or finishing your sentences? It’s not magic—it's training data. Think of it as the collection of textbooks, examples, and experiences an AI studies to learn a new skill.
This is the raw information we feed to an algorithm so it can learn to do something useful, like translating languages or generating images.
The Secret Ingredient Behind Every Smart AI
Imagine trying to teach a friend to bake a cake for the very first time. You wouldn't just hand them flour and eggs and wish them luck. You'd give them a recipe to follow. That recipe is the training data.
The recipe lists the ingredients and steps (inputs) and includes a picture of the finished, delicious cake (the desired output). By studying thousands of these recipes, your friend would start to recognize patterns—which flavors work well together, the right oven temperature for different cakes, and how to get the frosting just right.
An AI learns in a very similar way. It’s not born smart; it's made smart through training. The AI sifts through enormous datasets to connect the dots and understand the relationships between different pieces of information.
Expert Opinion: "People often get caught up in the complexity of the AI model itself, but the real magic is in the data. At its core, an AI is a brilliant student, and training data is its entire library of textbooks. The quality and diversity of those books directly determine how capable and intelligent the student becomes."
For instance, an AI built to catch spam emails is fed millions of messages already marked as "spam" or "not spam." By analyzing these labeled examples, it learns to spot the tell-tale signs of junk mail—like shady links, urgent language, or odd formatting. The more examples it sees, the sharper its skills become.
This learning process is the engine behind almost every AI application you use daily:
- Virtual Assistants: Your Alexa or Siri learns to understand your commands by training on huge libraries of human speech recordings and their corresponding text.
- Recommendation Engines: Netflix and Spotify study your viewing and listening history to predict what you’ll want to binge next.
- Image Generators: Tools like Midjourney analyze millions of images paired with text descriptions to learn how to create stunning visuals from a simple prompt.
Ultimately, training data is the fuel that powers the AI engine. Without it, the most sophisticated algorithm is just an empty shell, unable to learn, adapt, or perform any meaningful task.
To quickly grasp how this works, let's compare it to something we're all familiar with: how we learn.
Training Data at a Glance
| Concept | AI Training Data Analogy | Human Learning Comparison |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Input | The ingredients, recipe steps, and photos in a cookbook. | Reading textbooks, listening to a lecture, or watching a tutorial. |
| Learning Process | The AI algorithm analyzes thousands of recipes to find patterns. | Studying for an exam by reviewing notes and flashcards repeatedly. |
| Gaining Expertise | The AI becomes an expert at a specific task, like baking cakes. | A student becomes skilled in a specific subject, like math or history. |
| Final Outcome | A perfectly baked cake, created by following learned patterns. | Acing the final exam by applying the knowledge gained from studying. |
This comparison highlights that, at its heart, training an AI isn't all that different from teaching a person. The quality and volume of the "study materials" are what make all the difference. For a deeper dive into the foundational concepts, types, and importance of AI training data, a comprehensive guide can further illuminate its role in modern machine learning.
Getting to Know the Different Flavors of Training Data
Think of an AI model like a chef. Just as a chef needs different ingredients for a gourmet meal versus a simple soup, an AI requires specific "flavors" of training data depending on the job at hand. Not all data is the same, and understanding these differences is the first step to really getting how AI models learn.
Let's break down the main categories you'll run into.
This simple diagram shows how the AI model, the training data, and the final decision are all connected in a learning loop.
