Machine Learning for Data Analysis Made Simple
Ever feel like you're sitting on a locked treasure chest of data? You know valuable insights are hiding inside, but you just can't seem to find the key. If that sounds familiar, you're in the right place. This guide is all about machine learning for data analysis—think of it as a master key that unlocks patterns and predicts future trends you can't see with the naked eye.
Why Your Data's Best Story Is Still Unwritten

If you're surrounded by spreadsheets and dashboards, you're not alone. Most businesses today are swimming in information, from customer purchase histories to website clicks. Traditionally, data analysis has been about looking backward—running reports that tell you what happened last quarter or which products were top sellers. It’s useful, but it’s a bit like driving while only looking in the rearview mirror.
Machine learning completely changes the game. Instead of just summarizing the past, it teaches computers to find hidden connections in your data and make intelligent predictions about the future. This turns your data from a static record into an active, strategic tool that can help you get ahead.
From Detective Work to Fortune Telling
Think of a traditional data analyst as a skilled detective. They sift through evidence (data) to piece together the story of what happened. This is incredibly valuable for understanding performance and spotting historical trends.
Machine learning, on the other hand, adds a fortune-teller to your team. After the detective figures out what happened, the machine learning model can predict what will likely happen next. It learns from every past sale, customer interaction, and market shift to forecast future outcomes with stunning accuracy.
For example, a traditional report might show you that sales dipped in June. A machine learning model can go a step further and flag the specific customers most likely to stop buying next month, giving you a chance to step in with a special offer and prevent it.
"Your job will not be taken by AI. It will be taken by a person who knows how to use AI. So, it is very important for marketers to know how to use AI."
– Christina Inge, Marketing Analytics Expert
Unlocking Practical Business Insights
This isn't just abstract theory; it's about solving tangible business problems. The main idea is to automate the discovery of meaningful patterns that would be impossible for a human to spot. To get there, you can use a few different strategies. For a deeper dive, check out our guide on understanding AI technology and see how all the pieces fit together.
Here are just a few ways businesses are putting machine learning to work right now:
