What Is a Large Language Model and How Does It Work?
Ever wonder how your phone's autocomplete seems to read your mind, or how a chatbot can write a poem on the spot? The magic behind it all is a large language model (LLM), a super-smart artificial intelligence designed to understand and create text that sounds like it was written by a person.
Think of it as a massive step up from simple spell-check. An LLM doesn't just guess the next word; it can draft entire emails, answer complex questions, write creative stories, and even generate computer code. It learns these incredible skills by studying a mind-boggling amount of text and data from all over the internet.
Your Simple Guide to Large Language Models
So, how can a chatbot suddenly become a poet or summarize a dense research paper in seconds? The secret sauce is a large language model. It's helpful to think of it not as a simple computer program, but as a massive prediction engine for language.
Imagine a digital brain trained on a library so vast it contains a huge chunk of the internet. This training allows it to pick up on the subtle patterns of grammar, context, facts, and even different writing styles. Its main job is to figure out the complex web of connections in human language so it can chat and create in a way that feels natural and, well, human.
The "large" part of its name points to two key things: the colossal size of the dataset it learns from and the huge number of parameters it contains. You can think of these parameters as billions of tiny digital knobs that the model tunes during its training to refine its understanding and generate the perfect response.
What Makes an LLM Work?
The foundation of any LLM is a deep, complex neural network that learns to process language a bit like we do. It doesn't just see words on a page; it starts to understand the relationships between those words. This powerful ability comes from a field of AI called Natural Language Processing (NLP), which is all about getting computers to make sense of human language. If you want to go a bit deeper, check out our guide on what is natural language processing.
To get a better handle on what's happening under the hood, let's break it down into a quick summary table.
An LLM at a Glance
This table simplifies the three core components that make a Large Language Model tick.
| Component | Simple Analogy | What It Does |
|---|---|---|
| Neural Network | The "Brain" | A complex system of interconnected nodes that processes information and learns patterns. |
| Training Data | The "Library" | A massive collection of text and code (books, articles, websites) that the model learns from. |
| Parameters | The "Knobs & Dials" | Billions of internal variables that the model adjusts during training to improve its predictions. |
Essentially, when you give an LLM a prompt, it uses its "brain" and adjusts its "knobs" based on everything it read in its "library" to figure out what you're asking and how to respond.
When you type a prompt into an LLM, a simple, three-step dance happens in the background:
- It processes your input. The model takes your question or command (like "Write a subject line for an email about a team lunch") and breaks it down to understand what you're really asking for.
- It predicts the output. Drawing on its vast training, it calculates the most likely sequence of words that will form a useful and logical response. It's essentially playing a super-advanced game of "what comes next?"
- It generates the text. Finally, it assembles those words into something new, whether it's a catchy subject line ("Team Lunch This Friday!") or a multi-page report.
As AI expert Dr. Anya Sharma notes, "An LLM's true power isn't just knowing facts, but in synthesizing information. It connects dots across billions of data points to generate something genuinely new, which is why it can feel so creative and insightful."
For a quick, easy-to-digest overview of how these pieces fit together, take a look at a concise explanation of how AI like ChatGPT works. This whole process is what enables everything from simple Q&A bots to advanced tools for creative writing and analysis.
How Large Language Models Are Built
To really get what a large language model is, you have to look under the hood. It’s not magic—it's a fascinating, massive-scale process of teaching a machine to understand the messy, nuanced way humans communicate.
At the core of every LLM is a neural network, a complex web of algorithms loosely based on the interconnected neurons in our own brains. But the real breakthrough, the technology that makes modern LLMs possible, is a specific type called the transformer architecture.
This simple flowchart gives you a high-level view of the journey from raw data to a useful AI assistant.
