What is Federated Learning: A Simple Guide to How It Works
Ever wonder how your phone's keyboard seems to know your unique slang or how it suggests the perfect emoji? That's often the magic of machine learning at work. But how does it learn about you without sending all your private conversations to a company server? The answer is a clever approach called federated learning.
Think of it as training an AI model in a group project where no one is allowed to peek at each other's notes. Instead of collecting everyone's data in one giant, central database, the learning happens right on your device—whether that’s your smartphone, your laptop, or even a computer in a hospital.
The only thing shared is the knowledge gained, not your personal data. These small, anonymous updates are then cleverly combined to improve a shared AI model for everyone. It’s a privacy-first approach to AI, built from the ground up to respect your digital boundaries.

Understanding The Core Idea
Let's make this super simple with a practical example. Imagine a group of hospitals, each with its own confidential patient records. They all want to collaborate to build a breakthrough AI model that can detect a rare disease earlier, but they absolutely cannot share sensitive patient data due to strict privacy laws like HIPAA.
With federated learning, they don't have to. Each hospital can train a copy of the AI model on its own private data, right inside its own secure network. Then, they only share the anonymous insights—the "learnings" from the model—with a central coordinator. This coordinator aggregates the insights from all the hospitals to create a much smarter, more robust global model, which is then sent back to each hospital.
No patient data ever leaves the hospital, but every doctor and patient benefits from the collective knowledge.
Why This Matters For Privacy
This decentralized method is a huge step away from how AI used to be built. The old-school way involved collecting massive amounts of data in one place, creating a "honeypot" for hackers and raising serious artificial intelligence privacy concerns. It was a massive liability, especially with our most sensitive information.
Federated learning flips that model on its head. The AI model trains where the data lives. Your personal photos, private messages, and health information stay right where they belong—on your device.
The concept was first introduced by Google back in 2016 as a way to train a model collaboratively across many different devices without centralizing the data. It was a timely solution, arriving just as global privacy regulations like GDPR were tightening the rules on data collection. Only the model updates are ever exchanged, never the raw data itself.
Federated Learning vs Traditional Centralized AI
To really see the difference, it helps to put the two approaches side-by-side. The table below breaks down how federated learning fundamentally changes the game for data privacy and security.
| Aspect | Traditional Centralized AI | Federated Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Data Location | All data is collected and stored on a central server. | Data remains on individual user devices or local servers. |
| Privacy Risk | High. A single data breach can expose all user data. | Low. Raw, sensitive data is never shared or moved. |
| How It Learns | The model is trained on a massive, aggregated dataset. | A shared model learns from decentralized, local data updates. |
This shift is more than just a technical detail; it’s about building trust with users. As AI becomes more woven into our daily lives, respecting our digital boundaries isn't just a nice-to-have feature—it's an absolute necessity.
How Federated Learning Works Step by Step
So, how does an AI model actually learn without ever seeing the raw data it’s training on? The whole process is a clever, repeating cycle. Think of it as a group effort managed by a central server, but where the real learning happens across many individual devices, often called "clients."
Let's go back to our team of hospitals collaborating on a new diagnostic model. Instead of emailing sensitive patient files to a central database (a huge privacy violation!), they keep that data secure in their own hospital networks. A lead research institution sends out a basic diagnostic model, each hospital fine-tunes it using its local patient data, and then they only send back their anonymous adjustments—not the patient files themselves. These adjustments are then combined to create a much more accurate and robust final model for everyone.
The Core Cycle of Federated Learning
The real magic happens in a continuous loop. This cycle ensures the shared model is constantly improving, getting more accurate and useful with each pass. It all boils down to a clear, five-step sequence that keeps your privacy front and center.
This diagram shows you exactly how that cycle works, with the model moving from the central server to the devices and back again, getting a little bit smarter each time.
As you can see, your actual data never leaves your local device. Only the mathematical lessons learned from that data are sent back to be combined.
Let’s walk through what’s happening at each stage.
A Detailed Look at Each Step
This system is built for efficiency and security, repeating these steps over and over until the model reaches the accuracy we're looking for.
Start and Share the Model: It all begins at a central server, which creates an initial, or "base," version of a global AI model. A copy of this starter model is then sent out to a select group of devices—this could be thousands of smartphones, computers in different hospitals, or IoT sensors in a factory.
Train Locally on Your Device: Once your device gets the model, it starts training its copy using only the data you have stored locally. For example, your phone might use your recent text messages to improve its version of a predictive text model. Crucially, none of your personal messages ever leave your phone.