- Predicting Customer Churn: It can identify the subtle behaviors of customers at risk of leaving, giving you a crucial window to win them back.
- Forecasting Sales Demand: Companies can manage inventory more effectively by predicting product demand, which cuts down on both waste and lost sales.
- Personalizing Experiences: This is the magic behind Netflix’s show recommendations and Amazon’s “you might also like” suggestions.
At its core, you're teaching a computer to become an expert on your specific business data. You don't need a PhD in statistics to get the concept. The goal is simple: make smarter, faster, and more confident decisions by letting the data tell its most important stories.
How Machine Learning Actually Learns From Your Data
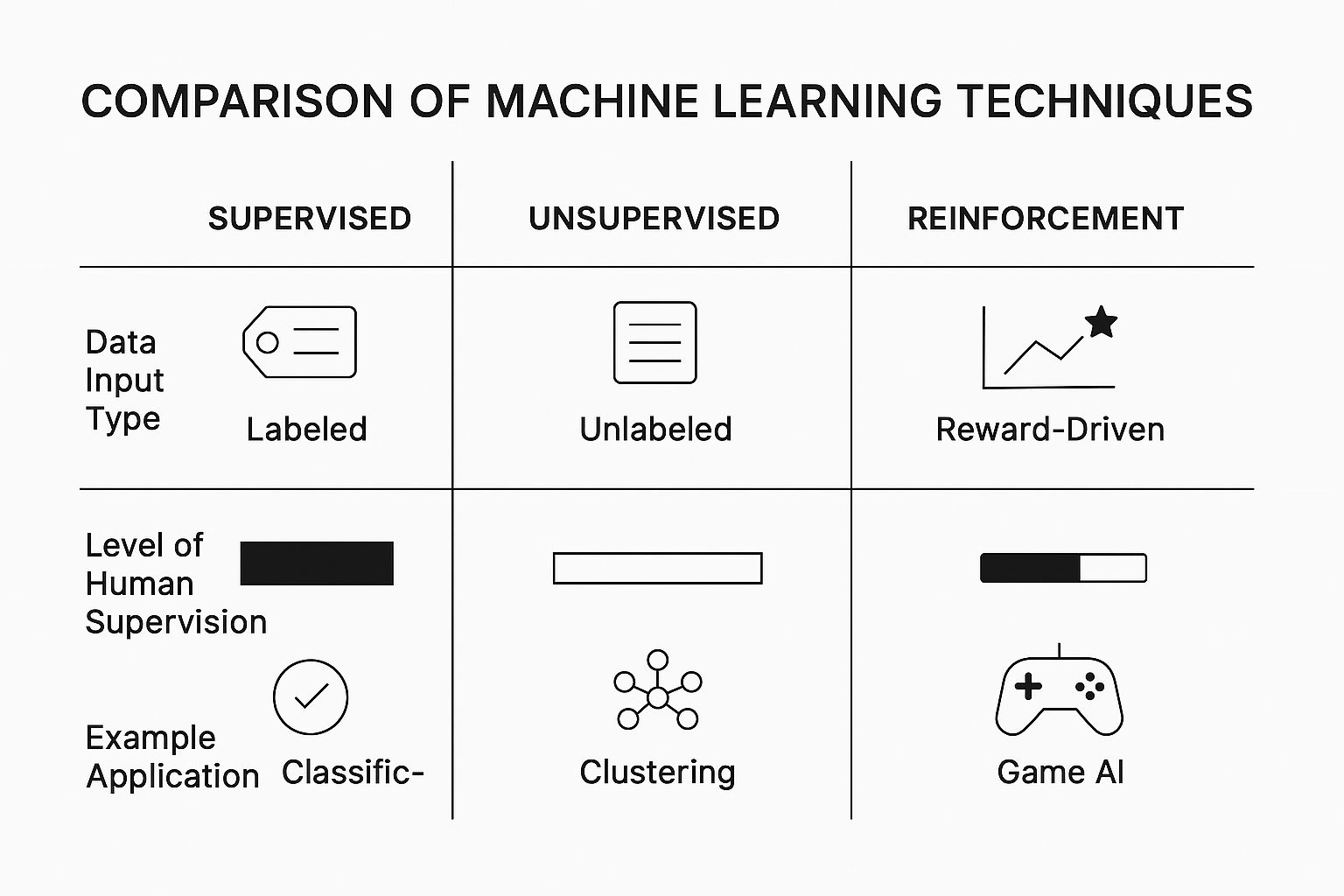
So, what does the "learning" part of machine learning really mean? It’s not some abstract magic. It's more like teaching a new skill, and just like with people (or puppies!), there are different teaching methods for different goals. When it comes to machine learning for data analysis, we generally rely on three core training styles.
Supervised Learning: Learning by Example
The most common approach is what we call supervised learning. Think of it as teaching a student with an answer key. You give the algorithm a huge dataset where the correct answers are already known—or "labeled."
A perfect real-world example is the Zestimate feature on Zillow. To predict a home's value, their model is fed a massive amount of historical sales data. Each house in the dataset has features (like square footage, number of bedrooms, zip code) and a label (the price it actually sold for). By analyzing millions of these examples, the model learns the intricate patterns connecting features to the final sale price, enabling it to make surprisingly accurate predictions for new, unlisted homes.
Unsupervised Learning: Finding Hidden Patterns
Next, we have unsupervised learning. This is more like giving a child a box of LEGOs without any instructions. They'll naturally start sorting the bricks by color, size, or shape, creating their own logical groups. They discover the structure on their own.
Unsupervised learning algorithms do the same with unlabeled data. Their goal isn't to predict a known outcome but to explore the data and uncover hidden patterns or natural groupings. For instance, Spotify uses this to power its "Discover Weekly" playlists. The algorithm analyzes your listening history, clusters you with users who have similar tastes, and then recommends songs popular within that cluster that you haven't heard yet. It’s a powerful tool for discovery.