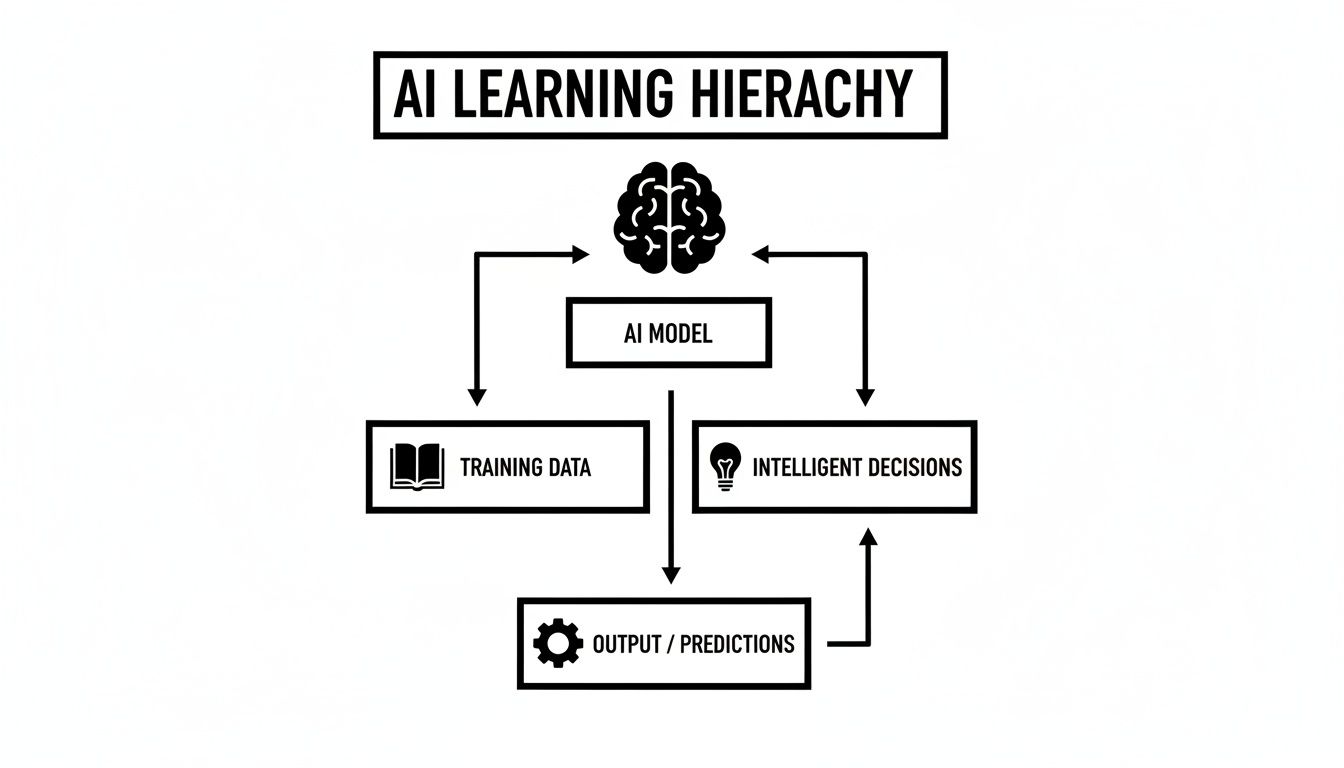
As you can see, high-quality training data is the essential bridge. It’s the textbook from which the AI "brain" studies to start making smart choices on its own.
Structured vs. Unstructured Data
The first big split in the data world is all about organization. Is your data in a neat filing cabinet or scattered across a messy whiteboard?
Structured data is the tidy stuff. It's organized neatly into a fixed format, like a spreadsheet or a database. Every piece of information has a clear home and a label, which makes it incredibly easy for a computer to read and process.
- Practical Example: Think of a customer sales database. You have clean columns for
Name,Purchase Date,Product ID, andPrice. An AI can slice and dice this kind of data effortlessly to spot trends, like figuring out your most popular product in a specific city.
Unstructured data is the complete opposite. It's a free-for-all of information with no predefined model or organization. In fact, this type of data makes up over 80% of all enterprise data today.
- Practical Example: Social media posts, emails, videos, and audio files are all classic examples of unstructured data. An AI has to work much harder to pull meaning from this "mess," like figuring out customer sentiment from thousands of tweets about your latest product launch.
Labeled vs. Unlabeled Data
Next, we get to labeling, which is like adding sticky notes to your data to tell the AI what it's looking at. This is often the most important part of teaching an AI a specific skill.
Labeled data has been tagged or annotated with useful information to provide context. It’s the equivalent of giving an AI flashcards—a picture on one side and the answer on the other. This process, usually done by humans, tells the model exactly what to look for.
- Practical Example: A collection of animal photos where each image is tagged 'cat', 'dog', or 'bird' is labeled data. It's absolutely vital for training an AI to recognize specific things, like a self-checkout machine identifying an apple versus an orange.
Unlabeled data is just raw information with no tags or explanations. Here, the AI gets a massive pile of data and has to find patterns and relationships all on its own, without an answer key.
- Practical Example: Imagine you want to group your customers into different market segments based on their browsing habits. With unlabeled data, the AI itself identifies clusters of similar users—a powerful way to discover insights you didn't even know to look for.
Expert Take: "The choice between labeled and unlabeled data really depends on your goal. For a specific task like identifying spam emails, you need meticulously labeled data. But if you want to discover hidden patterns in customer behavior, unlabeled data lets the AI explore and find connections you might have missed. It's about choosing the right tool for the job."
