Artificial Intelligence Explained Simply: Your Friendly Guide
Hey there! Let's get straight to it. At its heart, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is all about making computers smart—giving them the ability to do things that usually require human brains. We're talking about learning from experience, figuring things out, recognizing images, understanding what we say, and solving tricky problems.
Forget the Hollywood image of evil robots for a moment. Think of AI more like a super-smart assistant that learns as it goes, helping us get things done more efficiently. It's a tool, and this guide is here to explain it in a simple, no-nonsense way.
So, What Is Artificial Intelligence, Really?

Here's a little secret: you've probably already used AI multiple times today. When Netflix suggests a movie you actually want to watch, that’s AI. When Google Maps finds you a faster route to avoid a sudden traffic jam, that’s AI, too. It's already working behind the scenes in many of the apps you use every day.
The goal isn't to build a conscious machine like in the movies. It's about creating practical, smart systems that can sift through huge amounts of information, spot patterns we might miss, and make incredibly useful predictions.
Learning From Data (Just Like a Puppy)
Let's try a simple analogy. Imagine you're training a puppy. You don't give it a rulebook. Instead, you use rewards. You show it what to do, and when it sits, you say "good boy!" and give it a treat. When it chews on your shoes, you gently correct it. Through this process of trial and error, the puppy learns which actions lead to good things (like treats!).
AI systems learn in a similar way, but their "treats" and "lessons" come in the form of massive amounts of data. For an AI to learn how to identify a cat, it's not given a definition. Instead, it analyzes millions of pictures that humans have already labeled "cat." Each photo it sees helps it refine its internal pattern, making it better and better at its job.
This concept—learning from data—is the engine that makes modern AI work. The more good data you feed an AI system, the smarter and more capable it becomes.
“People often get caught up in the idea of sentient robots, but the reality of AI today is far more practical," says Dr. Anya Sharma, an AI researcher. "It's about pattern recognition at a scale humans can't achieve, which unlocks incredible new possibilities for everything from medicine to entertainment.”
That’s why getting a handle on AI is so important. It’s not some far-off sci-fi idea; it's a technology that’s already shaping our world. This guide is designed to demystify it all, giving you a clear, simple understanding of how it actually works.
AI At a Glance: Key Concepts Explained
To get started, let's break down the main building blocks of AI. This table gives you a quick snapshot of the key ideas we’ll explore.
| Concept | Simple Explanation |
|---|---|
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | The big-picture goal of making computers do things that normally require human intelligence. |
| Machine Learning (ML) | The most common way to achieve AI. It's about systems learning from data to find patterns and make predictions. |
| Neural Networks | A type of ML inspired by the human brain, used for more complex jobs like recognizing your face to unlock your phone. |
| Deep Learning | A more advanced version of neural networks with many layers, able to learn from huge amounts of data like videos or text. |
Think of these as the essential ingredients in the AI recipe. Understanding each one is the first step to seeing the bigger picture of what AI can do.
The Three Main Types of AI You Should Know
When most of us hear "artificial intelligence," our minds jump to a single, super-smart computer brain from a movie. But in reality, AI is more of a spectrum. It's helpful to think of it in three different stages of capability.
Right now, every single AI tool you've ever used fits into one specific category. The other two are still mostly in the realm of science and research, but they're key to understanding where this technology might be heading.
1. Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI)
This is the AI we have today. Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI), sometimes called "Weak AI," is designed to do one specific task—and do it incredibly well. It works within a very limited context and can't perform tasks outside of what it was trained for. "Weak" might sound like a put-down, but these systems are extremely powerful and often outperform humans at their one job.
You interact with ANI all the time. Here are a few practical examples:
- Your email's spam filter is a world-class detective for spotting junk mail, but it can't help you write a friendly reply.
- Spotify's recommendation algorithm can build a perfect playlist that feels like it read your mind, but it can't tell you the weather forecast.
- The face unlock on your phone is brilliant at recognizing you, but it can't recognize the song playing in the background.
Each of these is a specialist. They're amazing at their one job because they've been trained on tons of data related only to that specific function.
2. Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
This is where we start looking toward the future. Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) is the kind of AI that could understand, learn, and apply its knowledge to solve any problem, just like a human being. An AGI wouldn't need to be reprogrammed to take on a new challenge; it would be able to reason, adapt, and transfer its skills from one area to another.
As AI expert Kai-Fu Lee puts it, "AGI is the moment a machine can think as flexibly and intuitively as we do. It's the holy grail of AI research, but getting there is still one of the toughest puzzles in computer science."
An AGI could, in theory, learn to play the piano and then use its understanding of creative patterns to write a novel. This is the kind of AI you see in science fiction, and it's important to remember that a true AGI does not exist yet. We're still a long way off.