"The real power of unsupervised learning lies in discovery, not prediction. It helps you answer questions you might not have known to ask by revealing the inherent structure in your data."
– Dr. Ava Chen, AI Researcher
Each learning style has a different starting point and goal, depending on the data you have and what you want to achieve.
The key difference really boils down to whether the algorithm learns from a "correct answer" or is left to find the patterns for itself.
Reinforcement Learning: Learning from Experience
Finally, there’s reinforcement learning. This is all about trial and error, much like learning to play a video game. You don't know the best moves at first. Instead, you try things, score points for good actions (rewards), and lose points for bad ones (penalties). Over time, you learn which sequence of actions leads to the highest score.
This reward-driven system is ideal for training an algorithm to make optimal decisions in a complex, dynamic environment. The AI that plays a game like Chess or Go is a classic example. It isn't explicitly programmed with every strategy. It learns by playing against itself millions of times, constantly refining its approach to maximize its "reward"—winning the game. This process has led AI to discover strategies that human grandmasters never even considered.
To help clarify these distinct approaches, here’s a simple breakdown.
Three Core Types of Machine Learning
| Learning Type | What It Does | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Supervised | Learns from labeled data to make predictions. | Predicting house prices from historical sales data. |
| Unsupervised | Finds hidden structures in unlabeled data. | Customer segmentation for targeted marketing. |
| Reinforcement | Learns through trial and error to achieve a goal. | Training an AI to master a strategic game like Go. |
Understanding these three methods is the first step to seeing just how powerful machine learning can be. These techniques are at the heart of the booming data analytics market, which was valued at USD 50.04 billion in 2024 and is projected to skyrocket to USD 658.64 billion by 2034. You can discover more insights about this trend and see how it's reshaping entire industries.
Meet the Algorithms in Your Data Analysis Toolkit
If learning styles are the different strategies for thinking, then algorithms are the specialized tools you pull out of your machine learning for data analysis toolbox. Think about it like a carpenter's workshop. You wouldn't use a sledgehammer to drive a finishing nail, and you wouldn't use a screwdriver to cut a plank of wood. Each tool has a specific job, and knowing which one to grab is half the battle.
Let's get to know the "workhorses" of machine learning—the algorithms that do the heavy lifting in any analysis. We're not going to get lost in the weeds with complex math or code. Instead, we’ll focus on what these tools do and, more importantly, what kind of real-world problems they're built to solve.
Linear Regression: Predicting the Future with a Straight Line
Let's start with a classic: Linear Regression. Don't let the name throw you off; the idea behind it is incredibly simple. It's all about finding a straight-line relationship between two things.
Imagine plotting your daily ice cream sales against the temperature. You'd probably see a clear pattern: as the temperature climbs, so do your sales. Linear Regression is the tool that draws the "best-fit" line right through that scattered data.
Once you have that line, you can start making educated guesses. If the forecast calls for a 90-degree day next Tuesday, you can follow your line to estimate how many ice cream cones you're likely to sell. It's a simple but surprisingly powerful way to forecast numbers.
Where you might see it in action:
- Sales Forecasting: Predicting next quarter's revenue based on how much you plan to spend on marketing.
- Real Estate: Estimating a house's price based on its square footage.
- Resource Planning: Forecasting electricity demand based on the time of year and expected weather patterns.
This algorithm is your go-to when you need to answer questions like "how much?" or "how many?" It’s a foundational piece of any analyst's kit, providing clear, quantifiable predictions.
Decision Trees: Making Choices with Simple Rules
What if your problem isn't about predicting a number but about making a clear-cut decision? That's where Decision Trees come in. A Decision Tree works a lot like a game of "20 Questions," asking a series of simple yes-or-no questions to land on a final answer.