The New Kid on the Block: Synthetic Data
What happens when the data you need is too rare, too sensitive, or just too expensive to collect? That's where synthetic data steps in. This is data that's been artificially generated by algorithms to mimic the characteristics of real-world information.
It’s an amazing solution when privacy is a major concern, like in healthcare, or for creating unusual scenarios an AI needs to learn from, like a self-driving car encountering a rare obstacle on the road. If this has piqued your interest, you can dive deeper into what is synthetic data in AI in our detailed guide.
Demand for all these data types is exploding. The market for AI training datasets was valued at USD 1.9 billion in 2022, shot up to USD 2.7 billion in 2024, and is projected to reach an incredible USD 11.7 billion by 2032. This growth is a clear sign of just how fundamental good data has become.
How Raw Data Becomes AI Gold
Raw data, in its natural state, is rarely ready for an AI model to learn from. It’s often a jumbled mess—incomplete, full of errors, and packed with irrelevant noise. Think of it like a garden where beautiful flowers are being choked out by weeds.
This section will walk you through the essential process of transforming that chaotic information into a high-quality, structured asset that an AI can actually use.
Think of it like a master chef prepping ingredients for a signature dish. They don't just toss everything into a pot. They wash, chop, measure, and organize with precision. The same level of care is non-negotiable for creating effective training data. In fact, this careful preparation is arguably more important than the AI algorithm itself.

From Collection to Cleaning
The journey from raw information to a polished dataset starts with data collection and sourcing. This could mean anything from gathering customer feedback through surveys, scraping public images from the web, or tapping into massive databases of financial transactions. Where and how you get your data directly impacts its initial quality.
Once you have the raw materials, the real work begins with data cleaning. This step is exactly like meticulously weeding that garden. It’s all about spotting and fixing the countless problems that could confuse your AI model.
Common cleaning tasks include:
- Removing Duplicates: Identical entries can give certain examples unfair weight during training, so they need to go.
- Fixing Errors: This means correcting typos, fixing structural mistakes, or updating inaccurate information.
- Handling Missing Values: You have to decide what to do with the gaps—either fill them in with estimated values or remove the incomplete records altogether.
- Filtering Out Noise: This involves getting rid of any irrelevant data that doesn’t contribute to the learning goal.
This isn't just a simple chore; it's a critical quality control step. For a much deeper dive into this stage, check out our guide on data preparation for machine learning.
Labeling and Augmentation: The Final Polish
After cleaning, we move on to what is often the most labor-intensive step: data labeling and annotation. This is where we add context to the data, essentially teaching the AI what it's supposed to be looking for. It's how raw information gets its meaning.
Imagine you're training an AI for a self-driving car. You'd feed it thousands of road images, and human annotators would have to meticulously draw boxes around every single car, pedestrian, and traffic sign, labeling each one. This labeled data provides the "ground truth" the AI uses to learn how to see and interpret the world.
But what happens if you don't have enough data? That’s where data augmentation comes in. It’s a clever technique for artificially expanding your dataset by taking existing data and creating slightly modified copies.
Expert Insight: "The quality of a final AI model is a direct reflection of the care taken during data preparation. You can't build a skyscraper on a shaky foundation, and you can't build a brilliant AI on messy, poorly labeled data. The best teams spend most of their time here, not on the algorithm."
For instance, to make an image recognition model more robust against real-world scenarios, you could:
- Rotate an Image: Slightly turning a picture of a cat helps the AI learn to recognize it from different angles.
- Adjust Brightness: Changing the lighting conditions prepares the model for images taken at noon versus dusk.
- Flip Horizontally: Mirroring the image instantly creates a new, valid training example.
This process gives the AI more "experience" without the time and expense of collecting thousands of new images. Ultimately, this makes the model smarter, more accurate, and far more reliable when it encounters situations it hasn't seen before.
Real-World Examples of Training Data in Action
It’s easy to get lost in the technical definitions, but the real magic of training data comes to life when you see what it powers. You might be surprised to learn you're interacting with sophisticated AI models, and the data they were trained on, dozens of times a day. It’s so woven into our daily lives that we barely even notice it.
Let's pull back the curtain on a few familiar technologies and see how different kinds of training data make them work so well.