3. Artificial Superintelligence (ASI)
Finally, we have the most far-out concept: Artificial Superintelligence (ASI). This would be an intellect that is fundamentally smarter than the most brilliant human minds in virtually every field, from scientific creativity to social skills.
This is where the conversation gets very theoretical. An ASI wouldn't just be a little smarter; its intelligence would be on a level we can barely imagine. This raises huge ethical questions, making it a hot topic for philosophers and scientists. For now, ASI remains a purely theoretical idea that helps us think about the ultimate potential of what we're building.
How Does AI Actually Learn?
So, how does an AI go from being a blank slate to making smart predictions? It’s not magic, even though it can feel like it. The real engine behind most modern AI is a process called Machine Learning (ML).
Think about how you learn to ride a bike. You don't read a physics manual. You get on, you wobble, you fall, and you gradually figure out how to balance. You learn from experience. That's the core idea behind machine learning.
Instead of a programmer writing strict rules like, "if you see this, do that," they give the system a goal, feed it a lot of data, and let it figure out the patterns on its own. It's a shift from giving instructions to enabling a system to learn for itself, which is why AI can solve problems that are too complex for traditional programming.
The Building Blocks of AI Learning
To really get what's happening under the hood, let's look at three concepts that build on each other. Machine Learning is the foundation, but Neural Networks and Deep Learning are what unlock AI's most amazing abilities.
Let's use a simple example: teaching an AI to recognize a dog in a photo.
-
Machine Learning is the Basic Rulebook: This is the starting point. You show the computer thousands of pictures, some labeled "dog" and others "not a dog." The ML algorithm tries to find simple patterns—does it have floppy ears? A wagging tail? Fur? It learns a basic set of rules to make a guess.
-
Neural Networks are the Brain's Wiring: A Neural Network takes this a step further by mimicking the way our brain is structured. Instead of one big list of rules, it has layers of interconnected "neurons," each looking for a specific feature. One layer might spot ears, another might look for fur texture, and another identifies the shape of a nose. By working together, they form a much more detailed and accurate picture.
-
Deep Learning is the Expert's Intuition: Deep Learning is simply using very large, complex neural networks with many, many layers—that's where the name "deep" comes from. This is like a seasoned dog show judge who can identify a breed just by its posture. It’s not just recognizing individual features but understanding the very subtle and complex ways they fit together. This is how AI can do amazing things like understanding the nuance in our speech or powering a self-driving car.
"Grasping these three concepts is key to understanding AI today," notes a leading AI educator. "Machine Learning got the ball rolling, Neural Networks gave it a brain-like structure, and Deep Learning gave it the power to solve incredibly complex problems, like translating languages in real-time."
At the end of the day, each concept is just a more powerful version of the one before it, allowing AI to take on harder and harder challenges. The entire process of training these models is a fascinating journey, and you can see what it involves by looking at a complete machine learning workflow.
Visualizing the Core Concepts
This diagram helps show how these pieces fit together, from the broad field of AI down to its more specialized parts.
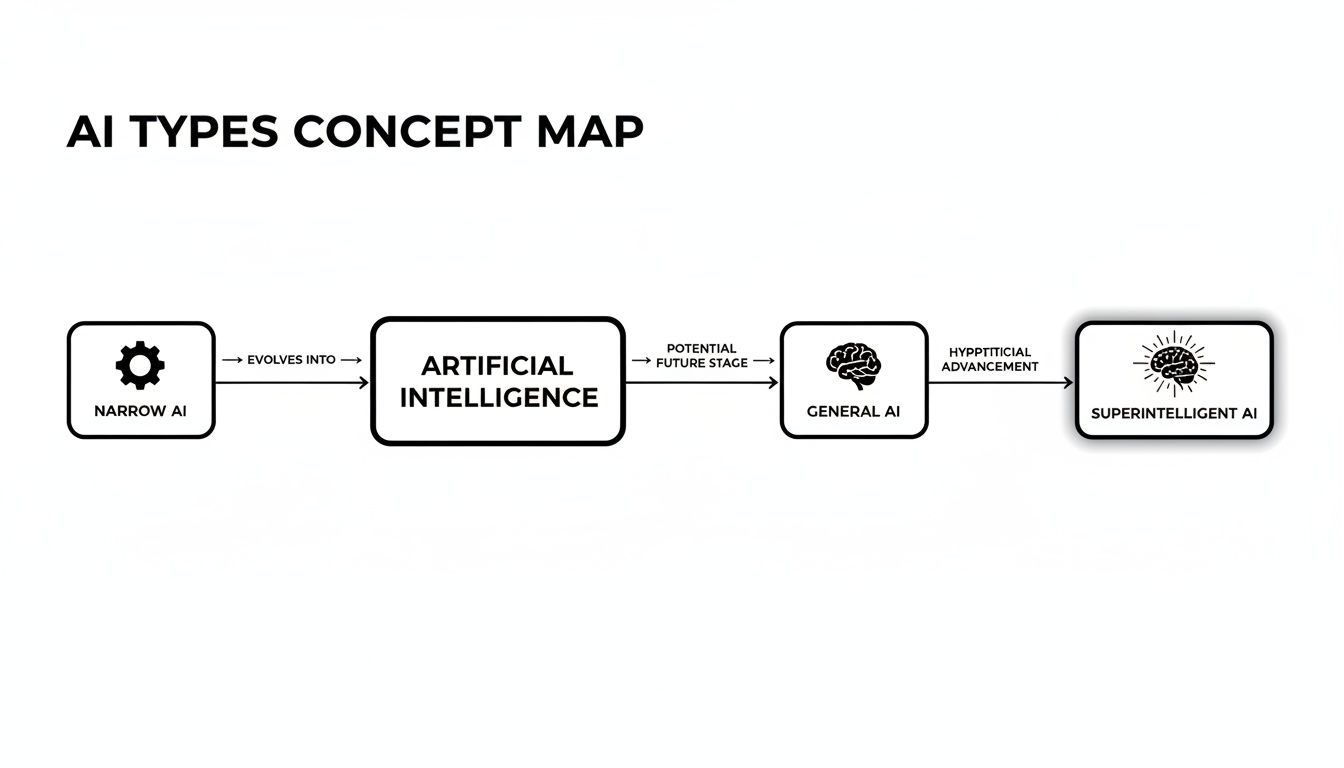
