10 Latest Advancements in Artificial Intelligence for 2025
Ready to dive into the most exciting developments shaping our world? The field of artificial intelligence is moving at lightning speed, and it’s not just for tech wizards anymore. From creative tools that generate stunning images to intelligent assistants that can manage complex tasks, we’re witnessing a seismic shift in what technology can do. These breakthroughs are changing everything, from how businesses operate to how we express our creativity.
This article is your friendly, straightforward guide to the 10 most important and latest advancements in artificial intelligence that you need to know about right now. We’re cutting through the noise to bring you what truly matters.
You won't find dense, technical jargon here. Instead, we'll break down complex ideas like Multimodal LLMs and AI Agents into simple, understandable terms. We will show you real-world examples of these technologies in action and share expert insights to help you grasp not just what is happening, but why it's significant for you. Whether you're a business leader looking to innovate, a creator exploring new tools, or simply curious about the future, this list provides the essential knowledge you need. Let’s get started.
1. Large Language Models (LLMs) with Multimodal Capabilities
One of the most transformative recent advancements in artificial intelligence is the rise of multimodal Large Language Models (LLMs). Think of them as AI that can see and hear, not just read. These are not your typical text-only chatbots. Instead, models like OpenAI's GPT-4V, Google's Gemini, and Anthropic's Claude 3 can understand, process, and generate content across various formats, including text, images, audio, and even video. This allows for a much richer and more intuitive way to interact with AI.
This leap in capability unlocks new, practical applications. For instance, imagine snapping a picture of the inside of your fridge and asking, "What can I make for dinner with these ingredients?" A multimodal AI could identify the food items and suggest a recipe. Or, a business analyst could upload a report containing complex charts, and Claude 3 could interpret the visual data and summarize the key findings in text. This ability to fuse different data types is what makes multimodal LLMs a groundbreaking development.
How Multimodal LLMs Work
At their core, these models learn to find connections between different types of data. They map words to the visual concepts they represent, creating a unified understanding. The following infographic illustrates the basic process flow from input to output.
