What Is Synthetic Data in AI? A Friendly Guide for Beginners
Ever wonder how an AI learns to drive a car through a blizzard or spot a rare, hard-to-find disease from a medical scan? The short answer is data. Mountains and mountains of it.
But what happens when you can't get enough real-world data, or the data you need is too sensitive, expensive, or just plain dangerous to collect? This is where synthetic data comes in to save the day. It's essentially artificially generated information that a computer creates to perfectly mimic the statistical patterns of real-world data, but without being a direct copy.
Think of it as a digital stunt double for the real thing.
What Is Synthetic Data, Really?
Imagine a chef creating a plant-based burger that has the exact texture, sizzle, and flavor profile of real beef. It looks and feels real, and you can cook with it just the same, but it was engineered in a lab without ever involving an actual cow. That’s precisely what synthetic data is for the world of AI. It’s a high-quality, realistic alternative when real-world data just isn’t an option.
This isn't just a neat trick; it's becoming an essential tool. For instance, a hospital can generate millions of synthetic patient records to train a diagnostic AI. These records perfectly mirror the patterns of real diseases—how they progress, who they affect, and how they show up in tests—but contain zero actual patient information. This completely sidesteps privacy concerns, allowing for incredible medical advancements without ever compromising sensitive health data.
The Rise of Artificial Data
The demand for this technology is absolutely exploding. The global market for synthetic data generation is projected to jump from USD 584 million in 2025 to a staggering USD 5,515 million by 2034. This kind of growth tells you just how critical this approach has become for building smarter, safer, and more ethical AI systems across all industries. You can read more about these market trends and what they mean for the future of AI.
To get a clearer picture of why this shift is happening, let's put real and synthetic data side-by-side.
Expert Opinion: As AI expert Andrew Ng puts it, "The trend in AI is shifting from big data to good data." Synthetic data is a powerful way to create that 'good data'—data that is clean, balanced, and perfectly tailored for the task at hand. When done right, it can be just as effective—or even better—for training a machine learning model.
Real Data vs Synthetic Data: At a Glance
Here’s a quick comparison to highlight the key differences between real-world information and its artificially generated counterpart for AI development.
| Attribute | Real Data | Synthetic Data |
|---|---|---|
| Privacy | High risk; contains sensitive information. | Zero risk; completely anonymous. |
| Cost | Very expensive to collect and label. | Cheaper and faster to produce. |
| Accessibility | Often scarce or legally restricted. | Can be generated on-demand. |
| Bias | Can contain and amplify societal biases. | Can be controlled to create fair data. |
As you can see, synthetic data offers a powerful solution to some of the biggest bottlenecks and risks that have traditionally held back AI development. It's a game-changer for anyone looking to scale their AI initiatives responsibly and efficiently.
How AI Creates Its Own Training Data
So, where does this "digital stunt double" data actually come from? It’s not magic, but a clever process where an AI essentially helps create its own study materials. Instead of just photocopying real data, the AI learns the fundamental rules and patterns of a dataset so deeply that it can generate brand-new, completely original examples that follow those same rules.
At its core, the process is pretty straightforward. You start by training an AI model on a real-world dataset. The model’s goal is to understand the statistical properties and characteristics of that data. Once it's learned enough, it can start producing new data points that look and feel just like the real thing, but are entirely artificial.
This simple three-step flow is a great way to visualize it.