Send Back a Summary of What Was Learned: After a round of training, your device doesn't send your data back. Instead, it creates a small, summarized update. This update is just a set of mathematical adjustments (technically called weights or gradients) that represent the improvements the model made based on your data.
Combine the Updates: The central server collects these small, anonymized updates from all the participating devices. It then intelligently combines, or aggregates, all these individual lessons to create a better, more refined global model. This is where the collective knowledge is pooled together.
Get the New, Smarter Model: Finally, this improved global model is sent back down to all the devices, ready for the next round. The cycle then repeats, with the shared model getting progressively smarter for everyone with each iteration.
This circular flow is the heart of federated learning, allowing powerful AI models to be built without creating a massive, central vault of user data.
Expert Opinion: "The beauty of federated learning is that it decouples model training from the need for direct access to raw data," explains Dr. Sarah Jenkins, an AI ethics researcher. "It allows us to build smarter, more personalized AI products while placing user privacy at the forefront of the design. It's about learning from the data without possessing the data."
The most common algorithm used to handle the aggregation step (Step 4) is known as Federated Averaging (FedAvg). The name says it all—it works by calculating a weighted average of all the model updates it gets from the client devices. This simple but incredibly effective approach ensures the final global model is a balanced consensus of what all the devices learned, preventing any single device from having too much influence.
Why Federated Learning Is a Game Changer
So, what makes federated learning more than just a clever technical trick? It’s a direct answer to one of the biggest challenges in modern tech: how to build helpful, intelligent AI without becoming a massive data vacuum cleaner. This isn't just an abstract idea; it's a huge opportunity driven by some very real and powerful trends.
Let's be honest, we’ve all become much more aware of our digital footprints. High-profile data breaches and a growing demand for personal privacy have completely shifted public opinion. People want smarter products, but not at the expense of their data. This shift is a huge reason why federated learning is gaining so much momentum right now.
Aligning With a Privacy-First World
Federated learning is the perfect solution for an era defined by strict data privacy laws. Regulations like Europe's GDPR and the healthcare-focused HIPAA in the United States have put serious guardrails on how companies can collect and use our personal data.
For companies, this isn't just about good ethics—it's about survival. Breaking these rules can lead to staggering fines and a loss of customer trust that’s nearly impossible to win back. Federated learning offers a way forward, allowing businesses to innovate and build better AI while respecting these legal and ethical boundaries. It unlocks progress in fields where data is simply too sensitive to ever leave its source, like in hospitals, banks, and government agencies. You can dive deeper into this balancing act in our guide to artificial intelligence privacy concerns.
This diagram shows the basic flow of how a central server and local devices work together without ever sharing the raw data.
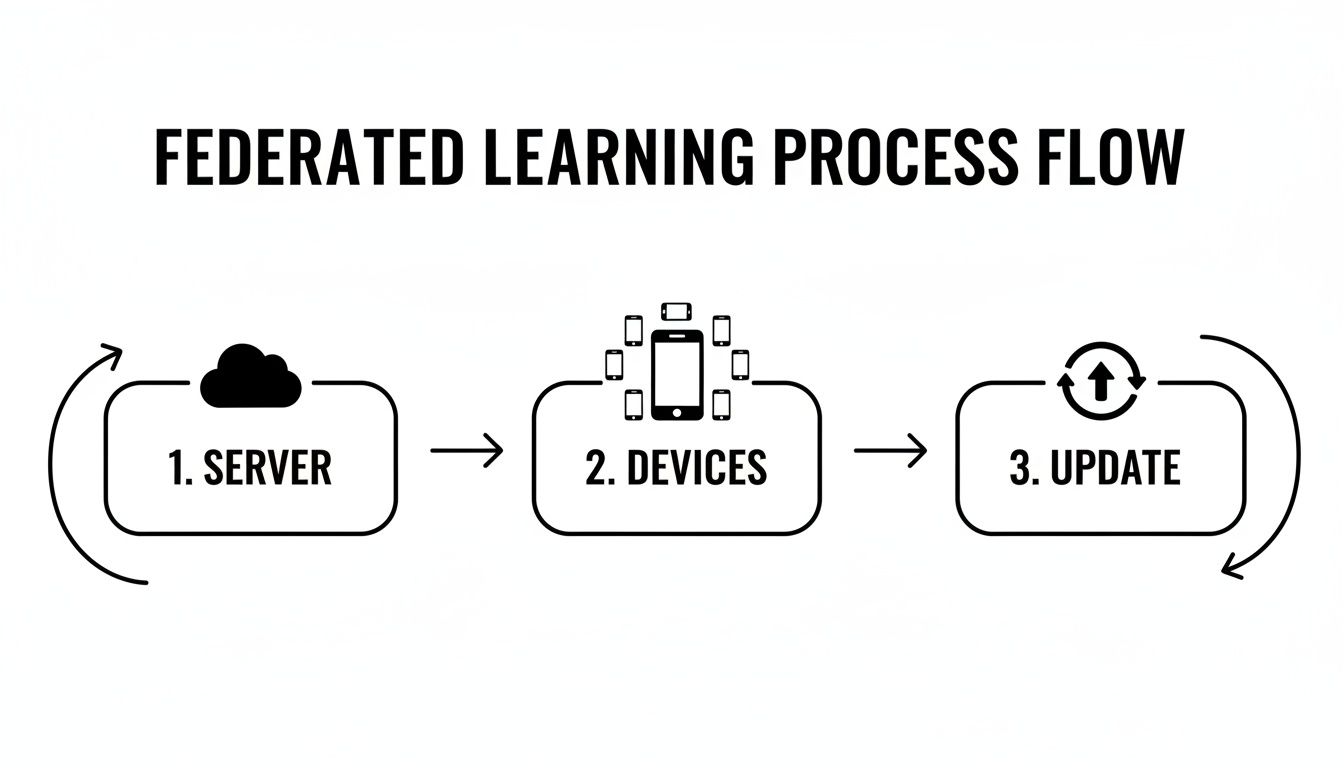
As the visual highlights, only the model updates—not the data itself—travel back to the central server for aggregation.