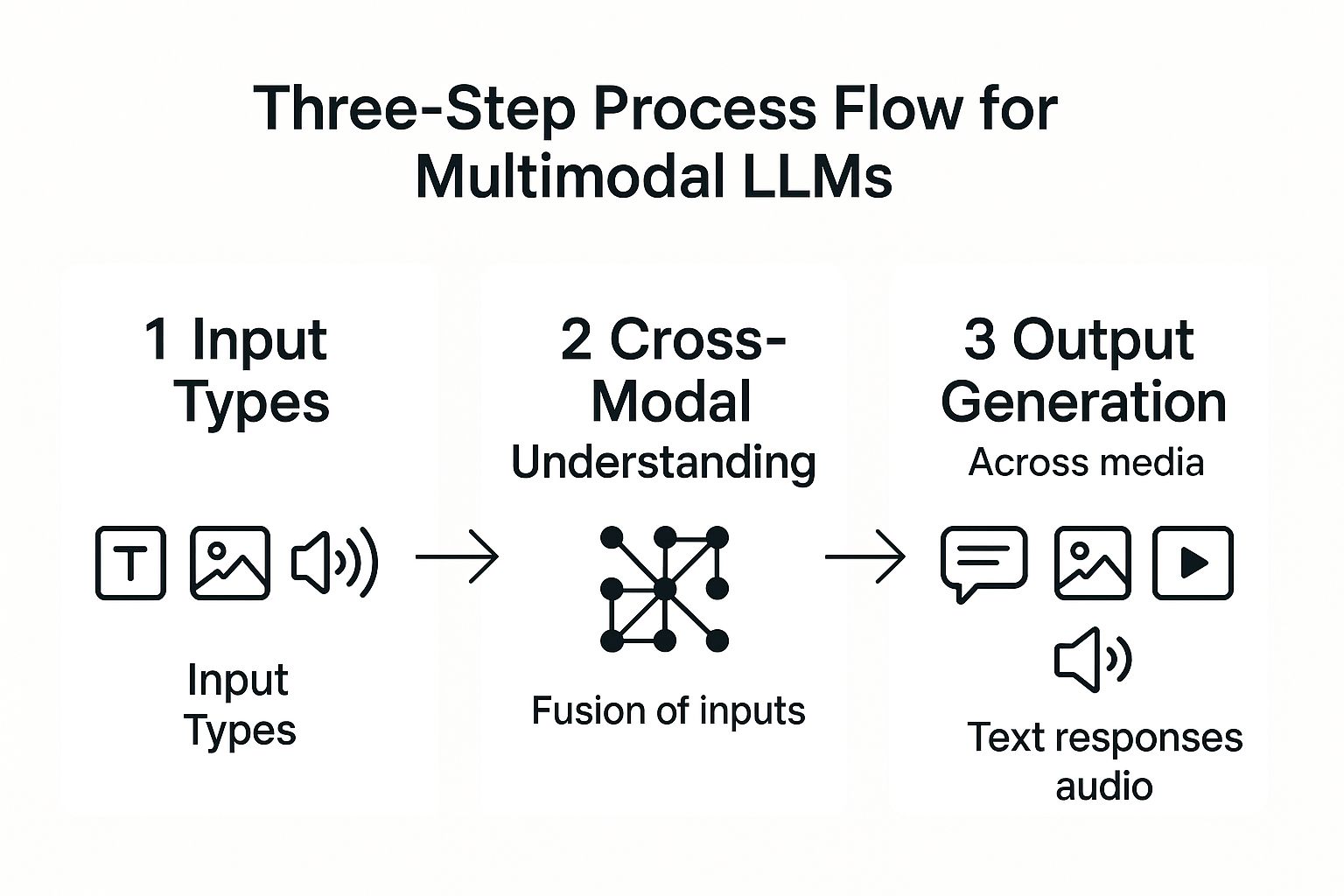
As shown, the process involves the AI seamlessly blending various inputs to produce a coherent, context-aware output.
Practical Tips for Using Multimodal AI
To get the most out of these powerful tools, follow these best practices:
- Provide Clear Context: When you upload an image or audio clip, tell the AI exactly what you want. For example, instead of just uploading a picture of a plant, ask, "What type of plant is this, and how much sunlight does it need?"
- Verify Critical Information: As Dr. Evelyn Reed, an AI ethics researcher, notes, "Multimodal AI is incredibly powerful, but it's still a tool, not an oracle. Always use your judgment, especially for important decisions." Double-check AI-generated analysis in high-stakes fields like medicine or finance.
- Consider Privacy: Be mindful of the data you share. Avoid uploading sensitive personal or proprietary information, as it may be used for model training.
2. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) Systems
One of the most practical latest advancements in artificial intelligence is the widespread adoption of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). In simple terms, RAG gives an AI a "cheat sheet" of up-to-date facts. It connects Large Language Models (LLMs) to live, external knowledge bases, addressing a core weakness of standard LLMs: their knowledge is frozen in time, leading to outdated or "hallucinated" answers. By dynamically fetching relevant, current information, RAG ensures AI responses are more accurate and trustworthy.
This is a game-changer for businesses. Imagine a customer service chatbot that, instead of giving generic answers, can instantly pull up your specific order details from the company's database and tell you exactly when it will arrive. That's RAG at work. Similarly, an internal HR bot can use RAG to access the latest company policy documents to give an employee a precise answer about their vacation benefits. RAG grounds the creative power of LLMs in factual, verifiable data.
How RAG Systems Work
RAG is a simple two-step process. First, when you ask a question, the system searches an external knowledge source (like a company's internal documents or a product database) for relevant information. Second, it gives that retrieved information to the LLM along with your original question. The model then uses this fresh context to generate a precise and informed answer. It’s like giving the AI an open-book test instead of making it rely on memory.