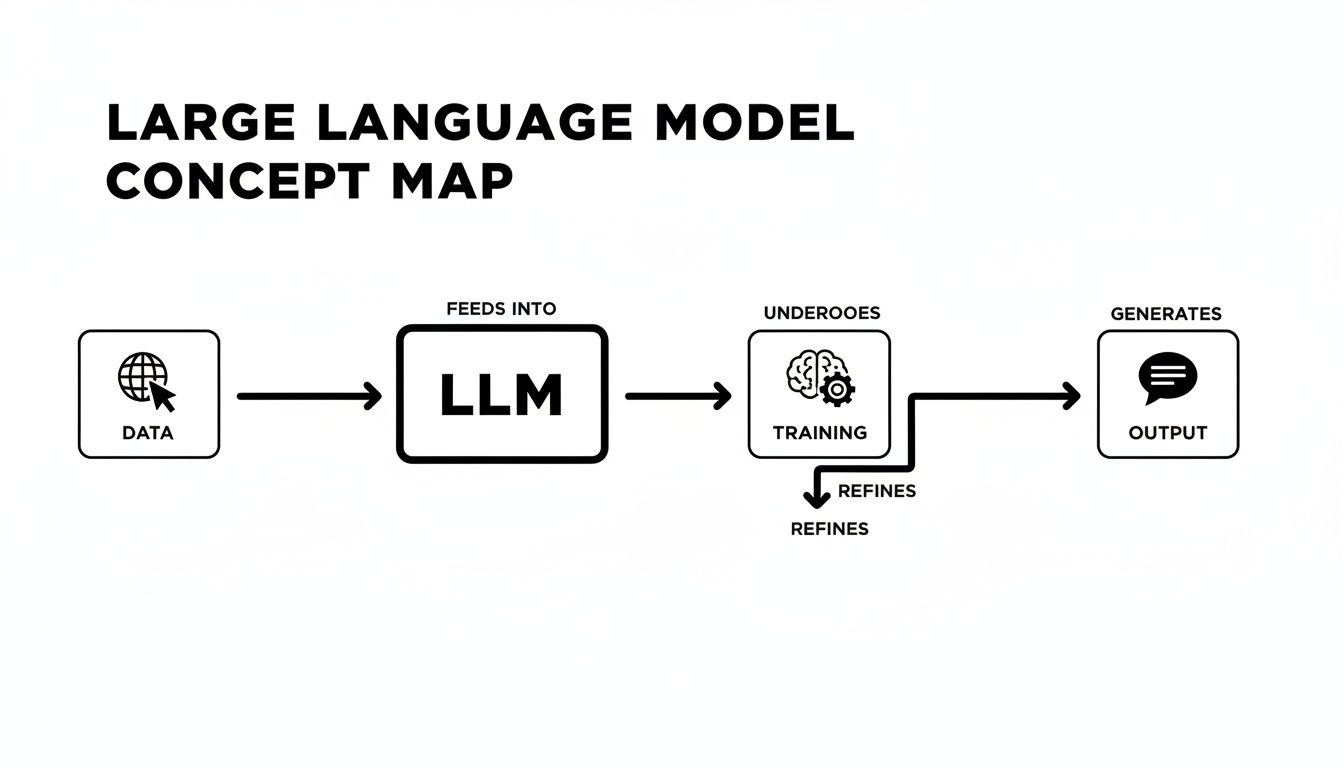
As you can see, it all begins with an enormous amount of data. This data is then used in a rigorous training process to build the model's intelligence, which ultimately lets it produce helpful, coherent text.
The Power of Attention
The secret sauce of the transformer architecture is its attention mechanism. Think about how you read a long, complicated sentence. You don't give every single word equal weight. Your brain instinctively hones in on the most important words to figure out what's actually being said. The attention mechanism does something very similar for the AI.
For example, in the sentence "The cat, which was sitting on the warm windowsill, chased the mouse," the attention mechanism helps the model understand that "cat" is the one doing the chasing, not the "windowsill." It's how the model deciphers context, untangles ambiguity, and understands the subtle relationships between ideas—something older AI just couldn't do.
"The attention mechanism was a true 'aha!' moment for AI researchers," says Ben Carter, an AI developer. "It taught models to see the forest and the trees—to understand both the broad topic and the specific words that give it meaning."