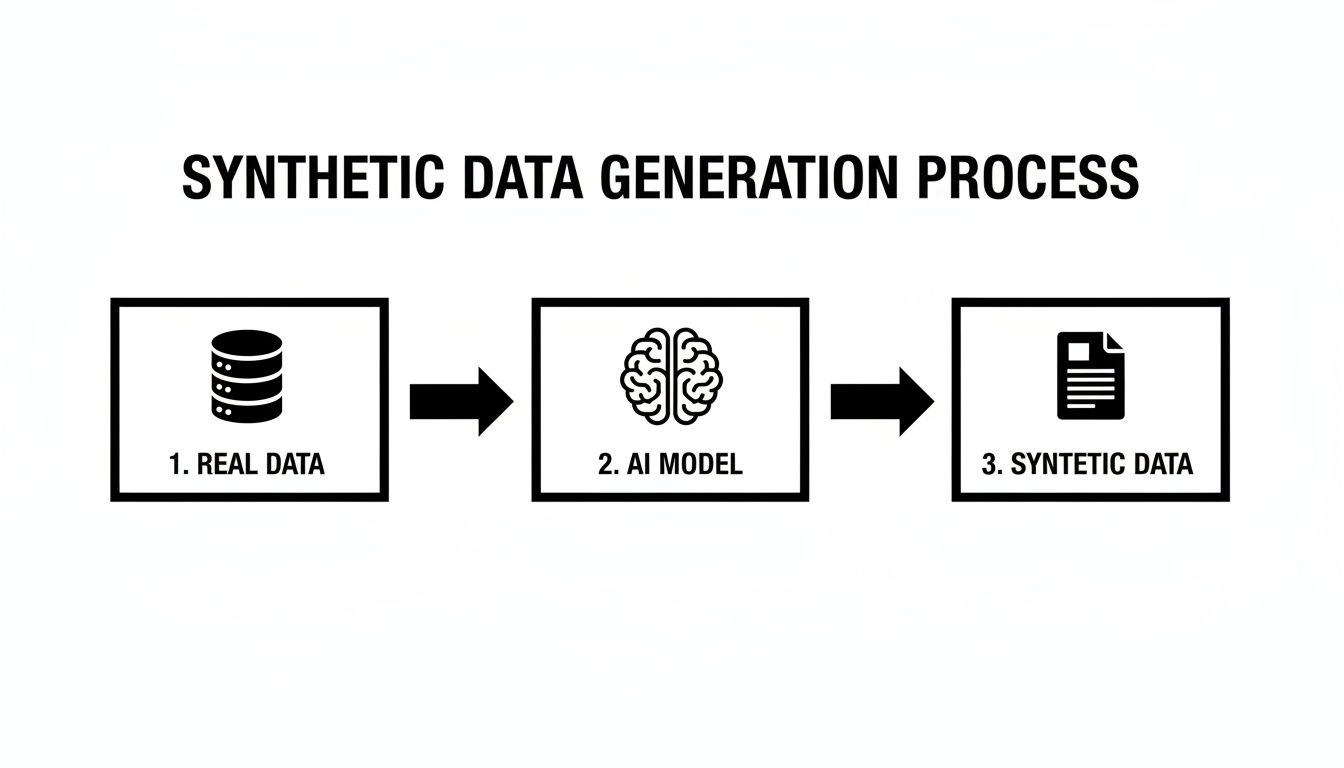
As the diagram shows, real-world data is used to teach an AI model, which then produces a totally new synthetic dataset. It’s a powerful cycle that can turn a limited or sensitive dataset into a vast and safe resource for training other models.
The Art Forger and the Detective
One of the most common and fascinating methods for creating synthetic data involves a model called a Generative Adversarial Network, or GAN. The name sounds complex, but the concept is surprisingly easy to grasp with a simple analogy.
Imagine a classic cat-and-mouse game between an art forger and an art detective. The GAN works in a similar way, with two competing AI models:
- The Generator (The Forger): This AI’s only job is to create fake data. To start, its forgeries are pretty clumsy and obviously fake.
- The Discriminator (The Detective): This second AI’s job is to examine data—both real samples and the forger's fakes—and determine which is authentic.
The generator creates a fake, and the detective immediately calls it out. "Nope, that's not real." The generator takes that feedback, learns from its mistakes, and tries again, this time with a slightly better forgery. Meanwhile, the detective is also getting smarter with every piece it inspects, sharpening its ability to spot even the most subtle imperfections. This back-and-forth happens millions of times, with both sides constantly improving.
Key Insight: This competitive dynamic is what makes GANs so effective. The constant pressure forces both AI models to get better and better. Eventually, the generator becomes so good at creating fakes that the discriminator can no longer reliably tell the difference between the synthetic data and the real thing. That's when you know your synthetic data is ready for action.