Practical Tips for Implementing RAG
To build an effective RAG system, consider these best practices:
- Curate Your Knowledge Base: The quality of your RAG system depends entirely on the quality of its "cheat sheet." Ensure your knowledge sources are accurate, well-organized, and regularly updated.
- Implement Smart Indexing: Use a vector database to convert your documents into numerical representations (embeddings). This allows for incredibly fast and efficient searches to find the most relevant information for any given query.
- Refine Your Retrieval Process: "The magic of RAG is in the retrieval," says AI architect Ben Carter. "You have to fine-tune how the system finds information. Too little context, and the AI is guessing; too much, and it gets confused." Continuously test and adjust your system for the best results.
3. AI Agents and Autonomous Systems
Another of the latest advancements in artificial intelligence is the emergence of sophisticated AI agents. Think of them as AI "doers," not just AI "talkers." They go far beyond simple command-and-response. Instead, they can plan, reason, and execute complex, multi-step tasks with minimal human help. These agents can use different digital tools, APIs, and websites to achieve a goal, marking a big shift from reactive AI to proactive, goal-oriented intelligence.
This is where AI gets really useful. For example, you could tell an AI agent, "Plan a weekend trip to San Francisco for two people on a $500 budget, focusing on historical sites." The agent could then browse for flights, find affordable hotels, look up museum hours and ticket prices, and present you with a complete itinerary. In business, an agent could automate processing an invoice by reading it, checking it against a purchase order, and scheduling the payment.

How AI Agents Work
Autonomous AI agents operate on a loop: they plan, act, and check their work. They take a big goal and break it down into smaller, manageable steps. Then, the agent uses the tools it has (like a web browser or a calculator) to complete each step, looks at the result, and adjusts its plan until the final goal is met. This capability has fueled many innovative artificial intelligence startup ideas focused on hyper-automation.
Practical Tips for Using AI Agents
To effectively leverage these autonomous systems, consider the following best practices:
- Start with Narrow Tasks: Begin by giving the agent a very clear, simple goal. For example, ask it to "summarize the top three news articles about AI today" before you try a bigger task like "create a complete marketing plan."
- Implement Safety Mechanisms: Since these agents can act on their own, it's crucial to set up guardrails. Set clear limits and have a "stop button" to halt the agent if it starts doing something unexpected.
- Test in Controlled Environments: As tech strategist Maria Flores advises, "Never let an autonomous agent loose on your critical systems without testing it in a sandbox first. Treat it like a new employee you need to train and supervise."
4. Edge AI and On-Device Processing
A significant shift in the latest advancements in artificial intelligence involves moving the "thinking" from the cloud directly onto your devices. This trend, known as Edge AI, puts powerful AI models right on your smartphone, car, or smart speaker. This enables real-time data processing without needing an internet connection, making AI faster, more private, and more reliable in our daily lives.
By running AI on-device, applications can respond instantly. For example, the face unlock on your phone works in a split second because the AI is running locally—it doesn't need to send your picture to a server. Similarly, the safety features in modern cars, like automatic emergency braking, use Edge AI to analyze sensor data and react to road conditions in milliseconds. This localized intelligence is becoming more powerful and efficient than ever before.
How Edge AI Works
Edge AI uses highly optimized, "lightweight" machine learning models that can run on the limited power of a local device. Think of it like a compressed file—it has most of the important information but takes up much less space. This allows complex tasks, which once required a powerful data center, to be performed directly on the hardware in your hand, ensuring instant responses and keeping your personal data on your device.
Practical Tips for Implementing Edge AI
To successfully deploy AI on edge devices, consider these best practices:
- Use Model Quantization: This technique reduces the size of your AI models, which is crucial for making them fit on devices with limited memory and power, like a smartwatch.
- Optimize for Specific Hardware: "You wouldn't run the same software on a laptop and a smartphone," says robotics engineer Kenji Tanaka. "Similarly, you need to tailor your AI models for the specific chip in the device to get the best performance."