The Two-Step Training Dance
Building an LLM is a massive undertaking that generally unfolds in two main phases. The incredible sophistication of these models comes from complex LLM training methodologies that demand immense data and computational power.
1. Pre-training: Building the Foundation of Knowledge
This is the first and most resource-intensive step. During pre-training, the model is exposed to an almost incomprehensible amount of text—we're talking trillions of words from books, articles, websites, and research papers. It's like making someone read a huge chunk of the internet.
The goal here isn't to teach the model specific tasks. Instead, it's about learning the fundamental patterns of human language:
- Grammar and Syntax: The underlying rules of how sentences are put together.
- Factual Knowledge: Information about people, places, events, and concepts.
- Reasoning Skills: The ability to make logical connections between different ideas.
This phase results in a powerful, general-purpose base model with a broad understanding of the world, at least as it's represented in the training data.
2. Fine-Tuning: Honing Specialized Skills
Once pre-training is done, developers can take that general-purpose model and give it specialized training. This is called fine-tuning. It involves training the model on a much smaller, curated dataset to sharpen its abilities for a particular job.
Here are some practical examples:
- Medical Textbooks: A hospital could fine-tune a model on medical journals to help doctors summarize the latest research or analyze patient notes.
- Customer Service Transcripts: A company can fine-tune a model on its past support chats to create a chatbot that's genuinely helpful and understands its specific products.
- Legal Documents: A law firm might fine-tune an LLM on thousands of contracts to assist lawyers with analysis or case discovery.
Think of fine-tuning like sending a college graduate to a specialized trade school. It takes their broad, foundational knowledge and applies it to a specific profession, making the model far more practical for real-world use.
The introduction of the transformer architecture in 2017 was the turning point for LLM development, completely changing the trajectory of AI. This breakthrough kicked off an explosion of new models. OpenAI’s GPT-1 appeared just a year later with 117 million parameters. By 2019, GPT-2 had 1.5 billion parameters, and by 2022, models like Google’s PaLM hit a mind-boggling 540 billion parameters, showing just how quickly this technology has scaled.
The Not-So-Sudden History of Language Models
It feels like today’s powerful AI assistants appeared out of nowhere, but their roots run deep. The dream of teaching machines to understand us isn't a new one. It's the result of a long, often slow journey filled with brilliant thinkers and quiet breakthroughs that paved the way for the tools we now use every day.
And this journey didn't start with chatbots or creative writing. It began with a much more practical, and monumental, challenge: translation.
From Codebreaking to Conversation
The core ideas behind language models go back much further than most people think. You could say the story truly kicks off in the 1950s. Researchers at IBM and Georgetown University teamed up to build a system that could automatically translate Russian phrases into English—a massive undertaking driven by the pressures of the Cold War.
While the results were basic (it could only handle about 60 sentences), this early work captured the imagination of what could be possible. If you're curious about this pioneering era, you can discover the full history of LLMs on toloka.ai.
The field took another big step in 1958 when Frank Rosenblatt introduced the Mark 1 Perceptron. It was one of the very first machines built to learn through trial and error, mimicking a simplified version of a brain. These early efforts, while primitive by today's standards, planted a crucial seed: the idea that machines could learn from data instead of just blindly following pre-written instructions.
A computer historian might point out that these early projects weren't really trying to create "intelligence." They were trying to solve a puzzle: how do you turn the messy, beautiful patterns of human language into something a machine can actually process?
The Statistical Revolution
For a long time, progress was pretty slow. The first systems were built on a mountain of complex, hand-coded rules. This approach was incredibly brittle; it just couldn't handle the unpredictability of real human language. The whole game changed in the late 1980s and early 1990s, when researchers at IBM started leaning on statistical methods.
Instead of trying to teach a computer grammar rules, they just fed it huge amounts of text and let it figure out the probabilities on its own. It learned which words were most likely to show up next to each other. This was a complete game-changer.