Think about how a bank might decide whether to approve a small loan. A decision tree model would break it down step-by-step:
- Is the applicant's credit score above 650? (Yes/No)
- If yes, is their annual income over $50,000? (Yes/No)
- If yes again, have they been at their current job for more than a year? (Yes/No)
Each question splits the data into branches, creating a flowchart that’s incredibly easy for anyone to follow. The final "leaves" of the tree give you the outcome, like "Approve Loan" or "Deny Loan."
"The real beauty of Decision Trees is their transparency. You can literally trace the path the model took to reach its conclusion. This makes it so much easier to explain the results to stakeholders who aren't data experts and builds trust in your findings."
– Ben Carter, Lead Data Scientist
This clarity makes them a favorite in fields where being able to explain your reasoning is non-negotiable, like finance and healthcare.
K-Means Clustering: Finding Your Tribes
So far, we’ve talked about supervised algorithms, which need neatly labeled data to learn. But what if you’re just sitting on a mountain of raw customer data and want to find the natural groupings hidden within it? That's a job for K-Means Clustering, a star of the unsupervised learning world.
Imagine you're a marketer with 10,000 customers. Creating a unique campaign for every single person is impossible. K-Means helps you automatically segment them into a specific number (K) of distinct groups, or "clusters," based on who they are and what they do.
For example, you could ask the algorithm to find three clusters (K=3) in your customer base. It might come back with:
- Cluster 1: High-spending, frequent shoppers who gravitate toward premium products.
- Cluster 2: Budget-conscious buyers who only show up during major sales events.
- Cluster 3: New customers who have only made one or two small purchases.
All of a sudden, your messy data is organized into actionable personas. You now have three distinct audiences you can speak to with tailored messages, making your marketing far more effective. K-Means is fantastic for discovering the hidden structure in your data, helping you move from a one-size-fits-all approach to something much more personal and effective.
Your First Data Analysis Project: From Messy to Meaningful

The theory is great, but what does this all look like when the rubber meets the road? Let's walk through a typical machine learning project to make the whole process feel more grounded. This journey—from a messy spreadsheet to a smart business decision—is the real heart of machine learning for data analysis.
To keep things concrete, let's imagine a local café wants to predict its busiest hours to build a better staff schedule. They've got a year's worth of sales data but no clue how to turn it into an actionable plan.
Step 1: Prepping the Data
Before we can even dream of using a fancy algorithm, we have to roll up our sleeves and tackle the most critical—and often, most tedious—step: getting the data ready. Raw data is almost always a mess. It’s like trying to cook a gourmet meal with ingredients still covered in dirt.
For our café, their raw data probably has all sorts of problems:
- Missing Values: Maybe a cashier forgot to log the customer count for a few hours.
- Inconsistent Formats: Some dates might look like "Jan 5, 2023" while others are "01-05-2023."
- Outliers: A simple typo could record 500 customers in an hour instead of the actual 50.
This initial cleanup is all about fixing these issues. We fill in the gaps, standardize the formats, and correct the obvious errors. It's tedious work, but it ensures our model learns from accurate information. The old saying, "garbage in, garbage out," is the golden rule here.
Step 2: Choosing and Training the Model
With our data finally clean and organized, it's time to pick the right tool for the job. The café wants to predict a number—the number of customers per hour. As we covered earlier, that's a classic regression problem. A simple Linear Regression model is a fantastic place to start.
Training the model is a bit like showing it thousands of flashcards. We feed our cleaned historical data into the algorithm, and it starts looking for connections. The model analyzes how different factors (like the day of the week, time, and even the weather) relate to the customer count.
Think of it like this: The model is trying to draw the perfect "best-fit" line through all the data points. It’s learning the underlying pattern that connects your inputs to your outputs so it can make solid predictions on data it has never seen before.
This learning phase is where the "machine" in machine learning really does its thing. Developers tackling these kinds of projects often use specialized platforms to speed up the process. You can explore some of the best AI tools for developers to get a sense of what's out there.