Your Personalized Entertainment Butler
Ever get that feeling that Netflix or Spotify just gets you? That uncanny ability to recommend your next favorite show or song isn't a coincidence—it's a recommendation engine trained on mountains of user data.
- AI Application: Content Recommendation (e.g., Netflix, Spotify, YouTube)
- Training Data Used: This is a rich mix of structured and unstructured data. Your viewing history, the ratings you give, and your preferred genres are all neat, structured data points. But so are your unstructured behaviors, like what you search for, how long you hover over a movie poster, and even the time of day you typically watch.
- How It Works: The AI model sifts through the collective behavior of millions of users, hunting for patterns. It learns that people who enjoyed "Stranger Things" also tend to get hooked on "The Witcher." This massive, constantly updating dataset allows the algorithm to make spookily accurate predictions about what you’ll want to watch or listen to next.
Keeping Your Inbox Squeaky Clean
One of the oldest and still most effective uses of machine learning is the humble spam filter. Without it, our inboxes would be an absolute disaster zone.
- AI Application: Email Spam and Phishing Detection
- Training Data Used: The model is built on a massive dataset of labeled text data. We’re talking about millions of emails that have been tagged by users or automated systems as either "spam" or "not spam."
- How It Works: The AI chews through this labeled data to learn the tell-tale signs of junk mail. It quickly picks up on common red flags like sketchy links, words in ALL CAPS, and urgent-sounding phrases like "action required." Every single time you mark an email as spam, you're contributing a tiny piece of training data that helps the model get just a little bit smarter.
Expert Opinion: "The most powerful AI isn't always the one with the most complex algorithm. More often than not, it's the one trained on the highest-quality, most relevant data. Everyday examples like spam filters and recommendation engines prove that a deep, data-driven understanding of the problem is the real key to success."
The Voice Assistants That Actually Understand You
When you ask Siri about the weather or tell Alexa to play a song, you're tapping into a very complex natural language processing (NLP) model. For these assistants to work, they need to be trained on enormous and incredibly diverse datasets.
- AI Application: Virtual Assistants (e.g., Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant)
- Training Data Used: The main ingredient here is countless hours of human speech recordings (audio data). This unstructured audio is then carefully paired with its text transcription, creating a massive labeled dataset. To be truly effective, this data has to capture a huge variety of accents, dialects, background noises, and speaking styles.
- How It Works: By analyzing all that audio and text, the AI learns to map specific sounds (phonemes) to words and phrases. This is what allows it to accurately translate your spoken commands into text the system can understand and act on. To get a better sense of how this works at scale, it's worth exploring the data-hungry nature of Large Language Models (LLMs).
AI as a Doctor’s Second Pair of Eyes
In the high-stakes world of healthcare, AI is making a real difference by helping doctors spot diseases earlier and more accurately than ever before.
- AI Application: Medical Image Analysis
- Training Data Used: These models are trained on vast libraries of labeled image data. Imagine a dataset with thousands of X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs. Each image has been meticulously annotated by expert radiologists who highlight tiny areas showing signs of tumors, fractures, or other health issues.
- How It Works: After studying this expert-labeled data, the AI learns to recognize subtle patterns in medical images that might be missed by the human eye. It doesn't replace the doctor; instead, it acts as a powerful diagnostic assistant, flagging suspicious areas for a human expert to review. This is a perfect example of why high-quality, expert-labeled data is absolutely critical when accuracy can be a matter of life and death.
Training Data Use Cases Across Industries
The examples above are just the tip of the iceberg. Nearly every industry is finding ways to put AI to work, and each application is powered by its own unique flavor of training data.
The table below shows how different sectors are using specific data types to solve real-world problems.
| Industry | AI Application | Type of Training Data Used | Real-World Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retail & E-commerce | Dynamic Pricing | Structured data (sales history, competitor prices, demand signals) | Optimized pricing that maximizes revenue and clears inventory |
| Finance | Fraud Detection | Labeled transactional data (flagged as "fraudulent" or "legitimate") | Real-time identification of suspicious transactions, saving billions annually |
| Automotive | Self-Driving Cars | Labeled image/video data from sensors (pedestrians, signs, other cars) | Enhanced vehicle autonomy and improved road safety |
| Agriculture | Crop Disease Detection | Labeled images of healthy and diseased plants | Early intervention to protect crop yields and reduce pesticide use |
| Customer Service | Chatbot Automation | Labeled text data (customer queries paired with correct answers) | 24/7 support for common questions, freeing up human agents for complex issues |
As you can see, the core principle is the same everywhere: find the right data, prepare it correctly, and use it to teach an AI model how to perform a specific, valuable task.