This adversarial process is just one approach. Other popular techniques, like Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) and diffusion models, are also used to generate high-fidelity data. The core principle remains the same: learn the essence of a real dataset to create something entirely new and usable.
Companies like Gretel.ai and Mostly AI have built platforms that put these powerful techniques into the hands of businesses. If you're curious to learn more about the models driving this, you can get a deeper understanding by reading our guide on what generative AI is.
Why Synthetic Data Is a Game Changer for AI

So, why is everyone in AI talking so much about synthetic data? It’s because it directly tackles some of the most stubborn problems developers have been wrestling with for years. This isn't just a minor tweak to the process; it fundamentally rewires how we build, test, and deploy AI models.
We're not just talking about making things a little cheaper or faster. Synthetic data opens up doors that were previously bolted shut by data limitations. From safeguarding privacy to building fairer AI, the benefits are real and they are massive.
Protecting Privacy in a Data-Hungry World
One of the biggest wins for synthetic data is its power to completely anonymize information. This is a huge deal, especially in fields like healthcare and finance. For instance, a hospital holds a goldmine of patient data that could train an AI to spot diseases earlier. But using that real data is an ethical and legal nightmare thanks to strict privacy laws.
Synthetic data is the perfect workaround. We can generate millions of artificial patient records that perfectly capture the statistical patterns of real diseases without ever exposing a single person's actual information. The AI gets the insights it needs with zero risk to individual privacy. It’s a win-win.
Fueling Innovation and Reducing Risk
Let's say a retail company wants to expand into a new city where they have zero sales history. How do they guess what products will sell or how to stock their shelves? Instead of flying blind, they can generate synthetic data that simulates local shopping habits, demographics, and economic conditions.
This lets them test out different strategies in a risk-free virtual world before they sink millions into a physical store. This ability to run "what-if" scenarios is invaluable across almost every industry, allowing businesses to innovate without the fear of costly failures.
Expert Opinion: According to Gartner, by 2024, 60% of the data used for the development of AI and analytics projects will be synthetically generated. This shows a massive shift in thinking: "The ability to generate data for scenarios you haven't seen yet is incredibly powerful. You're no longer limited by historical data; you can prepare your AI for the future."
Reducing Bias and Creating Fairer AI
A well-known monster in the AI closet is algorithmic bias. If you train a model on data that mostly represents one group, it's going to fail miserably when it encounters anyone else. For instance, an AI trained on medical scans from a single demographic might completely miss a diagnosis in a patient from a different background.
Synthetic data gives us a direct way to fight this. Developers can spot the gaps in their real-world data and intentionally generate new data to fill them. They can create more examples of underrepresented groups, ensuring the final AI model works fairly for everyone. This proactive approach to dataset enrichment is a critical step toward building responsible AI.
Preparing for the Unpredictable
Finally, synthetic data lets us train AI for rare but critical situations—the kinds of things that are too dangerous or impractical to test in the real world. Take a self-driving car. How do you teach it to handle a sudden rockslide on a winding road or a tire blowing out on the highway?
You certainly can't stage those accidents over and over again for practice. But in a simulation, you can run those scenarios thousands of times, from every conceivable angle. This hardens the AI against worst-case situations, making the technology fundamentally safer before it ever hits a public road.
Real-World Examples of Synthetic Data in Action

Theory is one thing, but seeing how synthetic data actually works in the wild is what really makes the concept click. This isn't just some lab experiment; it's a powerful tool being used right now to solve tough, practical business problems. From making our roads safer to protecting our bank accounts, synthetic data is already having a massive impact.
Let's dive into a few compelling stories of this technology in action.
Making Autonomous Vehicles Safer
Self-driving cars have an enormous learning curve. They need to absorb millions of miles of driving experience to navigate our chaotic roads safely. The huge problem here is that it's impossible—not to mention incredibly dangerous—to have them practice every rare but critical scenario in the real world. Just imagine trying to stage a deer suddenly jumping onto a dark, icy road.
This is where synthetic data for AI truly shines.