Step 3: Evaluating the Results
So, the model is trained. But is it any good? We need to test it. We do this by holding back a small portion of our data (called the "test set") that the model didn't see during training. Then, we ask the model to make predictions for this test set and compare its answers to what actually happened.
For our café, the model might predict 45 customers on a rainy Tuesday afternoon, when the real number was 48. That's pretty close! We use metrics like accuracy or Mean Absolute Error to boil performance down to a single score that tells us, on average, how far off our model’s predictions are.
If the score is good, we can trust the model. If not, it's back to the drawing board. Maybe we need more data, a different algorithm, or to engineer some better features.
Step 4: Making a Real-World Decision
This is the moment of truth. The whole point of this exercise is to turn data into action. The café’s new model can now generate a forecast for the upcoming week, predicting customer traffic for every single hour.
Armed with these predictions, the manager can build a data-driven schedule:
- Bring in an extra barista for the predicted lunch rush between 12 PM and 2 PM on weekdays.
- Cut back on staff during the expected lull on Wednesday afternoons.
- Prep more pastries ahead of the anticipated Saturday morning peak.
Projects just like this one are powering a global machine learning market that was valued at over USD 91.31 billion in 2025 and is projected to hit nearly USD 1.88 trillion by 2035. By following these steps, our little café has successfully turned a confusing pile of data into a real, money-saving business strategy.
Seeing Machine Learning at Work in Your Daily Life
It's easy to picture machine learning as some far-off concept brewing in Silicon Valley labs, but it's much closer to home than you think. This powerful approach to data analysis is already running in the background of your daily life, making things easier, safer, and more convenient. You're probably interacting with it dozens of times a day without even noticing.
Let's look at a few places you'll find it. That moment you finish a series on Netflix and a new row of "must-watch" shows appears? That’s not a lucky guess. It's machine learning for data analysis in action.
The platform's algorithm analyzes everything from your viewing habits and genre preferences to the actors you seem to like. It then cross-references your tastes with millions of other viewers to predict, with startling accuracy, what you’ll want to watch next. It’s a brilliant example of turning massive amounts of user data into a genuinely better experience.
From Entertainment to Security
This technology goes way beyond your streaming queue. Have you ever gotten an urgent text from your bank asking if you just bought something in another country? That's a machine learning model working to protect you.
These algorithms learn your normal spending patterns—where you shop, what you buy, and how much you typically spend. A transaction that falls outside that established baseline instantly gets flagged as potential fraud, stopping a thief in their tracks. It's real-time security that often works before you even know there's a problem.
Here are a few other common examples you'll recognize:
- Online Shopping: When Amazon shows you "products you might like," its recommendation engine is analyzing your search history, previous purchases, and what other shoppers with similar tastes have bought.
- Spam Filters: Your email inbox stays clean thanks to machine learning. These filters constantly adapt to new spammer tricks, learning to tell the difference between a legitimate message and junk mail.
- Navigation Apps: Google Maps and Waze use ML to analyze live traffic data from other drivers and historical patterns to give you the fastest route and a reliable ETA.
A New Frontier in Healthcare
Maybe the most profound impact of machine learning is happening in healthcare. Here, the stakes are much higher than recommending a movie—we're talking about saving lives. For example, radiologists now use AI-powered tools to help them analyze medical scans like X-rays and MRIs.
Trained on millions of anonymous images, these models learn to spot the earliest signs of diseases like cancer, sometimes with a precision that rivals or even surpasses the human eye. By pointing out subtle anomalies a doctor might miss, machine learning acts as a powerful second opinion, paving the way for earlier diagnoses and better treatment outcomes. In some cases, this type of analysis is paired with other automated systems. You can learn more about how related technologies work by reading our article on what robotic process automation is.
"AI is not here to replace us, but to augment our intelligence. In healthcare, it acts as a tireless assistant, helping clinicians see more and decide faster, which ultimately leads to better patient care."