Some of the key developments from this era included:
- Word Alignment: Techniques that let models match words between languages, like connecting "cat" in English to "gato" in Spanish.
- Corpus-Based Modeling: The practice of using massive collections of text (a "corpus") for training—a direct ancestor of how we train LLMs today.
- N-gram Models: A statistical method that calculates the odds of a word appearing based on the handful of words that came before it.
By 2001, a pretty sophisticated n-gram model, trained on over 300 million words, was outperforming everything else on language tasks. This focus on probability and patterns proved that by analyzing enough text, a machine could start to understand the structure of language. It laid the foundation for the neural network revolution that was just around the corner.
What Large Language Models Can Actually Do
So, we've covered the "how" behind these models. Now for the fun part: what can an LLM actually do for you? This isn't just about chatbot novelties; we're talking about practical, powerful tools that can handle an incredible range of tasks, from the mundane to the surprisingly complex.
The best way to think of an LLM is as a universal multitool for anything that involves language. It can dream up new content from scratch, boil down lengthy documents, translate between languages, and even act as a creative sparring partner for your next big idea. Its true power lies in its versatility—one minute it's a professional copywriter, the next it's a junior programmer.

From Blank Page to First Draft in Seconds
One of the most immediate benefits of LLMs is how they obliterate writer's block. We've all been there: staring at a blinking cursor, trying to will an outline into existence before painstakingly assembling paragraphs.
With an LLM, that entire process gets turned on its head. You can give it a simple prompt like, "Create a 500-word blog post outline on the benefits of indoor plants for mental health," and a logical structure appears in seconds. Need to flesh out a point? Just ask. This transforms hours of grinding into a few minutes of focused editing and polishing.
This isn't just for bloggers. The principle applies everywhere:
- Email Drafting: Turn a few scrawled bullet points like "Team lunch, Friday, noon, pizza place" into a polished, professional email ready to send.
- Social Media: Generate a full week's worth of creative Instagram captions or insightful LinkedIn posts in a single session.
- Creative Writing: Get unstuck by brainstorming plot twists or generating character dialogue for a script.
"Businesses that leverage LLMs for creative brainstorming and workflow automation are seeing productivity gains of over 40%," says Dr. Evelyn Reed, an AI Strategist. "It's about augmenting human creativity, not replacing it."
This isn't just hype. The impact is real and immediate. A recent study revealed that 72% of AI adopters saw a return on their investment within just three months, which shows just how quickly these tools can boost day-to-day productivity.
More Than Just Writing Text
While content creation gets most of the attention, an LLM’s abilities go much deeper. These are powerful analytical engines capable of making sense of vast amounts of information, tackling tasks that once took days of manual work.
They excel at understanding your intent and delivering exactly what you need. Instead of manually combing through a dense, 50-page report for the key takeaways, you can simply ask an LLM to "summarize this report into five bullet points." This skill alone is a massive time-saver for any professional.
Here are a few more advanced applications:
- Code Generation: A developer can describe a function in plain English, like "write a Python script that reads a CSV file and removes duplicate rows," and the LLM can spit out the code. This is great for everything from quick scripts to debugging tricky problems.
- Language Translation: Modern LLMs provide far more nuanced and context-aware translations than older tools, often correctly interpreting idioms and cultural specifics.
- Data Analysis: You can upload thousands of lines of customer feedback and ask an LLM to "identify the top three complaints and positive themes," turning raw text into actionable insights.
- Personalized Learning: An LLM can act as a patient personal tutor, explaining complex topics like quantum physics or macroeconomics in simple terms that are adjusted to your level of understanding.
The real magic of these models is their adaptability. A general-purpose model can handle all of the above right out of the box. For more specialized needs, you can provide additional training. Our detailed guide explains how to fine-tune an LLM to turn a generalist model into an expert in a specific domain, like legal contract analysis or medical research.
Once you grasp what these models are capable of, you start to see them not just as chatbots, but as genuine partners for creativity, analysis, and productivity.