- The Problem: Trying to collect enough real-world data for rare "edge cases" is painfully slow, ridiculously expensive, and just plain unsafe.
- The Synthetic Solution: Companies like Waymo and NVIDIA build hyper-realistic virtual worlds. Inside these simulations, they can generate an endless variety of hazardous road conditions, bizarre weather patterns, and all sorts of unpredictable events. A practical example? They can simulate a child chasing a ball into the street from behind a parked car, thousands of times, in different lighting and weather.
- The Result: An autonomous vehicle can "drive" millions of simulated miles in a tiny fraction of the time it would take on actual roads. It learns how to handle dangerous situations in a completely safe environment, making the final AI model far more robust and reliable before a single tire touches a public street.
The numbers really drive this point home. AI and machine learning model training now makes up over 31.7% of the entire synthetic data market. That massive share is fueled by industries like automotive, banking, and healthcare that need to simulate complex scenarios without real-world risks. Some companies even report they can develop their models up to 10 times faster this way. You can discover more insights about this growing market in the full report.
Protecting Your Finances Without Compromising Privacy
Banks and financial institutions are locked in a constant battle against fraud. They rely on AI to analyze transaction patterns and flag suspicious activity, but there's a big catch: strict privacy regulations mean they can't just use sensitive customer data however they want. This puts a major limit on their ability to build the most effective fraud detection models.
Expert Opinion: "With synthetic data, we can create a perfect, privacy-safe mirror of customer behavior," notes an executive from a leading fintech firm. "It allows us to innovate and strengthen security without ever touching real, sensitive information."
For a practical example, a bank can generate a dataset of millions of artificial credit card transactions. This data would include fake, but realistic, fraudulent patterns—like a series of small, rapid purchases followed by a large one—allowing their AI to learn how to spot these threats without ever looking at real customer accounts.
The same idea applies to creating realistic visual data. To get a better sense of how AI can transform visual content, it's worth exploring how Image to Image AI works.
Fine-Tuning Business Strategy for Startups
Picture a new online retail startup. Before they even launch, they need to get their inventory management system right, but they have zero historical sales data to train it on. How can they possibly predict which products will fly off the shelves or when demand might spike?
Instead of just guessing, they can generate synthetic sales data. By creating a realistic dataset that reflects customer demographics, seasonal trends, and purchasing habits, they can fine-tune their algorithms from day one. This helps them optimize stock levels and launch with a data-backed strategy, giving them a serious competitive edge right out of the gate.
Understanding the Limits and Ethical Questions
As powerful as synthetic data is, it’s no silver bullet. For every problem it solves, it introduces new challenges and important questions we need to wrestle with. Getting a handle on these limitations is the key to using this technology responsibly and, frankly, effectively.
One of the biggest hurdles is achieving high fidelity. In simple terms, this is about how well the synthetic data mirrors the complex patterns and subtle quirks of the real-world data it’s based on. If the generated data is a poor imitation, any model trained on it will stumble badly when it finally meets reality. Think of it like a flight simulator that doesn't correctly model turbulence—it creates a dangerous gap between training and the real world.
The Garbage In, Garbage Out Problem
There's an old saying in data science: "garbage in, garbage out." This rule applies with full force to synthetic data. The models that generate synthetic data have to learn from an initial seed of real data. If that seed data is flawed or biased, the synthetic data will inherit and sometimes even amplify those very same flaws.
For instance, imagine using a real-world dataset to train a hiring AI, but that dataset reflects a historical bias against a certain demographic. Any synthetic data you create from that source will bake that bias right in. The AI will learn the wrong lessons, and you could end up with a system that's just as unfair as the one you were trying to fix. This is a critical point to remember, and you can dig deeper into the risks by understanding what AI bias is and how it creeps into systems.
Expert Opinion: "The goal is to capture the statistical soul of the data, not just its surface-level features," warns a leading data scientist. "Without that depth, you're just creating a clean-looking but hollow copy that will mislead your AI."