As you can see, Deep Learning is a specific type of Machine Learning, and Machine Learning is the main way we create Artificial Intelligence today. This is why you'll often hear people use these terms interchangeably, but now you know exactly how they all relate.
A Brief History of AI Milestones
Artificial intelligence didn't just pop up overnight. Its story is a long one, stretching back decades and filled with big ideas, amazing breakthroughs, and even some quiet periods known as "AI winters." Knowing this history helps explain why AI is suddenly everywhere.
The whole thing arguably kicked off in the summer of 1956 at the Dartmouth Conference. This is where computer scientist John McCarthy officially coined the term "artificial intelligence," giving a name to the ambitious idea that machines could one day think.
From Theory to a Game-Changing Victory
For a long time, AI was mostly an academic concept. Progress was slow, and during the "AI winters," funding dried up because the technology couldn't live up to the hype. But all that research was laying the groundwork for something huge.
That moment arrived in 1997. IBM's chess-playing computer, Deep Blue, faced off against world chess champion Garry Kasparov. In a stunning match, the machine won. Deep Blue could analyze an incredible 200 million positions per second, proving that an AI could master a game that requires deep, complex strategy—a skill once thought to be uniquely human.
This wasn't just a win in a game; it was a huge psychological turning point. It showed the world that machines could do more than just calculate. They could "strategize," firing up public imagination and bringing serious investment back into the field.
"Deep Blue's victory was about more than just a chess game," an industry veteran recalls. "It was a clear signal that the processing power and smart algorithms needed for real AI were finally here. It set the stage for the data-driven world we live in now."
Connecting the Past to the Present
The success of systems like Deep Blue, combined with the rise of the internet and much faster computers, created the perfect conditions for the next big leap. All that early research finally had the two things it was missing: massive amounts of data to learn from and the powerful hardware needed to process it.
This led directly to the deep learning boom of the 2010s. The ideas behind neural networks had been around for decades, but now scientists could finally train them on gigantic datasets. This is what powers the AI we use every day, from the facial recognition on our phones to the voice assistants in our homes.
Every one of these modern marvels stands on the shoulders of those early experiments. Each step, from the first conference to Deep Blue's triumph, was a crucial part of the story. You can explore more of these significant developments in our article on recent artificial intelligence breakthroughs.
AI at Work in Your Daily Life

AI isn't some far-off sci-fi concept; it's already woven into your daily routine, often working so smoothly that you don't even notice. In fact, you probably interact with dozens of AI systems before you've even had lunch. The best AI is designed to just make things a little bit easier.
Think about opening Netflix. That "Top Picks for You" row isn't a random guess. A specialized AI analyzes your viewing habits—what you watch, when you pause, and what you skip. It compares your tastes to millions of other users to make a solid prediction about your next favorite show. This is a perfect, practical example of Narrow AI doing one thing extremely well.
Spotify's "Discover Weekly" playlist works similarly. Its algorithms analyze the sound of the music you love—the tempo, key, and mood. It then finds other songs with a similar acoustic vibe and cross-references them with what other listeners like you enjoy. The result is a surprisingly personal mixtape that feels like it was made just for you.