The Big Three Hurdles: Quality, Bias, and Privacy
Assembling a great training dataset isn't just about hoarding massive amounts of information. It's a delicate art, filled with some serious technical and ethical landmines that developers have to navigate carefully. Getting this part wrong doesn't just result in a clumsy AI—it can have real, damaging consequences out in the world.
The most immediate challenge is simply maintaining data quality. You’ve probably heard the old programmer's mantra, "garbage in, garbage out." Well, for AI, this isn't just a saying; it's the absolute law of the land. If your training data is riddled with errors, irrelevant junk, or inconsistencies, the AI model will learn those exact same flaws.
Think about it this way: trying to teach an AI to spot ripe strawberries using a dataset where half the pictures are actually red apples. The model would end up completely confused, its performance would be terrible, and you'd never be able to trust its judgment. This is precisely why meticulous data cleaning and preparation are non-negotiable.
The Critical Fight Against AI Bias
Even more insidious than simple errors is the problem of AI bias. This crops up when your training data doesn't paint an accurate picture of the real world, causing the model to develop unfair preferences that can lead to some seriously discriminatory outcomes.
For instance, imagine a company trying to build a hiring AI. If they train it only on résumés from their most successful past employees—who just so happen to be mostly men—the AI will learn to associate "successful" with male candidates. It might start penalizing résumés with female-sounding names or experience from women's colleges, not because those candidates are any less qualified, but because the data it learned from was already skewed.
Bias can sneak into your data from a few common sources:
- Historical Bias: This is when the data reflects old, ingrained societal prejudices. An AI trained on historical loan data might unfairly deny applications from certain neighborhoods simply because of discriminatory lending practices from the past.
- Sampling Bias: This happens when the data isn't collected randomly, so one group is overrepresented. A facial recognition system trained mostly on images of people with light skin will inevitably struggle and be less accurate when identifying individuals with darker skin tones.
- Measurement Bias: This occurs when data is collected or labeled inconsistently for different groups, warping the results.
Expert Insight: "Bias in AI is not a technical glitch; it's a reflection of human blind spots embedded in the data we feed it. The responsibility isn't just to build a functional model, but to build one that is fundamentally fair and equitable for everyone it impacts."
The fallout from biased AI is a huge deal, which is why developers have to be proactive about building datasets that are diverse and truly representative. To dig deeper into this topic, check out our complete guide on what is AI bias.
Protecting Privacy in a Data-Hungry World
Last but certainly not least is the enormous challenge of privacy. Let's face it, some of the most powerful training data is deeply personal—think medical records, financial histories, or even private conversations you've had with a smart speaker. Using this kind of information irresponsibly isn't just unethical; it can be downright illegal.
Regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) have put strict guardrails around how companies can collect, store, and use personal data. To stay on the right side of the law, organizations have to put data protection first.
This often means using techniques like anonymization, which involves stripping out personal identifiers like names and addresses from the data. Another method is data aggregation, where individual data points are bundled into larger groups to obscure personal details. Ultimately, building trust with users means being transparent about what data is being collected and how it's being used to make AI systems better for everyone.
The need for responsible data practices is only growing. As of 2026, 34% of companies are already using AI in their training programs, with another 32% aiming to do so within two years. Those who have adopted AI-driven training report a 20% boost in productivity, and over 80% of firms plan to use AI-enabled learning tools by 2027. You can explore more on AI's impact on training at VirtualSpeech.com.
So, What's Next on Your AI Journey?
You’ve made it this far, which means you now have a solid foundation in what training data is and why it's the absolute lifeblood of any AI system. This understanding is what separates casual observers from those who can actually build, critique, or invest in AI with confidence.
The world of AI is moving incredibly fast. To put it in perspective, the global machine learning market is expected to rocket from USD 91.31 billion in 2025 to a staggering USD 1.88 trillion by 2035. That astronomical growth isn't just about fancy algorithms; it's fueled almost entirely by the insatiable need for better, cleaner, and more relevant training data. If you're curious, you can dig deeper into these machine learning market trends.
So, how do you take this newfound knowledge and put it into action? It all depends on your goals.
For the Curious AI Enthusiast
If you're fascinated by AI and want to see how the sausage is made, the best thing you can do is dive into some real data. Theory is great, but getting your hands dirty is where the real learning happens.