Unlocking New Opportunities for Collaboration
Beyond just staying compliant, federated learning enables collaboration that was previously impossible.
Imagine two rival banks that want to team up to detect a sophisticated fraud ring that's hitting both of their customers. Under normal circumstances, neither bank would ever dream of sharing its confidential customer transaction data with a competitor. It’s a complete non-starter.
With federated learning, they don't have to. Each bank can train a shared fraud detection model on its own private data and contribute only its learnings—the model updates—to a central, shared model. The result is a more powerful, accurate system that benefits everyone without exposing a single piece of confidential information.
This collaborative power is driving major investment and growth. The Federated AI Learning market was valued at USD 250.6 million in 2024 and is projected to explode to USD 9,809.4 million by 2034, growing at an incredible 44.3% compound annual growth rate. This growth is fueled by its unique ability to sidestep the need to centralize sensitive data, a critical advantage for industries facing the strictest regulations.
Expert Takeaway: "Federated learning isn't just a defensive move to comply with privacy laws," says a leading AI strategist. "It's an offensive strategy. It enables businesses to build smarter, more trustworthy products that people actually want to use, turning privacy from a liability into a real competitive advantage."
Real Examples of Federated Learning in Action
You might think federated learning is just a futuristic concept, but it’s already working behind the scenes on the devices you use every single day. This technology has quietly moved from research labs to the real world, powering helpful features that make our digital lives smoother and more private.
The most common example is probably right in the palm of your hand: your smartphone's predictive keyboard.

Whether you use Gboard on Android or the native iOS keyboard, the AI is constantly learning your personal slang, acronyms, and common phrases to guess what you’ll type next. It does this by training a small model right on your phone with your typing data. The key here is that your messages never leave your device. Only the abstract model updates—the lessons learned—are sent to a central server to be combined with updates from millions of others, improving the keyboard for everybody.
Revolutionizing Healthcare Collaboration
Beyond everyday tech, federated learning is making huge strides in sensitive fields like healthcare. Hospitals hold vast amounts of valuable medical data that could train powerful diagnostic AI, but privacy regulations like HIPAA make pooling that data almost impossible.
Federated learning breaks down that barrier. Let's get practical: take the challenge of training an AI to detect rare brain tumors from MRI scans. A single hospital might only have a few dozen examples, which is nowhere near enough to build a reliable model.
This is where multiple hospitals can team up to build a far more powerful tool without sharing the underlying patient data.
- Local Training: Each hospital trains a copy of the model on its own private MRI scans. This sensitive patient data never leaves the hospital’s secure network.
- Sharing Insights, Not Data: Instead of sending the scans, the hospital sends only the anonymous mathematical updates from its training session to a central aggregator.
- A Smarter Global Model: The aggregator combines these updates to create a much more robust and accurate model, which is then distributed back to all participating hospitals.