Popular Large Language Models and Their Strengths
The field of LLMs is packed with incredible tools from major tech players and open-source communities. While many share core capabilities, they often have distinct personalities and strengths. Here’s a quick look at some of the most well-known models available today.
| Model Name | Developed By | Best Known For |
|---|---|---|
| GPT Series (e.g., GPT-4) | OpenAI | Advanced reasoning, strong conversational abilities, and creative text generation. |
| Gemini | Multimodality (understands text, images, and audio) and deep integration with Google's ecosystem. | |
| Claude 3 | Anthropic | Strong performance on long documents, an emphasis on safety, and a more "constitutional" approach to AI. |
| Llama 3 | Meta | High-performing open-source models that are popular with developers for fine-tuning and custom applications. |
This is just a snapshot, of course. The landscape is constantly evolving, with new models and updates appearing all the time. But it gives you an idea of the major players and where they shine.
Understanding the Risks and Limitations
As impressive as large language models are, they are far from perfect. It's easy to fall into the trap of thinking of them as all-knowing oracles, but a much healthier mindset is to see them as brilliant—yet sometimes flawed—assistants. To use them wisely, you have to understand where they stumble.
Knowing their limitations isn’t about pessimism; it's about being a responsible and effective user. It teaches you when to trust an LLM’s output and, more importantly, when to hit the brakes and double-check its work. This critical awareness is the key to getting real value from AI without falling into common traps.

The Problem of AI Hallucinations
One of the most bizarre and critical limitations of LLMs is what researchers call "hallucination." This is when an AI states false information with complete confidence, presenting it as if it were a hard fact. The model doesn't "know" it's lying; it's just generating text that is statistically likely based on the patterns in its training data.
Imagine asking an LLM for a book recommendation and it confidently suggests The Crimson River by a famous author—except neither the book nor the author's connection to it exists. The LLM might invent a historical event, cite a scientific study that doesn't exist, or attribute a fake quote to a real person, all while sounding completely authoritative.
This is a crucial takeaway: An LLM is optimized to be plausible, not necessarily truthful. Its confidence level is not a reliable measure of its accuracy.
This is exactly why you must always verify any critical information you get from an LLM, especially when it involves facts, statistics, or important data. Never take its output as the final word without checking it against trusted, independent sources.
Inheriting and Amplifying Human Bias
LLMs learn from a massive snapshot of the internet, which means they absorb all the good, bad, and ugly parts of human expression. As a result, they can inherit and even amplify existing societal biases related to race, gender, and culture that are present in the text they were trained on.
For instance, if a model learns from historical documents where doctors are overwhelmingly referred to with male pronouns, it will likely default to using "he" when generating new text about the medical field. These biases—some subtle, some not—can easily reinforce harmful stereotypes if you're not careful.
Here are a few ways this bias can show up:
- Stereotypical Associations: If you ask it to describe a "nurse," it might be more likely to use female pronouns, reflecting historical data biases.
- Unfair Representation: It could underrepresent certain demographic groups or produce content that reflects outdated social views.
- Echo Chambers: By generating text that aligns with the most common viewpoints in its data, it can unintentionally sideline alternative perspectives.
Developers are constantly working on new methods to filter out this bias, but it's a persistent and complex challenge. As a user, staying aware of this helps you evaluate the AI's output with a more critical eye and question its underlying assumptions.
Privacy and Environmental Concerns
Beyond the quality of their answers, two other major issues surround LLMs. The first is data privacy. When you use a public LLM, your conversations can be stored and used for future training. It is absolutely essential that you never share sensitive personal, financial, or confidential business information with a public AI tool.
The second issue is their environmental impact. Training a massive language model requires a staggering amount of computing power. This, in turn, consumes huge amounts of electricity and creates a significant carbon footprint. One expert famously noted that training a single large model can have an environmental cost equivalent to hundreds of transatlantic flights. While the industry is pushing for more efficient models, the ecological cost of building these digital brains is a serious factor in their long-term development.