Explore Public Datasets: Head over to platforms like Kaggle or Google's Dataset Search. These sites are treasure troves of datasets that have been used to train actual AI models. You’ll find everything from pictures of cats to complex financial data.
Analyze and Visualize: You don't need to be a data scientist to start. Just download a dataset and poke around. See how it’s organized, what the labels look like, and try to imagine the kind of model it could build.
For the Aspiring Business Builder
If your goal is to launch an AI-powered product or service, remember this: your data strategy is your business strategy. A brilliant idea is worthless without the high-quality data needed to bring it to life.
Expert Takeaway: Forget about the algorithm for a minute. The first question you need to answer is, "What's my data plan?" A crystal-clear strategy for how you'll get, clean, and label high-quality, relevant data is the single most important factor for success.
Here’s a quick checklist to get you started on the right foot:
Define Your Problem: What specific, painful problem will your AI solve? Your answer dictates exactly what kind of data you need to hunt down.
Source Your Data: How will you get it? You could collect it yourself, buy it from a vendor, or start with public datasets. Each path has its own trade-offs.
Plan for Quality and Ethics: Don't treat this as an afterthought. From day one, you need a plan for cleaning your data, checking for hidden biases, and ensuring you comply with all privacy laws.
Find the Right Tools: The process of preparing data is tough. Look into platforms like Scale AI or Appen that can help you manage the most time-consuming parts, like data labeling and quality control.
Frequently Asked Questions About Training Data
Jumping into AI always sparks a ton of questions, especially about the fuel that makes it all work: training data. Let's tackle some of the most common ones I hear all the time with some straightforward answers.
How Much Training Data Does an AI Need?
This is the classic "how long is a piece of string?" question. The honest answer is, it depends entirely on the job you're asking the AI to do.
A fairly simple model, say one that sorts customer feedback into "happy" or "unhappy" buckets, might get the hang of it with just a few thousand examples. But for something vastly more complex, like the models behind ChatGPT, you need a dataset that mirrors the scale of the public internet—we're talking trillions of words—to grasp the subtle nuances of human language.
It really boils down to three things:
- Task Complexity: The tougher the problem, the more examples the AI needs to see. Identifying a cat in a photo is one thing; diagnosing a rare disease from a medical scan is another entirely.
- Model Size: Big, powerful models are data-hungry. They have more parameters to tune, and that requires a massive amount of information to get right.
- Data Quality: This is the big one. High-quality, clean, and accurately labeled data is incredibly powerful. You can often get far better results with a smaller, pristine dataset than a massive, messy one.
Where Does All This Data Come From?
Training data comes from everywhere. Sometimes it's purpose-built, with armies of human annotators painstakingly labeling every single pixel in an image to teach a self-driving car what a pedestrian looks like. Other times, it's scooped up from enormous public sources.
You'll typically see data coming from:
- Public Datasets: Goldmines like Kaggle and Google Dataset Search are filled with thousands of free datasets that researchers and developers use every day.
- Web Scraping: It's common for companies to gather publicly available info from the web, like pulling product reviews from e-commerce sites or articles from news outlets.
- Internal Data: Businesses often sit on a treasure trove of their own data. Things like sales history, customer support chats, or operational logs are perfect for training AI models tailored to their specific needs.
Can an AI Be Trained on Bad Data?
Oh, absolutely. And the outcome is always a mess. It's the perfect illustration of the age-old computing principle: "garbage in, garbage out." If you train an AI on data that's wrong, biased, or just plain incomplete, the model will faithfully learn and replicate every single one of those flaws.
Think about it: an AI trained on skewed historical data might end up making biased hiring recommendations. A medical AI that only learned from one demographic might fail to spot diseases in other patient groups. This is precisely why cleaning and preparing the data is probably the most critical part of the entire AI development cycle.
Is More Data Always Better?
Not at all. It's a common misconception. While having more data can certainly help, data quality and relevance will always beat sheer quantity.
A smaller, meticulously curated dataset will almost always build a better AI than a gigantic, sloppy one. In fact, some fascinating research has shown that models trained on just a few hundred hand-picked, highly informative examples can outperform models trained on 100,000 generic ones. The future isn't just about big data; it's about smart data. I'd take 1,000 perfect examples over a million mediocre ones any day of the week.
At YourAI2Day, our mission is to demystify the concepts and tools that are changing our world. Whether we're diving deep into AI ethics or reviewing the latest software, we aim to deliver clear, practical insights for everyone. You can explore more of our work on our website.