- Consider a Hybrid Approach: For very complex tasks, you can mix edge and cloud processing. For example, your smart home camera could use Edge AI to detect motion (a quick, simple task) and then send only that specific clip to the cloud for more advanced analysis, like identifying a person.
5. Generative AI for Code (AI-Powered Development)
Generative AI for Code is like having a super-smart programming partner available 24/7. It uses advanced AI to understand, write, and debug code. Tools like GitHub Copilot and Amazon CodeWhisperer can automatically write repetitive code, suggest fixes for bugs, and even build entire functions from a simple description you write in plain English. This advancement is one of the latest advancements in artificial intelligence that empowers developers to focus on creative problem-solving instead of tedious syntax.
How Generative AI for Code Works
These tools have been trained on billions of lines of public code. They learn the patterns and structures of different programming languages. When you start typing, the AI predicts what you're trying to do and suggests the next block of code, effectively "completing your thought" in real-time.
Examples of AI-Powered Development Tools
- GitHub Copilot in VS Code for context-aware code completion
- Amazon CodeWhisperer optimized for AWS development
- Tabnine offering AI-driven suggestions across IDEs
- Replit Ghostwriter for real-time collaborative coding
Practical Tips
“Use clear comments to guide the AI, almost like you're giving instructions to a junior developer. But always, always review and test the code it generates. It's a powerful assistant, not a replacement for your expertise,” suggests Alex Chen, Senior AI Engineer at TechLabs.
- Review and test AI-generated code thoroughly
- Be specific in your comments and prompts
- Combine AI suggestions with your own knowledge
When and Why to Use AI-Powered Development
Use these tools to speed up routine tasks, like setting up a new project or writing standard functions. It's especially useful for learning a new programming language or getting unstuck when you have a bug.
Learn more about Generative AI for Code (AI-Powered Development) on domain.com
6. Diffusion Models for Content Creation
One of the most visually stunning recent advancements in artificial intelligence is the rise of diffusion models. These are the engines behind incredible AI image generators like DALL-E 3, Midjourney, and Stable Diffusion. They can create breathtakingly high-quality images, videos, and even audio from just a simple text description. It's like having a world-class artist on call who can bring any idea to life in seconds.
This technology has opened up creativity to everyone. A small business owner can now generate unique images for their social media posts without hiring a photographer. An author can create concept art for their characters, and a musician can generate album covers. This shift from manual creation to AI-powered generation is a massive breakthrough for creative industries.
How Diffusion Models Work
Imagine a clear photograph. Now, imagine slowly adding tiny bits of static or "noise" to it until it's completely unrecognizable. Diffusion models are trained to do the exact reverse. They start with a field of random noise and, guided by your text prompt, carefully remove the noise step-by-step to "uncover" a brand new, coherent image. This gradual refinement process is what allows for such detailed and realistic results.
Practical Tips for Using Diffusion Models
To create compelling content with these tools, try these best practices:
- Be Highly Specific: The more detail you give, the better the result. Instead of "a car," try "a futuristic, sleek, red sports car driving on a rain-slicked neon-lit city street at midnight."
- Use Negative Prompts: Tell the model what you don't want. Adding a negative prompt like "no extra limbs, blurry, text" can help clean up the final image and remove common AI mistakes.
- Iterate and Experiment: Don't expect perfection on the first try. Tweak your prompts, try different styles, and generate several versions. As digital artist Chloe Park says, "The best AI art comes from a conversation with the model. You suggest an idea, it shows you something, and you refine it together." For more options, explore various AI tools for content creation on yourai2day.com.
7. Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF)
A major breakthrough in making AI models more helpful and safe is Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF). In short, this is the training method that teaches AI good manners. It goes beyond just feeding AI raw data by adding human judgment to align the model’s behavior with our values. It’s the reason why models like ChatGPT can decline harmful requests and provide polite, conversational answers, marking a significant step in the latest advancements in artificial intelligence.