This approach lets medical centers benefit from a massive, collective dataset, leading to earlier and more accurate diagnoses—all without ever compromising patient confidentiality.
Expert Insight: "Federated learning is the key that unlocks collaborative medical research at a global scale," notes a medical AI researcher. "It allows us to build life-saving diagnostic tools by learning from diverse datasets while rigorously upholding the patient privacy that is central to medical ethics."
Securing the Financial World
The finance industry runs into the same privacy wall. Banks need to spot sophisticated fraud patterns that stretch across different institutions, but they can't legally share customer transaction data. Meanwhile, fraudsters are constantly evolving their tactics.
Federated learning lets these institutions fight back together. Picture a consortium of banks aiming to build a better fraud detection system.
- Each bank trains a shared fraud model on its own proprietary transaction data, keeping everything safe behind its firewall.
- They contribute only the anonymous model learnings—not the transaction data itself—to a central server.
- The aggregated global model can then spot subtle, widespread fraud techniques—like a series of small, suspicious transactions across multiple banks—that would be invisible to any single bank operating in a silo.
This collaborative method works. Financial firms have seen major improvements in fraud detection accuracy with federated models, helping them stop criminals and cut down on losses without ever putting sensitive customer information at risk. It’s a perfect example of what is federated learning’s power to solve real-world problems where data privacy is non-negotiable.
Understanding the Challenges of Federated Learning
While federated learning is a powerful way to build privacy-first AI, it's not a magic wand. Like any sophisticated technology, it brings its own unique set of hurdles to the table. For anyone looking to use it, getting a clear-eyed view of these challenges is the first step toward a successful project.
One of the biggest obstacles is what experts call data heterogeneity. It’s a fancy term for a simple concept: the data on each person's device is often completely different from the next.
Think about it. You're training an AI to suggest the next song in a playlist. My phone is full of 90s rock, while your phone is packed with K-pop. Our local models will learn radically different lessons. Trying to combine these conflicting insights into a single, effective global model can be a real struggle.
Dealing with Diverse and Unbalanced Data
This kind of data diversity can hurt a model's performance. In federated learning, data is usually non-IID, which means it's not independent and identically distributed. In plain English, the data on one device doesn't look like the data on another.
This statistical mismatch is a major headache. For example, if a text recognition app is learning from handwriting that varies wildly by region, or an image model is trained on datasets with different demographic skews, the final model's accuracy can drop by up to 35%.
To get around this, researchers are building smarter algorithms. One promising approach is FedDyn, which dynamically tweaks the training process on each device to better align with the global objective. This method has been shown to close the performance gap caused by data differences by as much as 28%. You can dive into the specifics in the full research paper on dynamic regularization.
This core problem leads to a few other related issues:
- Model Bias: If some types of data are rare across the network (e.g., very few left-handed users), the final model can end up biased, performing poorly for those minority groups.
- Slower Convergence: The global model can take a lot longer to become accurate when it's trying to average out so many different local viewpoints.
- Personalization Problems: A model that tries to be a jack-of-all-trades for everyone might end up being a master of none, failing to provide a truly personal experience.
The Headaches of Coordination and Security
Beyond the data itself, just managing a federated network is a massive engineering feat. Coordinating potentially millions of devices—each with its own processing power, connection speed, and availability—is incredibly complex. Phones go offline mid-training. Some devices are too slow to contribute on time. It's a messy, real-world environment.
Security is the other major concern. Even though raw data stays on the device, the model updates sent back to the server aren't completely invulnerable.
Expert Takeaway: "Although federated learning is designed for privacy, it's not inherently foolproof," warns a cybersecurity analyst specializing in AI. "Clever adversaries can sometimes analyze the model updates to infer sensitive information about the underlying training data. This is why robust federated systems almost always layer in extra security measures."
To defend against these threats, developers rely on privacy-enhancing technologies. Techniques like differential privacy, which adds calculated statistical noise to updates, and secure aggregation, which uses cryptography so the server can only see the combined result, are essential. These extra layers are non-negotiable for building a trustworthy system.
Putting a strong AI governance framework in place is crucial for managing these risks from day one and ensuring the entire system remains secure and reliable.
The Future of AI Is Collaborative and Private
Federated learning isn't just another clever machine learning technique; it signals a fundamental shift toward a more responsible and private future for AI. At its heart, it makes a simple but powerful promise: you can get brilliant, personalized AI experiences without having to surrender your privacy. That’s the big idea that changes everything.