The Ethical Tightrope Walk
The incredible realism of modern synthetic data also forces us to confront some serious ethical questions. When AI can generate perfectly convincing—but completely fake—human faces, voices, and videos, the potential for misuse is massive. This technology could easily be weaponized to create misleading content, impersonate individuals, or spread disinformation on a scale we've never seen before.
Thinking about these ethical implications isn't meant to scare you away from synthetic data. It’s about going in with your eyes open. The trick is to approach this powerful tool with a strong sense of responsibility, building safeguards and ethical guidelines into your workflow right from the start. By acknowledging the risks, we can better focus on harnessing the immense positive potential of synthetic data in AI.
How to Get Started With Synthetic Data
So, are you curious enough to try generating some synthetic data yourself? Getting your hands dirty is more straightforward than you might think, and you definitely don't need a Ph.D. in data science to start experimenting.
The trick is to begin with a clear, manageable goal. Don't try to boil the ocean on your first attempt. Maybe you just want to create a few hundred extra customer profiles to test a new app feature, or perhaps you need to balance out a small dataset for a personal project. The whole point is to take small, confident steps.
A Simple Workflow for Beginners
Think of your first project as following a simple roadmap. This approach breaks down what sounds like a complex process into a handful of achievable tasks.
- Define Your Goal: First, what do you actually need this data for? Are you trying to beef up a small dataset, create anonymous data you can share safely, or fix a nasty bias problem? Be specific. A good starting point could be: "I want to generate 1,000 synthetic customer records to test my new checkout flow."
- Find a "Seed" Dataset: You’ll need a small, clean sample of real-world data to act as a template for the AI model. This is the foundation for everything else. If you're unsure how to prep your data, our guide on data preparation for machine learning is a great place to start.
- Choose a Beginner-Friendly Tool: You don't have to build a generator from scratch. Platforms like Gretel.ai offer free tiers to get you started, and open-source libraries like the Synthetic Data Vault (SDV) are perfect for experimentation.
- Generate and Evaluate: Run the tool and create your new dataset. The final step is crucial: compare its statistical properties to your original seed data. Does it look and feel real enough? Does a synthetic customer's age make sense with their purchase history?
Expert Tip: "Start small and validate often. Your goal isn't to perfectly clone reality, but to create data that's useful for your specific task. Check your work at every step!"
The world of synthetic data generation is buzzing with activity. You have specialized companies like Synthesis AI that focus on computer vision data, while others are dedicated to ensuring the data meets strict regulatory standards.
The good news for businesses is that these tools are becoming incredibly accessible. A recent report found that 68% of vendor offerings are API-first and cloud-native, designed to plug right into the major platforms you already use. You can discover more insights about the market landscape to get a feel for how fast things are moving. This rapid growth is making it easier than ever for anyone to see what synthetic data in AI can really do.
Common Questions About Synthetic Data
It's natural to have a few questions when you're first diving into the world of synthetic data. It's a new frontier for many, so let's clear up some of the most common things people ask.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Is synthetic data as good as real data? | It really depends on what you need it for and how well it's generated. High-quality synthetic data can sometimes be even better than real data, especially if your original dataset is small, messy, or biased. The goal isn't just to mimic reality, but to create a dataset that's perfectly suited for training your AI model. |
| Can synthetic data completely replace real data? | Not entirely. Think of it more as a powerful amplifier than a total replacement. You almost always need an initial "seed" of real data to teach the generative model what to create. From there, synthetic data can expand that small sample into a massive, perfectly labeled, and privacy-compliant dataset. |
| Is it legal and ethical to use? | For the most part, yes—and that’s one of its biggest advantages. Because synthetic data doesn't contain any real personal information, it’s a fantastic way to navigate strict privacy laws like GDPR. The ethical side, however, depends on how you use it. Creating deepfakes or intentionally biased data is a major ethical red line, so responsible use is absolutely crucial. |
Hopefully, that clears things up! The key takeaway is that synthetic data isn't just about creating "fake" information; it's about engineering better, safer, and more effective data for specific AI training tasks.
Ready to explore how AI can work for you? At YourAI2Day, we break down complex topics and bring you the latest tools and insights. Discover more on our website.