This alignment process is crucial for building trust. By having humans rank different AI-generated answers, developers can fine-tune the model to be more helpful, harmless, and honest. A practical example is when a chatbot gives two different answers and a human trainer picks the better one. The AI learns from this choice. This method is key to creating safer, more reliable AI assistants that you'd actually want to talk to.
How RLHF Works
The process starts by creating a "reward model" based on human preferences. Humans are shown several AI-generated responses to the same prompt and are asked to rank them from best to worst. The reward model learns to predict which kinds of answers humans prefer. Then, the main AI model is trained to get the highest possible score from this reward model, effectively steering it toward better behavior.
Practical Tips for Implementing RLHF
To effectively use RLHF for model alignment, consider these best practices:
- Ensure Diverse Feedback: Use a wide group of human trainers from different backgrounds to avoid teaching the AI a narrow set of biases.
- Implement Quality Control: As lead AI safety researcher Dr. Anya Sharma states, "The quality of your AI's behavior is a direct reflection of the quality of the human feedback it receives. Clear guidelines for trainers are non-negotiable."
- Balance Multiple Objectives: It's a constant balancing act. You have to train the AI to be helpful, safe, and factually accurate all at once. Focusing too much on one can sometimes make the others worse.
8. Mixture of Experts (MoE) Architecture
One of the most significant recent advancements in artificial intelligence isn't a new model but a smarter way to build them: the Mixture of Experts (MoE) architecture. Instead of one huge, "know-it-all" AI trying to handle every question, MoE uses a team of smaller, specialized "expert" networks. A smart "router" looks at your request and sends it to the best expert for the job. This lets models become incredibly powerful without becoming slow and inefficient.
This is a huge deal for efficiency. It means we can build smarter AI without needing way more computing power for every single task. It's widely believed that top models like GPT-4 use this design. For example, when you ask a coding question, the router sends it to the "programming expert," while a question about poetry goes to the "creative writing expert." The other experts stay inactive, saving a massive amount of energy.
How MoE Works
MoE is a "divide and conquer" strategy. The router first analyzes your request and decides which of its many specialists is the best fit. Only the chosen experts are "woken up" to process the request, while the others remain dormant. This selective activation is the secret to its efficiency and a key part of the latest advancements in artificial intelligence.
Practical Tips for Implementing MoE
For developers working with this architecture, optimizing performance is key:
- Ensure Load Balancing: It's important to make sure the router is spreading the work out evenly. You don't want one expert getting all the requests while others do nothing.
- Monitor Expert Utilization: Keep an eye on which experts are being used. "If one expert is never getting picked, it might mean the router needs retraining, or that the expert itself isn't very good," explains data scientist Omar Rashid.
- Use Auxiliary Losses: During training, developers add a secondary goal that encourages the router to use a wider variety of experts. This helps ensure all the experts are well-trained and ready to contribute.
9. Neural Architecture Search (NAS) and AutoML
Neural Architecture Search (NAS) and AutoML are making it easier for everyone to use AI. Think of them as an "AI that builds other AI." They automate the incredibly complex and time-consuming process of designing an effective neural network. What used to take a team of experts weeks of manual work can now be done in hours. This means more people and smaller companies can create high-quality AI models without needing a PhD.
These systems work by trying out thousands of different network designs to find the one that works best for a specific task, like identifying cats in photos or predicting stock prices. They automatically test and tweak the designs, learning over time what makes a good AI model.
How NAS and AutoML Work
NAS systems generally follow a simple loop:
- Suggest: Come up with a potential AI model design.
- Test: Train the design on some data and see how well it performs.
- Learn: Keep the good designs and use what was learned to make better suggestions next time.
AutoML platforms wrap this entire process into a user-friendly package, helping with everything from preparing the data to deploying the final model.
“AutoML is breaking down the barriers to AI,” says Dr. Lina Perez, a machine-learning researcher. “It allows a small business to build a custom AI solution that, just a few years ago, would have only been possible for a tech giant.”
Real-World Examples
- Google AutoML: Lets you upload your images or text and automatically builds a custom model.