– Dr. Evelyn Reed, Medical AI Ethicist
These examples make it clear that machine learning is far more than a buzzword; it's a practical technology that's already reshaping our world. This widespread adoption is also a massive economic driver. The global artificial intelligence (AI) market, which heavily includes machine learning, was valued at around USD 390.91 billion in 2025 and is projected to explode to USD 1,811.75 billion by 2030. You can discover more insights about AI market growth on Grand View Research to see the full forecast.
From your daily commute to critical medical diagnoses, machine learning is already here, and its influence is only just beginning.
How to Start Your Machine Learning Journey Today

So, you're ready to jump into machine learning for data analysis? That's great news. The best part is, you don't need a doctorate in mathematics to get your hands dirty. It all starts with being curious and wanting to ask better questions of your data.
Think of the next few steps as building your starter toolkit. The first and most important tool to grab is Python. It's a programming language famous for being relatively easy to read and write, and it serves as the foundation for almost everything in the data science world.
Once you have a handle on Python basics, the real fun begins. You'll want to get familiar with a few key libraries—these are free, open-source toolkits that handle the heavy lifting for you.
Your Essential First Steps
Here’s a breakdown of where to focus your energy initially:
- Pandas: Forget the bear. In data analysis, Pandas is your go-to for wrangling data. It lets you load, clean, and manipulate data in tables, essentially acting like a super-powered spreadsheet you control with code.
- Scikit-learn: This is your machine learning workhorse. Scikit-learn comes packed with ready-to-use algorithms like Linear Regression and Decision Trees. It lets you build and test models without having to code every single mathematical formula from scratch.
"The fastest way to learn is by doing. Don’t just read about a concept—find a dataset and try it out. That hands-on experience is what truly builds skill and confidence."
– Alex Ramirez, Data Science Educator
To put these tools into practice, you’ll need some data. The internet is full of fascinating datasets perfect for learning. A classic place to start is the Titanic dataset, where you can use information about passengers—like their age, ticket class, and gender—to build a model that predicts who was likely to survive.
With a user-friendly language like Python, a couple of powerful libraries, and an interesting dataset, you have all the ingredients you need. The path forward is surprisingly clear. Now it's your turn to take that first step.
Got Questions? We've Got Answers
Stepping into a new field always kicks up a few questions. Let's walk through some of the most common ones that come up when people first start exploring machine learning for data analysis.
Do I Really Need to Be a Math Whiz for This?
Definitely not, especially when you're just starting out. While the core theories behind advanced ML are built on some heavy-duty math, you can get surprisingly far with a solid understanding of high school-level concepts.
Think of it like driving a car. You don't need to be a master mechanic who can strip down an engine and rebuild it just to drive to the store. Modern libraries and tools do the heavy lifting, letting you focus on the important parts: defining the problem correctly and making sense of the answers.
What’s the Real Difference Between Data Analysis and Machine Learning?
They're closely related, for sure, but they have different goals. Traditional data analysis is mostly about looking in the rearview mirror—it uses data to explain what has already happened. It’s perfect for creating reports and understanding past performance.
Machine learning, on the other hand, uses that same data to look ahead through the windshield. It builds models that can predict what’s likely to happen next.
Here's a simple way to frame it: Traditional data analysis reports yesterday's news, while machine learning forecasts tomorrow's weather. One describes the past; the other predicts the future.
Do I Need Huge Amounts of Data to Get Started?
Not necessarily! The "big data" buzz can be a bit misleading and scare people off. While more high-quality data is almost always a good thing, the relevance and cleanliness of your data are way more important than sheer size.
For many everyday business problems, a clean dataset with just a few hundred or a few thousand well-organized entries is plenty to build a powerful model. You don't need a database the size of Google's to get started. In fact, you can find tons of free, public datasets online that are perfect for honing your skills today.
At YourAI2Day, our goal is to make the world of AI understandable and accessible for everyone. Explore our resources and stay ahead of the curve.