The Future of AI and Human Language
So, where are large language models headed? The technology is moving at a breakneck speed, and what's coming next looks set to change our relationship with AI in some fundamental ways. We're on the cusp of moving beyond simple text into a world where AI can see, hear, and create across different formats.
One of the biggest areas of development is multimodality. This is all about giving a single model the ability to understand and generate content across different types of media—not just words on a page. Think about describing a complex scene to an AI ("a golden retriever wearing sunglasses on a skateboard") and having it instantly create a photorealistic image or even a short video clip that brings your words to life. This is where things are going, tearing down the walls between language, sight, and sound.
Smarter, Smaller, and Safer AI
While the massive, cloud-based models get most of the attention, there’s a serious push to create smaller, more efficient models. The idea is to build AI that can run right on your personal devices, like a smartphone or laptop, without constantly needing an internet connection. This shift would make AI faster, much more private, and available to far more people.
We're already seeing the beginnings of this trend:
- On-device assistants that can organize your calendar or summarize your emails without shipping your personal data off to a server.
- Real-time language translation apps that work even when you're offline, a game-changer for anyone traveling abroad.
At the same time, there's a huge and growing focus on AI safety and alignment. Researchers are working tirelessly to make these models more dependable and to ensure their operations line up with human values. The objective is to build AI that isn't just intelligent, but also helpful, harmless, and honest.
As one expert in AI ethics puts it, "The true measure of success won't be how smart we make AI, but how wisely we integrate it. The future is about building partners, not just tools."
This journey is really just getting started. As large language models continue to evolve, they will become more capable, more woven into our daily lives, and—with any luck—more aligned with what we want to achieve. The best way to get ready for what's coming is to stay curious and informed.
To keep learning, feel free to explore the other guides and resources we have across YourAI2Day.
Your LLM Questions, Answered
As you dive deeper into the world of AI, you’ll naturally start asking more questions. It's a complex topic! Let's clear up a few of the most common questions people have about large language models.
Can an LLM Actually Think or Feel?
This is a big one, and the short answer is no. While an LLM’s responses can feel incredibly human—even empathetic at times—they don’t have consciousness, personal beliefs, or emotions. They aren't "thinking" the way we do.
At their core, these are incredibly sophisticated pattern-matching machines. Their entire job is to predict the next most probable word in a sentence based on the mountains of text they’ve been trained on. It's all a matter of statistical probability, not genuine understanding or feeling.
"An LLM's output feels intelligent because it mirrors the patterns of human intelligence found in its training data," says an AI research scientist. "It's a reflection of our collective knowledge, not a mind of its own."
Are All Chatbots Large Language Models?
Not all of them, no, but the most advanced ones you hear about today absolutely are. Think of the simple chatbots you might have encountered a few years ago; they often relied on rigid, pre-programmed rules and could only handle specific keywords. If you asked something outside their script, they'd say, "Sorry, I don't understand."
Modern conversational AI tools like ChatGPT or Gemini are in a different league. The LLM is the powerful "brain" behind them, which is what allows them to grasp context, manage complex requests, and hold a surprisingly natural conversation.
How Can I Start Using an LLM Today?
Getting your hands on an LLM is surprisingly easy, and you can often start for free. Some of the most powerful models are available through public web interfaces, which are perfect for anyone just wanting to see what all the fuss is about.
Here are a few simple ways to start experimenting:
- Ask for a summary. Grab a long news article, paste it in, and ask the LLM to "explain this to me like I'm 12."
- Brainstorm ideas. Feeling stuck? Ask for a creative spark. Try a prompt like, "Give me ten gift ideas for a friend who loves hiking and cooking."
- Explain something complex. Use it as your personal tutor. A prompt like, "Explain quantum computing to me using a simple analogy" can work wonders.
The best way to get a feel for what these models can do is to simply play around with them. Give them practical, everyday tasks and see what happens.
At YourAI2Day, we're here to help you explore the world of artificial intelligence with confidence. Dive deeper into our guides and resources to continue your learning journey. Find out more at https://www.yourai2day.com.