- EfficientNet: A family of highly efficient AI models for image recognition that were discovered by NAS.
- Microsoft NNI: An open-source toolkit for developers to automate their AI experiments.
- Amazon SageMaker Autopilot: An end-to-end AutoML service that handles all the heavy lifting.
Practical Tips for NAS and AutoML
- Be very clear about your goal and your budget before you start.
- Use smaller datasets for initial experiments to save time and money.
- Give the system hints based on what you already know about your data.
- Always test the final AI model thoroughly before using it for real-world decisions.
10. Quantum-Classical Hybrid AI Systems
One of the most forward-looking advancements in artificial intelligence is the mashup of quantum and classical computing. These hybrid AI systems use the best of both worlds. Regular computers handle most of the work, but they pass off the super-tricky parts to a quantum processor. Quantum computers are brilliant at solving specific, mind-bogglingly complex problems that would take a normal supercomputer millions of years. This approach promises massive speedups for certain AI tasks.
This is opening up new possibilities in fields like medicine and finance. For instance, a drug company could use a hybrid system to simulate how molecules interact, dramatically speeding up the search for a new cure. A bank could use it to find the absolute best investment strategy out of trillions of possibilities. While still in its early days, this technology represents a peek into the future of computation.
How Quantum-Classical Hybrid AI Works
A hybrid system is like a manager and a specialist. The classical computer (the manager) runs the show and identifies a part of the problem that's perfect for a quantum computer. It sends that specific task to the Quantum Processing Unit (the specialist). The QPU uses weird quantum physics principles to explore a huge number of possible solutions all at once. Once it finds the best one, it sends the answer back to the classical computer to finish the job.
Practical Tips for Exploring Quantum AI
To get started with this emerging technology, consider these best practices:
- Focus on Specific Problems: Don't try to use quantum AI for everything. It's only good for very specific types of problems, like optimization or complex simulations.
- Start with Simulators: "Before you even think about using real quantum hardware, play around with simulators," recommends physicist Dr. Samuel Jones. "They run on your regular computer and are a great way to learn how to build quantum algorithms without the cost and complexity."
- Collaborate with Experts: Quantum computing is a deeply specialized field. Partner with experts to guide your experiments and help you understand the results.
- Leverage Cloud Platforms: You don't need to build your own quantum computer. Services like Azure Quantum or Amazon Braket let you access and experiment with quantum hardware through the cloud.
Latest AI Advancements Comparison Matrix
| Item | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements 🔄 | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Large Language Models (LLMs) with Multimodal Capabilities | High: requires advanced multimodal frameworks and GPUs | Very high: needs high-performance GPUs, large memory | Natural, comprehensive AI-human interaction; better reasoning | Complex multimedia processing, medical imaging, customer service | Broad application; enhanced context understanding; real-time multimodal processing |
| Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) Systems | Medium-high: involves integration of retrieval and generation | Moderate to high: external databases, vector search systems | Up-to-date, accurate, and contextually relevant responses | Domain-specific Q&A, enterprise knowledge retrieval, reducing hallucinations | Dynamic factual accuracy; customizable knowledge sources; reduced AI errors |
| AI Agents and Autonomous Systems | High: complex multi-step planning and integration | High: depends on tool/API integration and monitoring | Automated execution of complex tasks with minimal human intervention | Workflow automation, autonomous research, business process automation | Goal-oriented autonomy; 24/7 operation; improved efficiency and consistency |
| Edge AI and On-Device Processing | Medium: requires model optimization and hardware adaptation | Low to medium: edge devices with limited compute | Real-time, privacy-preserving AI without cloud dependency | Mobile AI, IoT devices, scenarios needing low latency and offline use | Low latency; enhanced privacy; reduced bandwidth; offline capability |
| Generative AI for Code (AI-Powered Development) | Medium: integrates into development environments with AI models | Moderate: runs on developer machines or cloud IDEs | Increased developer productivity; faster coding and debugging | Software development, code generation, bug fixing, education | Significantly boosts coding speed; lowers entry barrier; 24/7 assistance |