From Entertainment to Navigation
This predictive power isn't just for fun; it's also what helps you get where you're going. When you open Google Maps, it isn't just showing you the shortest route. It’s predicting the fastest one right now.
To do this, it analyzes a massive, real-time stream of anonymous location data from other phones on the road. This allows it to spot traffic jams as they form and reroute you before you get stuck. It’s a classic machine learning system, always learning from fresh information.
"The best applications of AI often feel invisible," explains a tech journalist. "They don't announce themselves; they just seamlessly integrate into our lives to solve a problem, whether it's finding the perfect movie or avoiding a traffic jam."
The Rise of Conversational AI
Of course, some AI is much more front-and-center. The customer service chatbots you talk to online are a great example. These systems have been around for a while, starting with early experiments like ELIZA way back in 1966. But things really took off with the release of OpenAI's GPT-3 in 2020, a language model trained on a massive 175 billion parameters.
Its successor, ChatGPT, completely changed the game. It skyrocketed to 100 million users in just two months after its 2022 launch, becoming the fastest-growing app in history. You can trace this entire evolution in the history of AI and chatbots.
These examples help paint a clearer picture for anyone looking for artificial intelligence explained simply. It's not about walking, talking robots. It's about smart, data-driven systems built to make predictions that customize our entertainment, optimize our travel, and answer our questions.
The Big Questions About AI's Future
Whenever a powerful new technology comes along, it's natural to wonder where it's all heading. The conversation around AI is filled with both incredible excitement and some very real concerns. On one hand, AI has the potential to help us solve some of humanity's biggest problems.
Just think about it. AI models can help researchers find new medicines by spotting patterns in biological data that humans might miss. They can help us create more efficient energy grids to fight climate change. These aren't just sci-fi dreams; they're the kinds of breakthroughs that are now within reach.
But it's just as important to be realistic about the challenges. Many people are worried about jobs, and it's true that AI will automate certain tasks. There are also serious questions about data privacy and the risk of algorithmic bias, where an AI might accidentally learn and amplify unfair human prejudices from the data it's trained on.
Finding a Balanced Path Forward
Navigating this new world requires a thoughtful approach. Instead of seeing AI as some unstoppable force, it’s much more helpful to see it as a powerful tool that needs careful guidance from people. The key is responsible development.
This means we need to focus on a few core principles:
- Human Oversight: We need to keep people in the loop to make the final decisions and correct the AI when it makes mistakes.
- Transparency: We need to build systems that we can understand, so we know why an AI made a particular recommendation.
- Fairness: It's our job to actively look for and remove biases from the data we use to train these systems.
"The goal isn't to build an AI that thinks for us, but one that helps us think better," says one AI ethics expert. "The real future of AI lies in collaboration between human creativity and machine intelligence. Human oversight is non-negotiable."
Ultimately, the future of AI is in our hands. By focusing on ethical guidelines and responsible innovation, we can steer this technology toward a future that maximizes its benefits while keeping the risks under control. To get a more complete picture, check out our detailed guide on the various AI benefits and risks shaping this important conversation.
Your AI Questions Answered
Even after covering the basics, a few questions always pop up. Let's tackle some of the most common ones that people have when they're first learning about artificial intelligence.
Is AI the Same as Machine Learning?
That's a great question, and the short answer is no, but they're very closely related. The easiest way to think about it is to picture AI as the entire field of making computers intelligent.
Machine learning is the most popular tool we use right now to create that intelligence. It’s a part of AI where systems learn from data to make predictions, instead of a developer having to write code for every single possibility. So, most of the AI you see today is powered by machine learning.
Will AI Replace Human Jobs?
It's much more likely that AI will change jobs rather than outright replace them. AI is amazing at handling repetitive, data-heavy tasks, which frees up people to focus on things we do best: creativity, strategic thinking, and complex problem-solving.
"Think of it as a powerful assistant," one expert suggests. "The goal is to free up people to focus on more meaningful, creative, and strategic work, not to replace them."
Essentially, new jobs will pop up that involve managing and working alongside these AI systems.
How Can I Start Using AI Today?
Good news—you probably already are! Every time you use a navigation app, get a recommendation on a streaming service, or see your photos automatically organized, that's AI at work.
If you want to be more hands-on, start with something fun and easy. Try using a tool like ChatGPT to help you write an email or brainstorm ideas for a trip. The best way to begin is to find a small, routine task in your day and see if there's an AI tool designed to help with it.
Ready to continue your AI journey? At YourAI2Day, we provide the latest news, tools, and insights to help you understand and use artificial intelligence. Explore more by visiting our main site.