This privacy-first model opens the door to solving massive global challenges that were once too difficult to tackle. Imagine hospitals across continents collaborating to build a more accurate cancer detection model. Or think of banks joining forces to shut down sophisticated financial fraud rings. With federated learning, they can pool their collective insights to create a much more powerful AI, all without a single piece of sensitive data ever leaving their secure systems.

Powering the Next Wave of Edge AI
Looking ahead, federated learning is perfectly suited to drive the next major leap in technology: edge AI. This is all about running AI models directly on the devices at the "edge" of the network—your phone, your smart car, your fitness tracker, and millions of other connected gadgets.
Instead of constantly sending your data to the cloud for processing, these devices learn and adapt right where they are. Federated learning is the framework that lets them share what they've learned and get smarter together, all while your personal information stays safely on your device.
This approach paves the way for a future where our technology is:
- Faster and more responsive because it processes data locally, cutting out network lag.
- More reliable since it can still function properly even without a stable internet connection.
- Inherently more private by its very design, as your data never has to leave your control.
The real takeaway here is that grasping concepts like what is federated learning is essential for anyone trying to understand where technology is headed. It’s not just for data scientists; it’s about the principles that will shape the tools we all use every single day.
The future of AI also depends on making it easier for more people to build things. Getting familiar with technologies like no-code backend AI solutions can give more creators the power to build the next generation of smart applications. Armed with this knowledge, you’re ready to explore the exciting and fast-moving world of artificial intelligence.
Frequently Asked Questions
Even after covering the basics, a few questions often pop up when people start thinking about how federated learning works in the real world. Let's tackle some of the most common ones.
Is Federated Learning Completely Secure and Private?
That's the big one, and it's a critical question. At its core, federated learning is designed for privacy—its main purpose is to keep raw, sensitive data on your device. That alone is a massive improvement over traditional methods where all your data gets sent to a central server.
But it's not a silver bullet. Researchers have found that it's sometimes possible for a determined attacker to infer information about your data just by analyzing the model updates that get sent back. It's not easy, but it's a potential vulnerability.
That's why a truly robust system doesn't rely on federated learning alone. It layers on additional privacy-enhancing technologies:
- Differential Privacy: This technique adds a carefully measured amount of statistical "noise" to the model updates. This makes it mathematically almost impossible to reverse-engineer and identify any single individual's contribution.
- Secure Aggregation: This uses cryptographic methods to ensure the central server can only see the final, combined update from a group of devices. It never gets to inspect any individual update, adding another powerful layer of protection.
So, think of it this way: federated learning is the foundation for privacy, but these extra measures are what make the house truly secure.
What Is the Difference Between Federated Learning and Distributed Learning?
It's really easy to get these two mixed up, since they both involve using multiple machines to train a model. The real difference comes down to why they do it and where the data comes from.
In classic distributed learning, the main goal is pure performance. You typically have one massive dataset, owned by a single organization, that’s just too big to train on one machine. So, you split it up across a cluster of powerful servers in a data center to get the job done faster. The data is usually uniform and centrally managed.
Think of it like this: Distributed learning is a team of professional chefs in one huge industrial kitchen, all working from the same master recipe to prepare a giant banquet faster. Federated learning is more like asking thousands of home cooks around the world to share tips for improving a recipe without ever revealing their secret family ingredients.
With federated learning, the data is inherently spread out across millions of user devices, like phones or laptops. This data is not uniform; it's personal, messy, and varied. Here, the primary goal isn't just speed—it's privacy. The whole point is to learn from this diverse, decentralized data without ever having to collect it.
Can I Use Federated Learning for My Own Project?
Absolutely! What used to be a highly specialized field accessible only to tech giants is now open to developers everywhere. Thanks to some fantastic open-source frameworks, you can start building and experimenting with federated learning without a massive budget.
If you're looking to get your hands dirty, the best starting point is to dive into the tutorials for these tools. You can even simulate an entire federated network on your personal computer. A few of the most popular frameworks are:
- TensorFlow Federated (TFF): Google’s powerful and comprehensive framework for experimenting with federated computation.
- PySyft: Part of the OpenMined community, this library puts a heavy emphasis on secure and private AI.
- Flower: A really flexible, framework-agnostic option that integrates smoothly with popular tools like PyTorch and scikit-learn.
These toolkits give you all the building blocks you need to start exploring and creating your own privacy-first AI applications.
At YourAI2Day, we're committed to breaking down complex topics and giving you the knowledge to navigate the future of technology. Stay informed and explore more with our in-depth guides.