| Diffusion Models for Content Creation | High: requires extensive training on large datasets | High: computationally intensive for training and inference | High-quality, controllable generation of images, video, audio | Artistic content, design, media production, creative experimentation | Exceptional realism; versatile media support; fine control over output |
| Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) | High: complex training pipeline with human annotation | High: human effort for feedback and computational resources | Safer, more aligned, and context-appropriate AI behavior | AI safety, ethical alignment, conversational agents | Improved alignment; reduced bias and harm; better user trust |
| Mixture of Experts (MoE) Architecture | High: complex routing and load balancing | High: multiple expert networks and memory storage | Scalable, efficient models with specialized expertise | Large-scale language modeling, multi-task learning, efficiency-focused AI | Massive parameter scalability; efficient computation; task specialization |
| Neural Architecture Search (NAS) and AutoML | High: requires automated search algorithms and tuning | Very high: computationally expensive during search | Optimal, customized architectures with reduced development time | Model design automation, enterprise ML, hardware-aware optimization | Democratizes ML; discovers novel architectures; saves development effort |
| Quantum-Classical Hybrid AI Systems | Very high: early-stage hybrid algorithm development | Very high: quantum hardware access and classical compute | Potential exponential speedups in optimization and pattern recognition | Specialized optimization, cryptography, drug discovery, finance | Quantum speedup potential; novel problem-solving approaches; future-ready designs |
What's Next on the AI Horizon?
The journey through the latest advancements in artificial intelligence reveals a landscape buzzing with transformative potential. We've explored everything from the game-changing multimodal capabilities of Large Language Models, which now understand images and sounds, to the precision of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) that grounds AI responses in factual data. These are not distant, futuristic concepts; they are tangible tools actively reshaping industries and our creative processes.
The overarching theme is clear: AI is becoming more specialized, efficient, and autonomous. Autonomous AI agents are starting to tackle complex, multi-step tasks on our behalf, while Edge AI brings powerful processing directly to our devices, ensuring speed and privacy. For developers, generative AI for code is not just a helper but a genuine collaborator, accelerating innovation at an unprecedented scale. Similarly, diffusion models have democratized content creation, turning simple text prompts into stunning visual art and media.
Your Path Forward in the AI Revolution
Understanding these breakthroughs is the first step, but engaging with them is where the real value lies. The key takeaway is that the barrier to entry for leveraging powerful AI is lower than ever. You don't need to be a data scientist to benefit from these innovations.
Here are some actionable next steps to turn this knowledge into practice:
- Experiment with Multimodal Tools: Start using AI assistants that can interpret images or documents. Try uploading a picture of your refrigerator's contents and ask for a recipe, or have an AI summarize a complex chart from a PDF. This hands-on experience builds practical intuition.
- Explore AI-Powered Development: If you're a coder or aspiring to be one, integrate a tool like GitHub Copilot into your workflow. See firsthand how it can streamline debugging, suggest code blocks, and help you learn new programming languages more efficiently.
- Engage with AI Agents: Test a simple AI agent to automate a personal task, like planning a trip itinerary or organizing your digital files. Observing how these systems break down goals into executable steps is the best way to grasp their power.
The most crucial insight is that these individual advancements are beginning to converge. An autonomous agent might leverage a Mixture of Experts (MoE) model for efficiency, use RAG to pull in real-time information, and employ diffusion models to generate a report with custom visuals. This synergy is what defines the current wave of latest advancements in artificial intelligence, making it an incredibly exciting time to be involved. By staying curious and proactive, you position yourself not just as a spectator but as an active participant in shaping the future.
Ready to move from theory to application? The world of AI changes daily, but you don't have to navigate it alone. YourAI2Day is your dedicated resource for practical guides, tool reviews, and the latest news, all broken down for easy understanding. Stay ahead of the curve and discover how to implement these advancements today by visiting YourAI2Day.







